Devices and methods for cardiovascular reflex control via coupled electrodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045]The following detailed description should be read with reference to the drawings in which similar elements in different drawings are numbered the same. The drawings, which are not necessarily to scale, depict illustrative embodiments and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention.
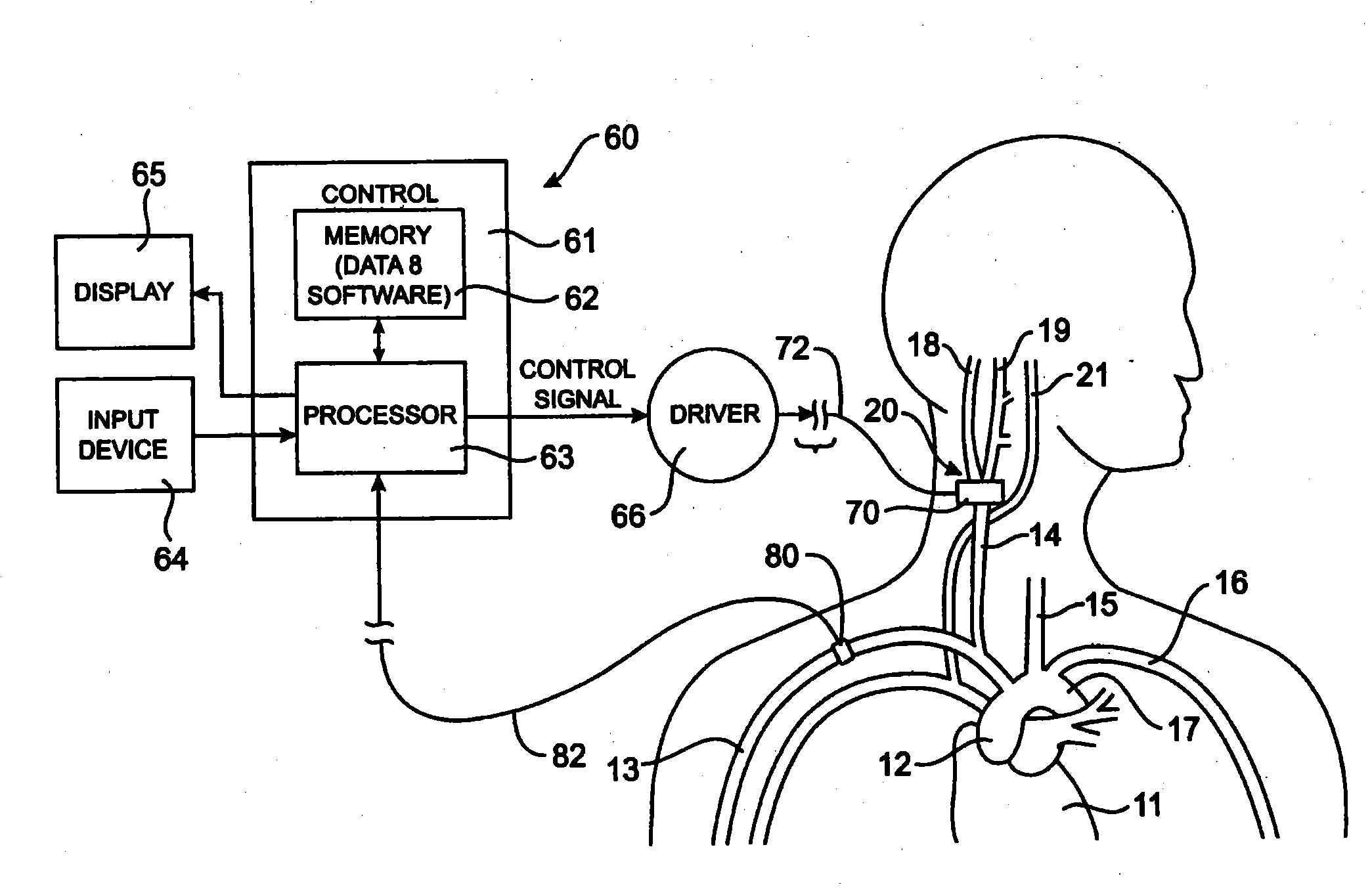
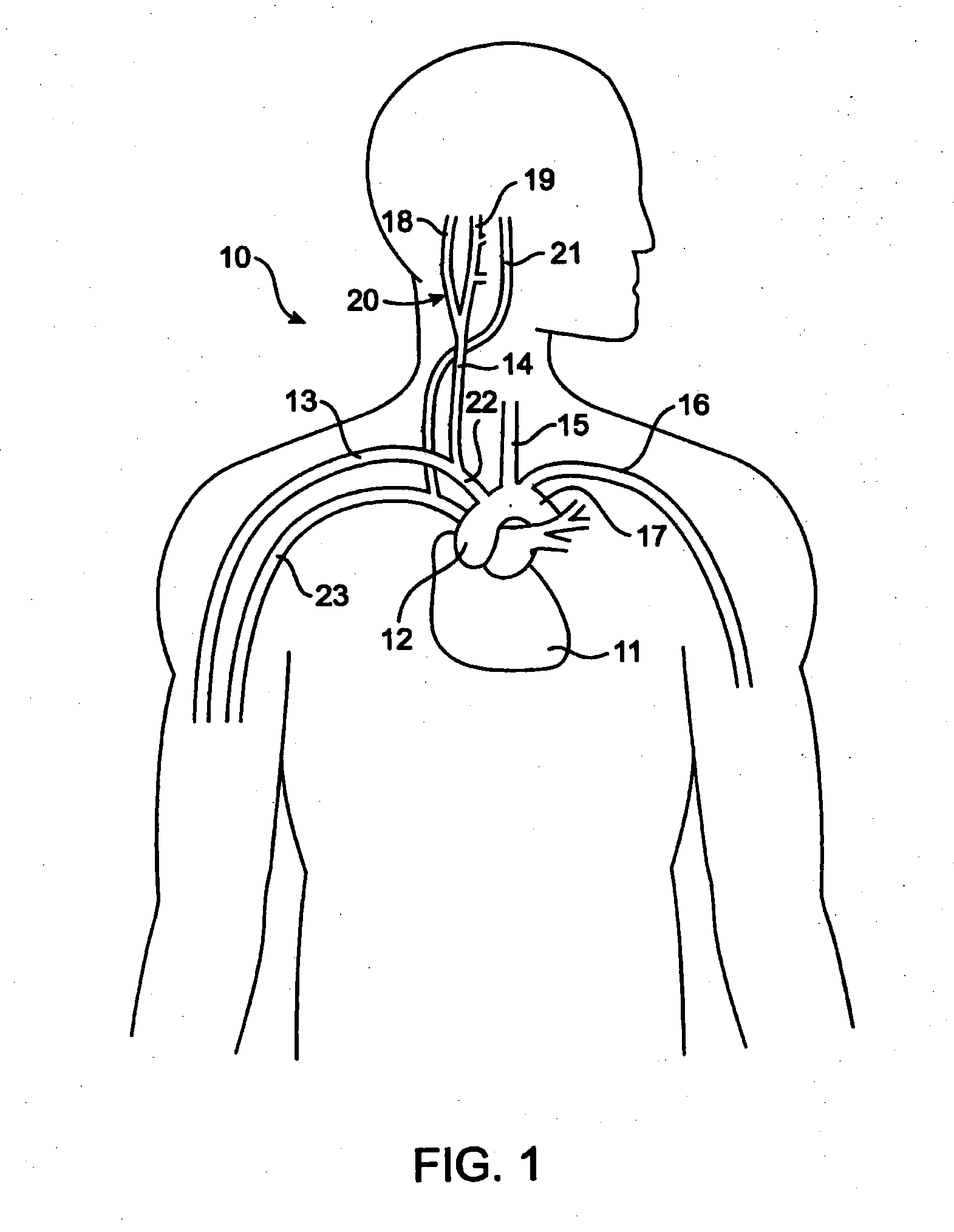
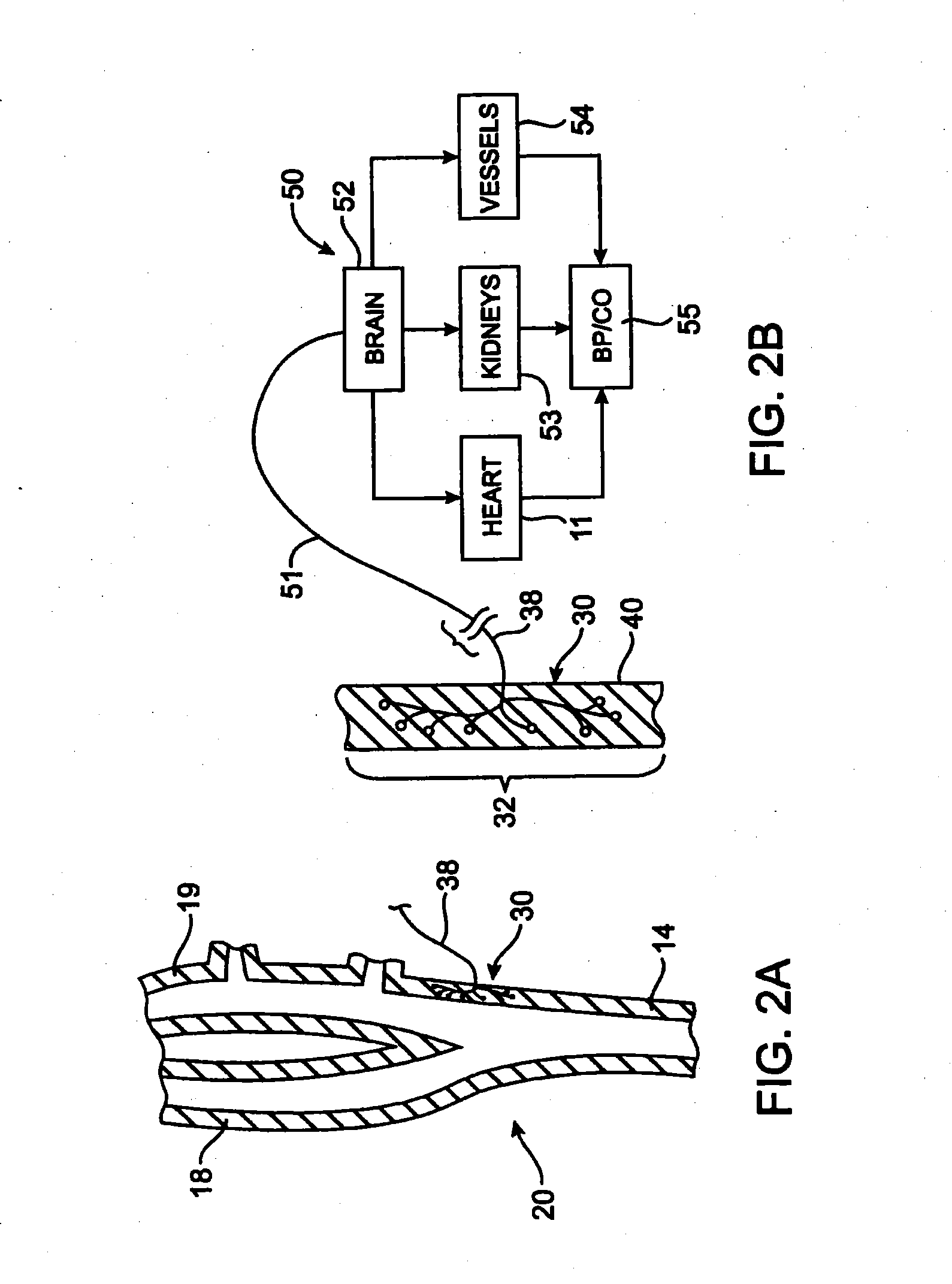
[0046]To better understand the present invention, it may be useful to explain some of the basic vascular anatomy associated with the cardiovascular system. Refer to FIG. 1 which is a schematic illustration of the upper torso of a human body 10 showing some of the major arteries and veins of the cardiovascular system. The left ventricle of the heart 11 pumps oxygenated blood up into the aortic arch 12. The right subclavian artery 13, the right common carotid artery 14, the left common carotid artery 15 and the left subclavian artery 16 branch off the aortic arch 12 proximal of the descending thoracic aorta 17. Although relatively short, a distinct vascular segment referred to as the brachioce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com