Prevention of cheating in on-line interaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
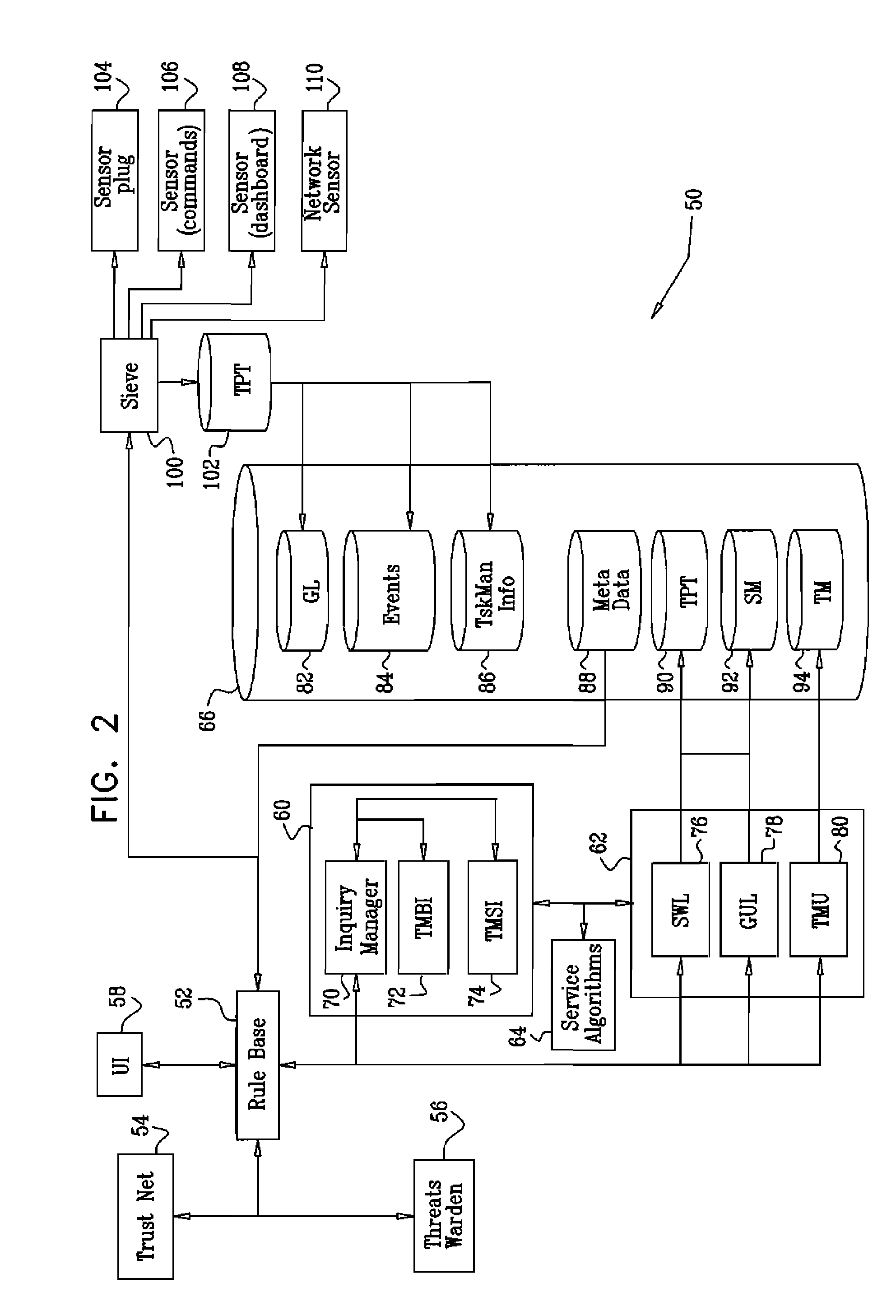
Method used
Image
Examples
operational example
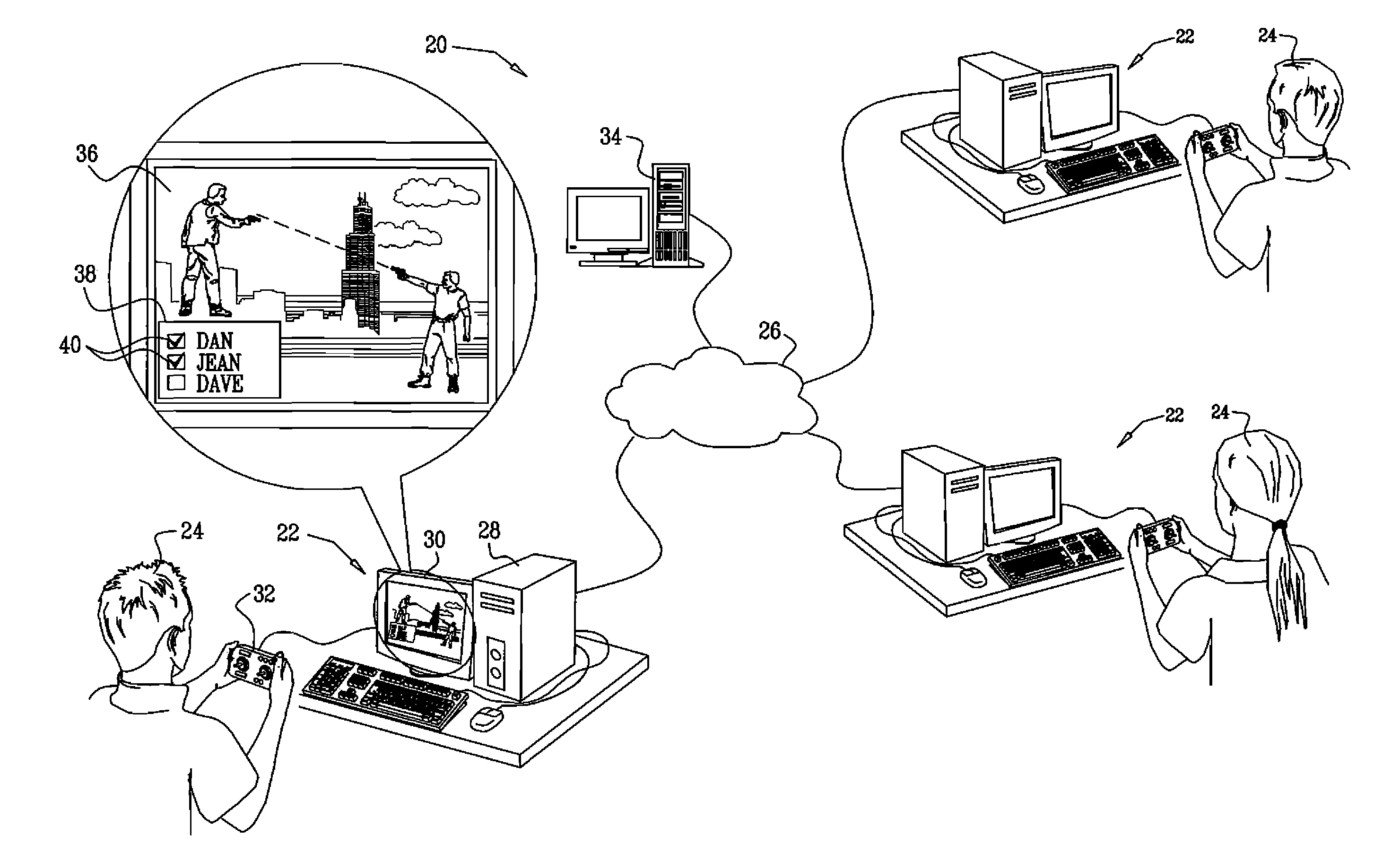
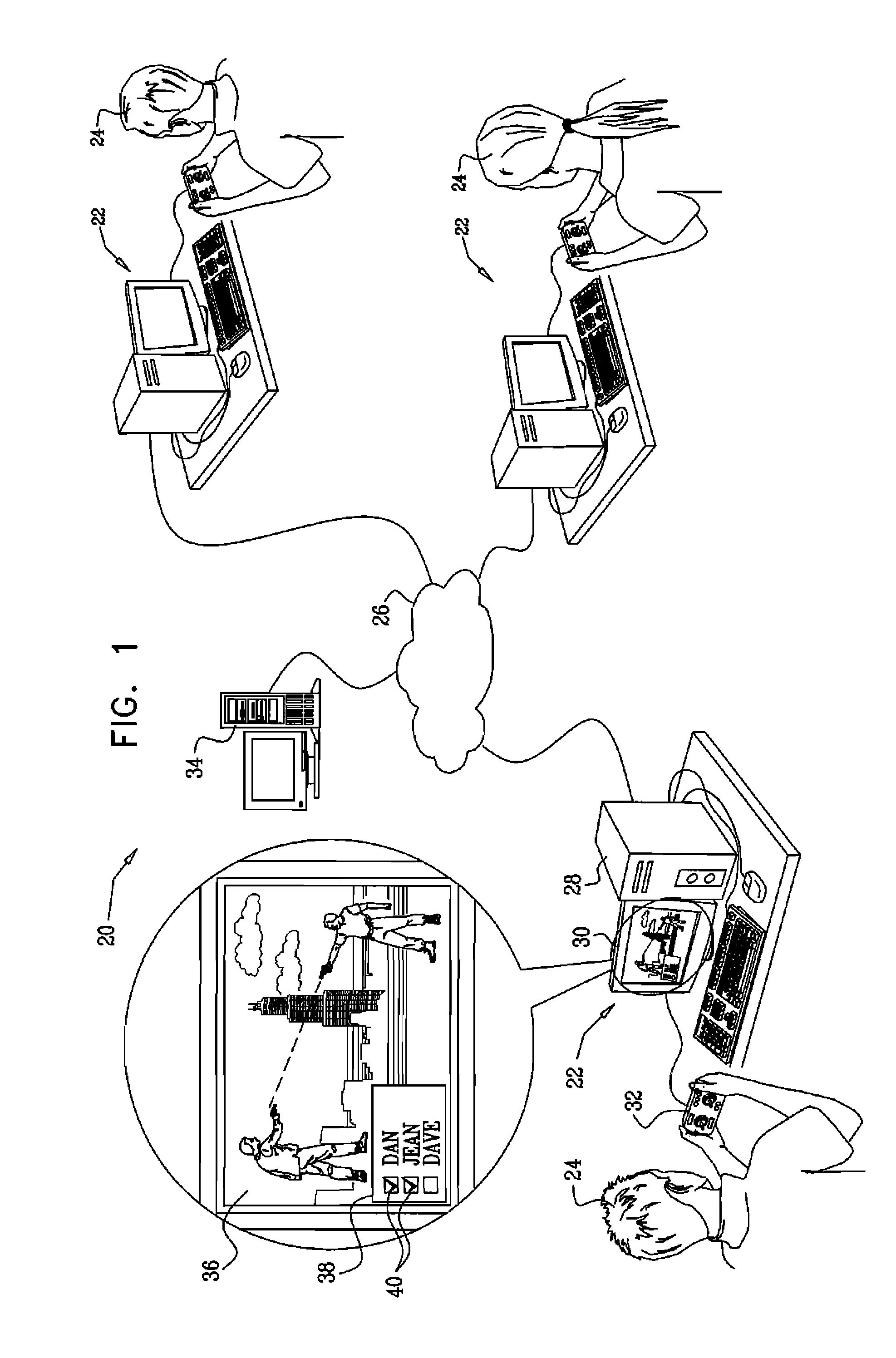
[0195]The following scenarios provide an example of the operation of program 50 in on-line game protection. These scenarios deals with a common type of cheating, which is classified as “Cheating by Exploiting Lack of Secrecy” in the above-mentioned article by Yan and Randell. This method of cheating involves exchange of packets between peers, wherein a participant cheats by inserting, deleting or modifying game events, commands or files that are transmitted over the network. The example is described with reference to an on-line game known as “GunZ—The Duel” (MAIET Entertainment, Korea), but the characteristics of this example are equally applicable to many other games.
[0196]As explained above, the main session types of program 50 include game installation session, game / user learning session and protection session for the on-line game. These sessions follow three sub-scenarios of protection: Scenario A—existing complete previous knowledge, Scenario B—existing partial previous knowled...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com