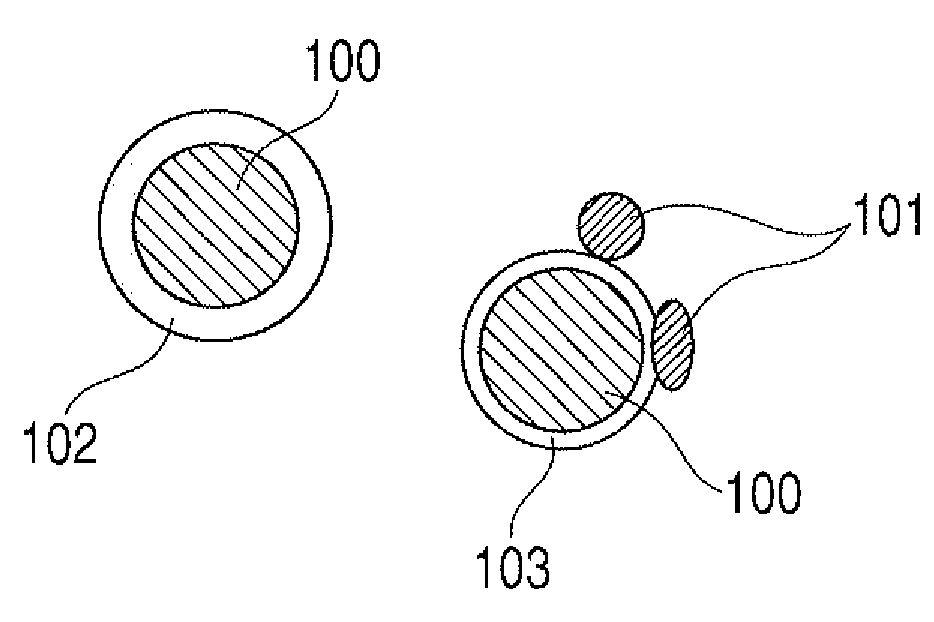
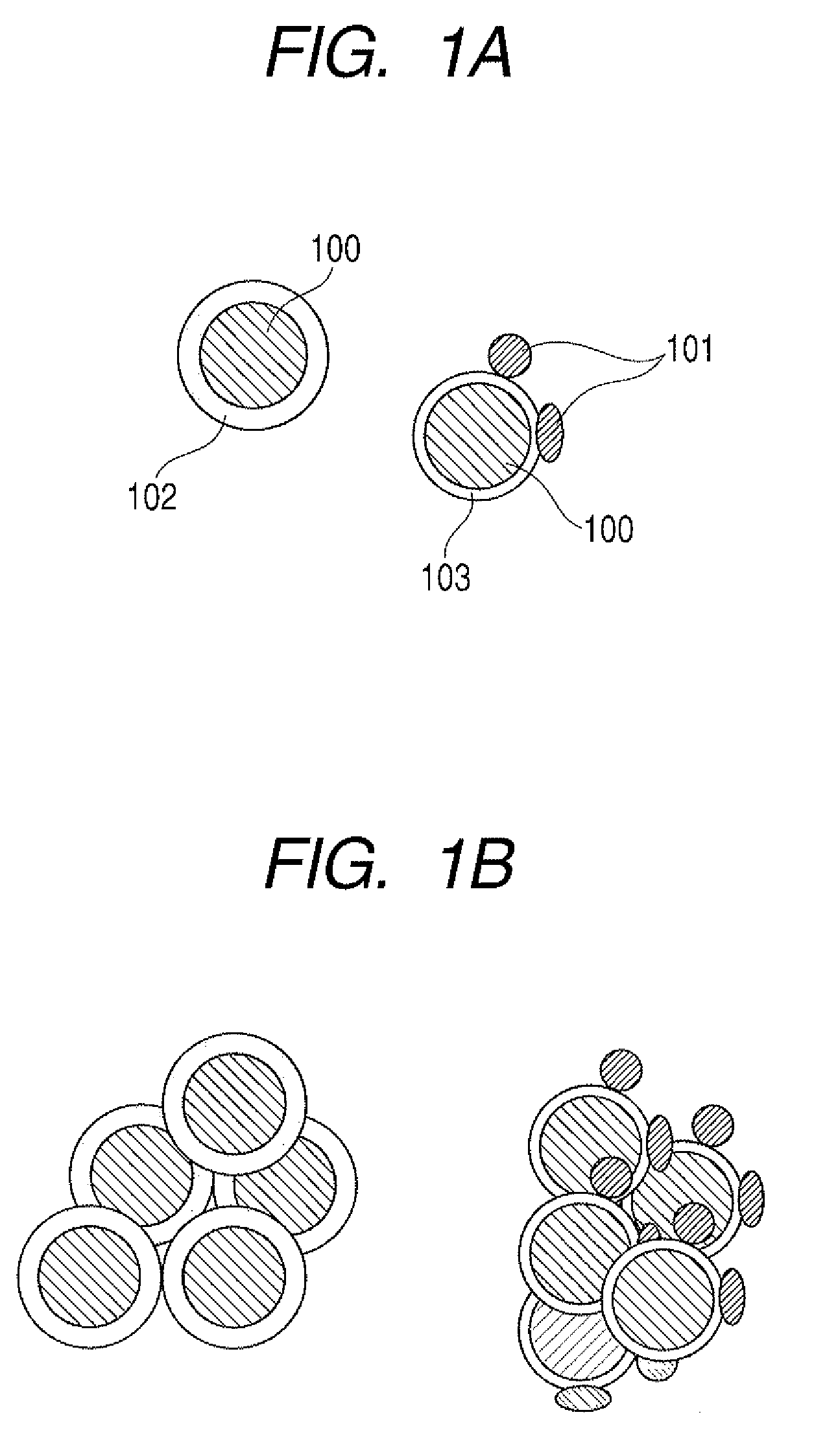
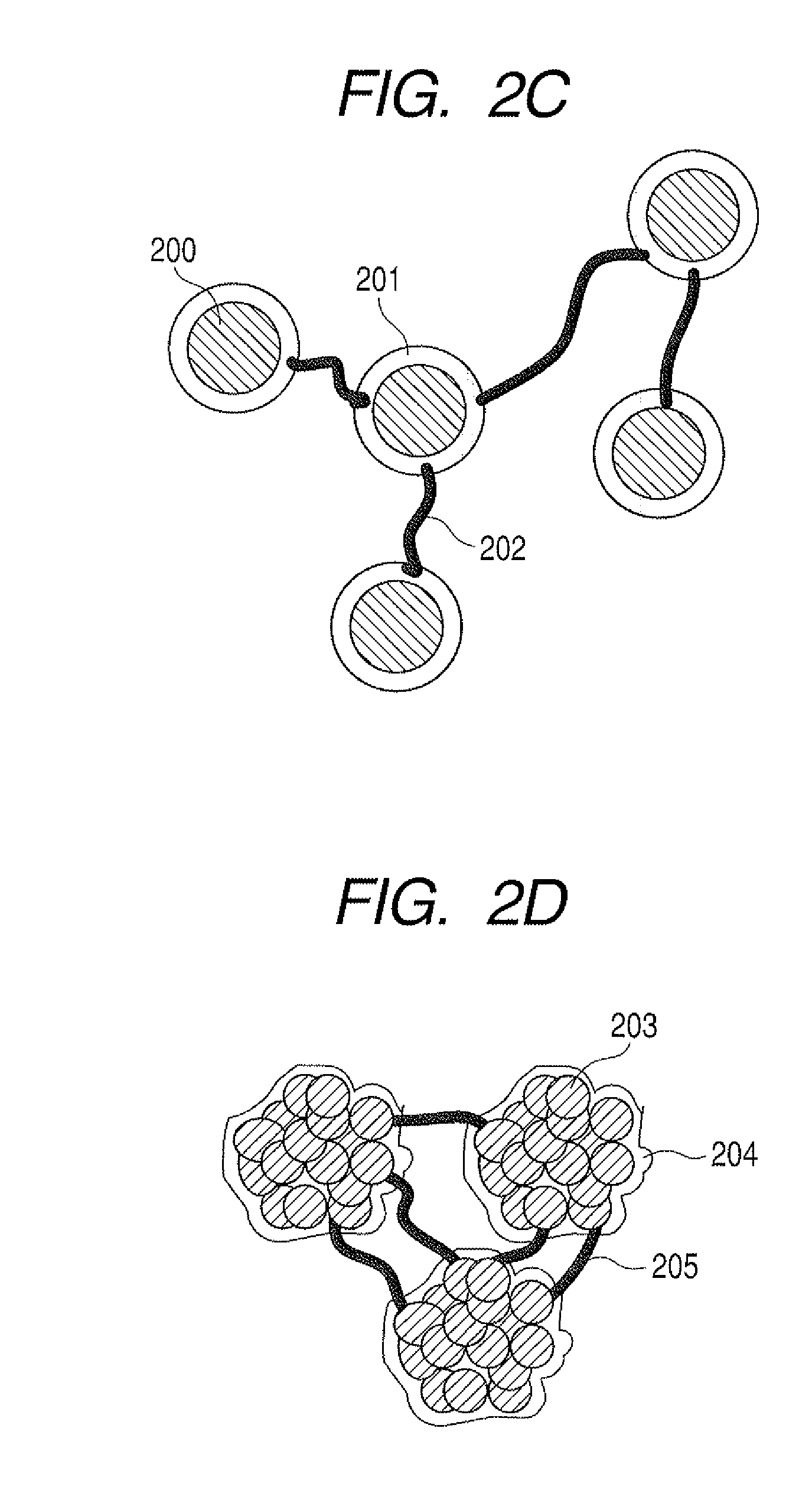
Method of producing lithium ion-storing/releasing material, lithium ion-storing/releasing material, and electrode structure and energy storage device using the material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0333]Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail by way of examples.
[0334][Preparation of an Electrode Material (Active Material) for the Negative Electrode of the Energy Storage Device]
[0335]An example of a method of preparing a powder material to be used as an active material for the negative electrode of the energy storage device in the present invention will be given below.
[0336]Examples of procedure for preparation of powder material
[0337]Preparation by Thermal Plasma Method
[0338]Here, nanoparticles serving as a negative electrode material were synthesized with a radiofrequency (RF) inductively coupled thermal plasma-generating apparatus in accordance with the following procedure. The above inductively coupled thermal plasma-generating apparatus is constituted of a