Upgrading heavy hydrocarbon oils
a technology of hydrocarbon oil and heavy oil, which is applied in the direction of hydrocarbon oil refining, petroleum industry, water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to bring remote, heavy oil resources closer, and the oil produced from a significant number of oil reserves around the world is simply too heavy to flow under ambient conditions,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Heavy Oil Upgrading Using Emulsion Mixing
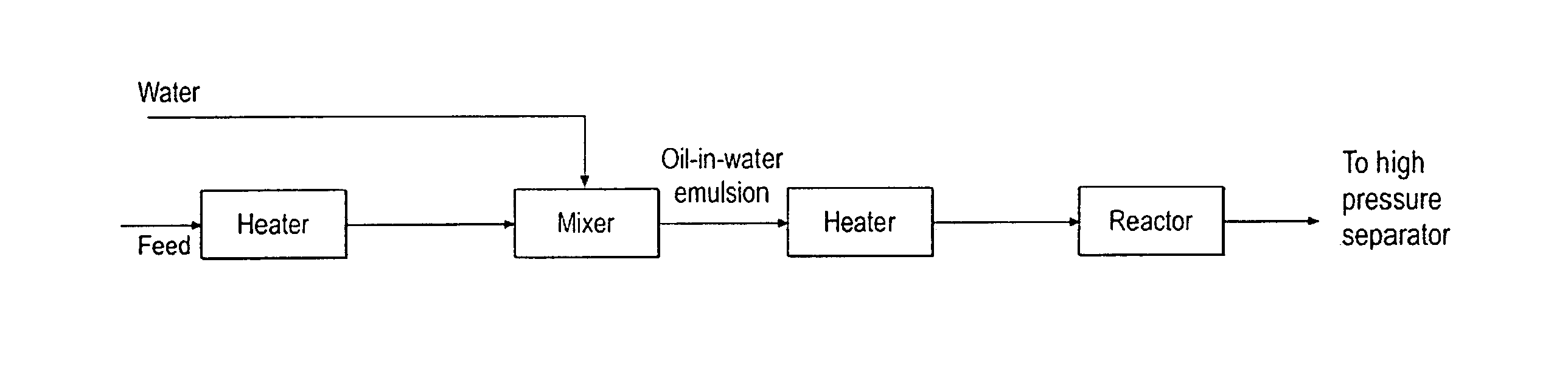
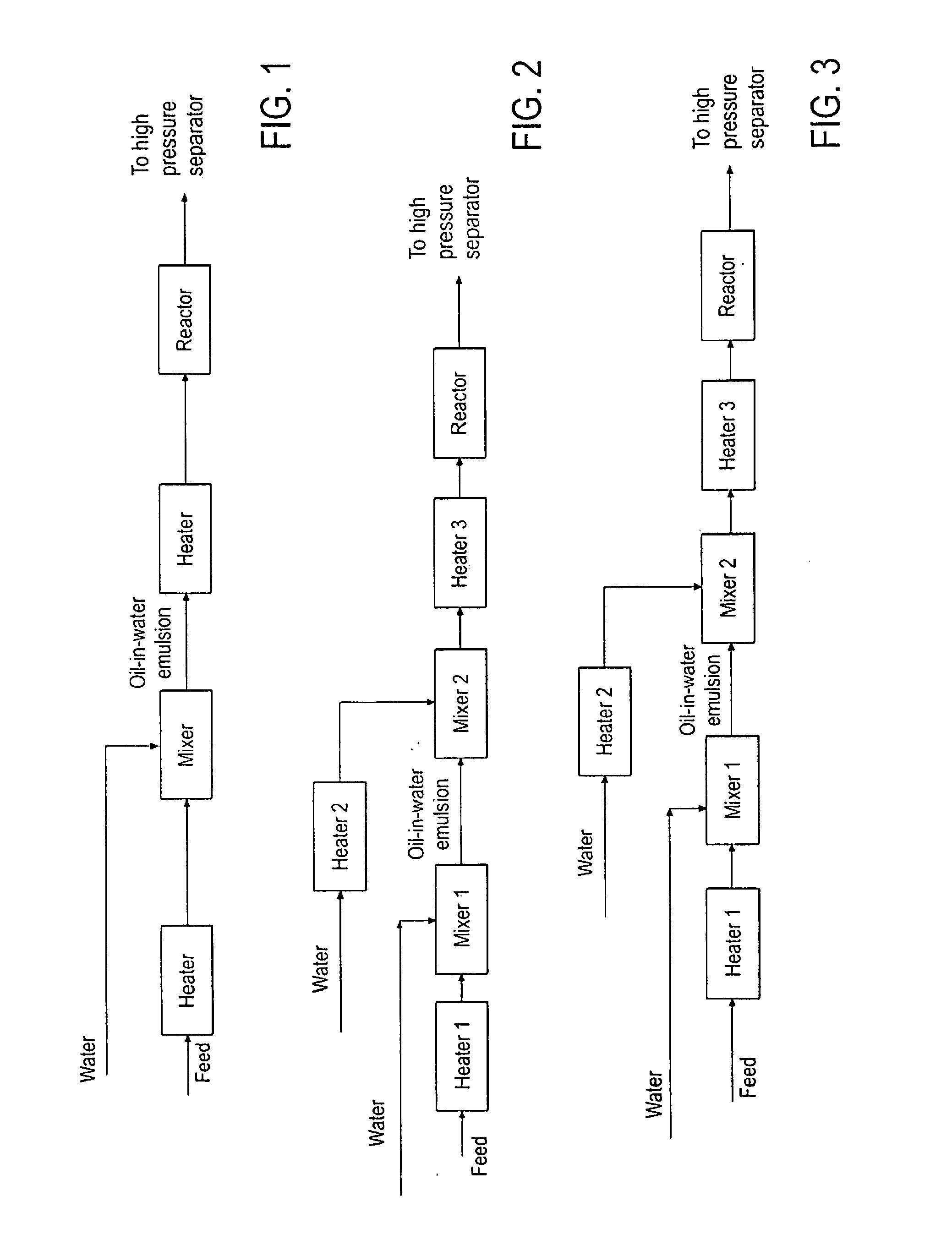
[0053]The experiment was performed using a continuous system. A feed oil, which was a heavy crude with API=12.8, which was diluted with a diluent hydrocarbon at a ratio of 5:1 (20 vol % of diluent) and water was heated to 150° C. before entering a micromixer. The heated crude was mixed with water in the micromixer to form a water-oil emulsion, which was injected into a stream of supercritical water at temperature of 400° C. The total water to oil ratio (volume at room temperature) was 3:1. The oil-supercritical water mixture was then injected into a reactor at temperature of 400° C. and pressure, of 3400 psig. The upgraded product, which formed a homogeneous phase with supercritical water, was withdrawn from the top of the reactor and send to high pressure separator which was operated at the same pressure but lower temperature to achieve oil-water separation. The dreg stream was removed from reactor bottom.
[0054]The diluted heavy crude oil pr...
example 2
Reference Run Using In-Line Mixer
[0056]In order to demonstrate the improved performance by using emulsion mixing, a reference run using in-line mixer to mix water and oil was performed under the same operation conditions (temperature, pressure, water to oil ratio). Feed oil (diluted heavy crude of Example 1) was preheated to 130 C, and then mixed with supercritical water in an inline mixer. Water-oil stream flow through a 20 ft spiral coil immersed in a high temperature sand bath (same as reactor temperature) to further improve water-oil contact, and then fed to the reactor. The upgraded product, which formed a homogeneous phase with supercritical water, was withdrawn from the top of the reactor and send to high pressure separator which was operated at the same pressure but lower temperature to achieve oil-water separation. The dreg stream was removed from reactor bottom.
[0057]The liquid product (syncrude) from this reference run has the following properties: 22 API gravity at 60 / 60...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com