reactor connected with a vacuum pump and a thermal plasma torch. The thermal plasma torch is provided with a gas introducing portion for generating plasma and a raw material powder-introducin...
example tp1
[0339]The above radiofrequency (RF) inductively coupled thermal plasma-generating apparatus was used. First, the inside of the reactor was evacuated to a vacuum with the vacuum pump, and an argon gas and a hydrogen gas as gases for generating plasma were flowed at flow rates of 200 liters / min and 10 liters / min, respectively, and the total pressure of the gases was controlled to 50 kPa. A radiofrequency of 4 kHz was applied to the induction coil with an electric power of 80 kW so that plasma was generated. Next, a powder raw material obtained by mixing 97 parts by weight of a silicon powder having an average particle diameter of 4 μm and 3 parts by weight of zirconia having an average particle diameter of 1 μm was fed into the thermal plasma at a feeding rate of about 500 g / h together with an argon gas flowed at a flow rate of 15 liters / min as a carrier gas. The raw material was subjected to a reaction for a predetermined reaction time, whereby a fine powder material was obtained. Th...
example tp2
[0342]Nanoparticles were obtained by the same operations as in Example TP1 described above except that a powder raw material obtained by mixing 95 parts by weight of a silicon powder having an average particle diameter of 4 μm and 5 parts by weight of zirconia having an average particle diameter of 1 μm was used instead of the powder raw material obtained by mixing 97 parts by weight of a silicon powder having an average particle diameter of 4 μm and 3 parts by weight of zirconia having an average particle diameter of 1 μm.
[0343]FIG. 8 shows the high-resolution image of the resultant powder with a TEM.
[0344]In the high-resolution image with a TEM of FIG. 8, an amorphous phase having a thickness of 0.5 nm to 5 nm was observed on the surface of crystalline silicon having a diameter of 5 nm to 100 nm.
[0345]Comparison between the results of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of Examples TP1 and TP2 (see FIG. 17) showed that the amount of silicon oxide of Example TP2 was small, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com