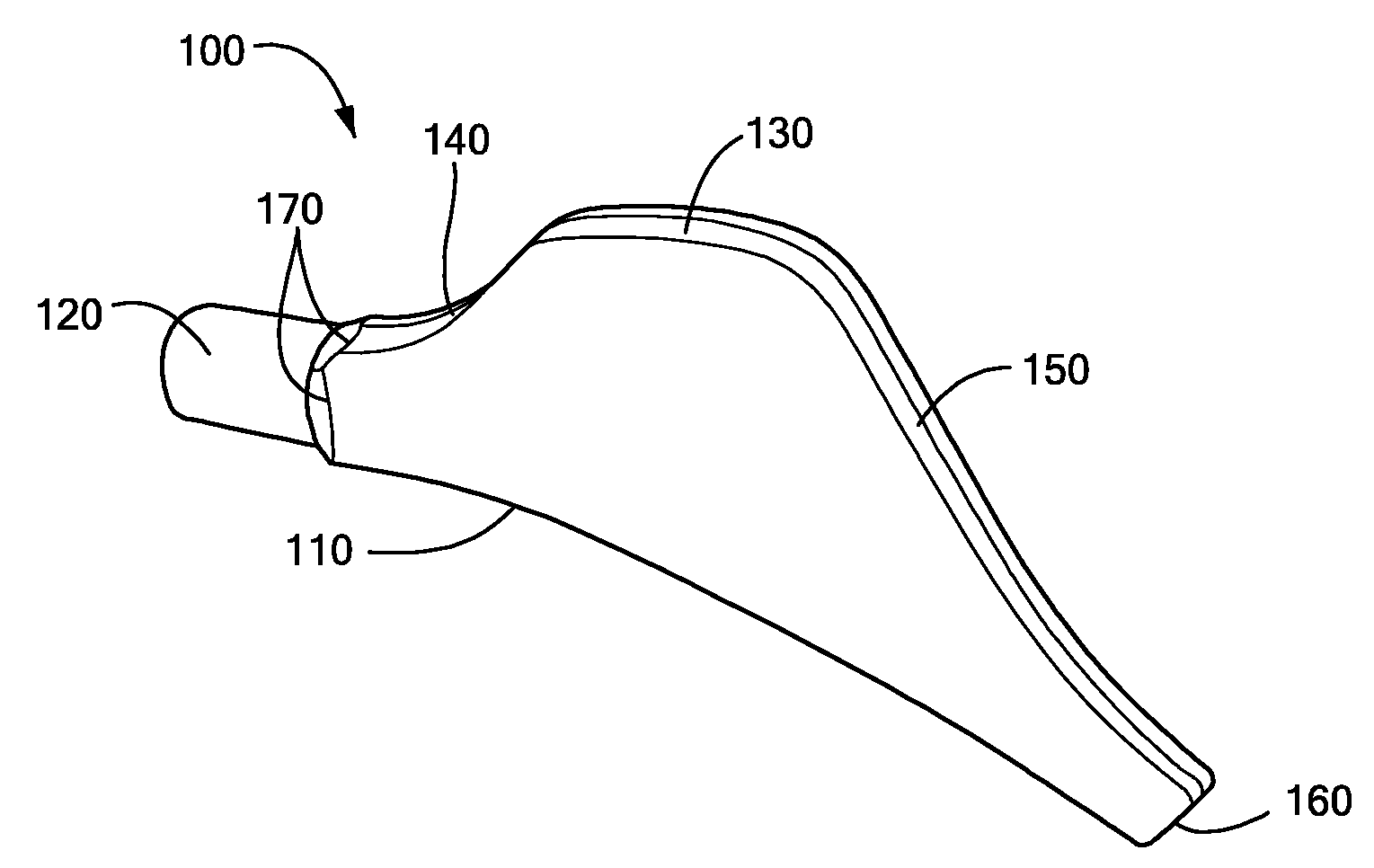
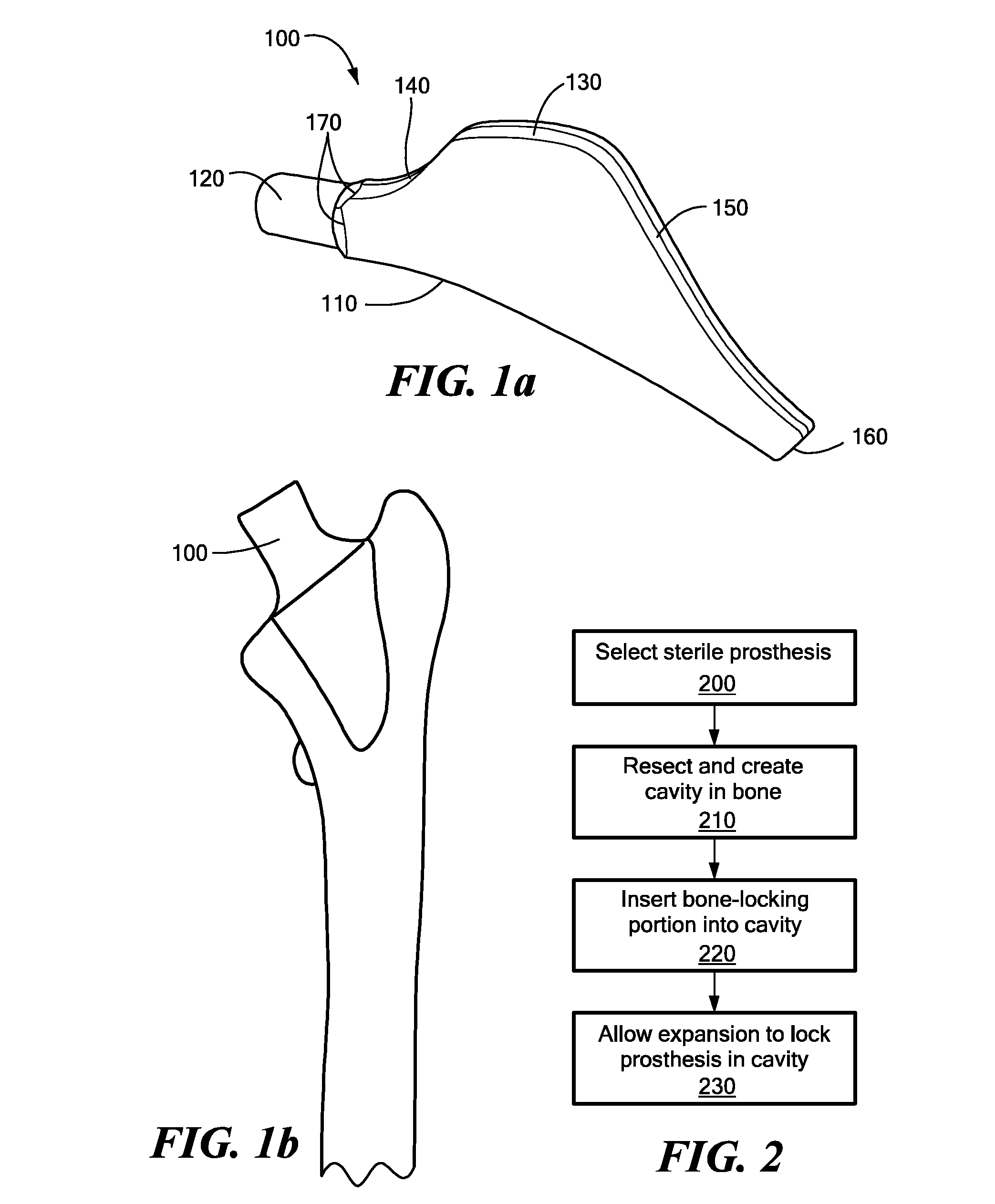
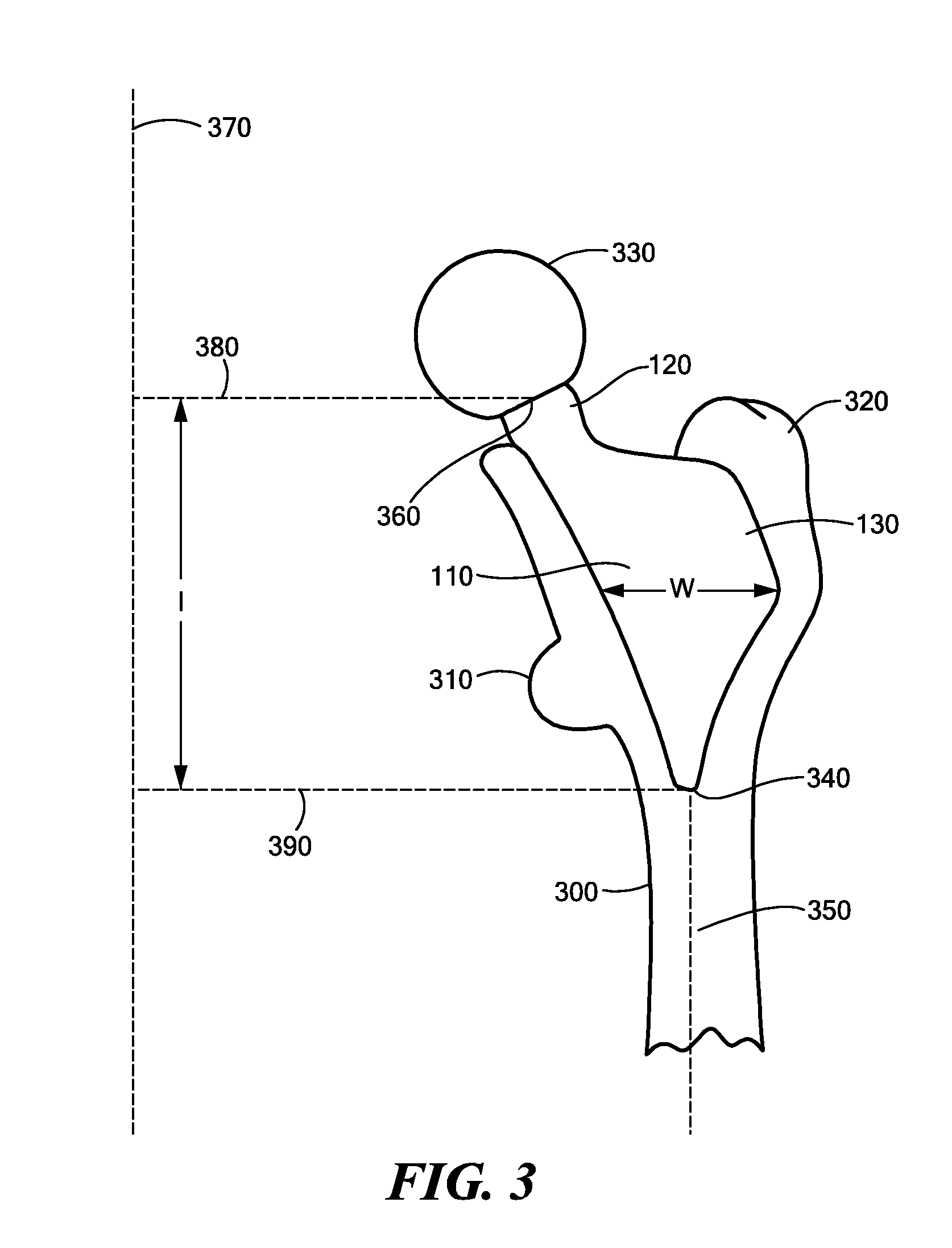
Proximally Self-Locking Long Bone Prosthesis
a long bone prosthesis and self-locking technology, applied in the field of medical implants, can solve the problems of joint cartilage damage, mechanical pain, eventual destruction of joint cartilage, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the sealing, maintaining the flexibility of the diaphysis, and improving the sealing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Finite Element Modeling of a Long-Stemmed Implant
[0073]A computational model of a long-stemmed Nitinol prosthesis was created using finite element modeling techniques. The results warn that long-stemmed prosthetics with Nitinol stems may be susceptible to bending-induced fracture.
[0074]FIGS. 9a and 9b show a finite element model geometries used and designated as “Hip A” and “Hip B” respectively. The material properties for the finite element analyses were assumed to be linear elastic and isotropic. CoCrMo and Nitinol used in these analyses were assumed to follow Hooke's Law, and frictional forces could be neglected since the applied force was much higher than the frictional forces. All finite element models were assumed to be linear and un-cemented. The force(s) transmitted from walking were assumed to be transmitted from the femur into the implant, where the force then was transmitted to the ball. From there, the force was then transmitted into the liner and cup. The force transmit...
example 2
Finite Element Modeling of an Implant According to FIG. 1a
[0081]To confirm the hypothesis that a short-stemmed Nitinol prosthesis 100 with a lateral flare according to FIG. 1a would be sufficiently robust, further finite element modeling was performed to simulate the fatigue endurance strength properties of a short-stemmed prosthesis. A quasi-static analyses was performed with the commercial finite element analysis (FEA) code ABAQUS / Standard version 6.5-1. Three dimensional elements and a large displacement formulation were used. Two material models were used for this report: the first was a Nitinol material model assuming a superelastic response with an Af temperature of 30° C. and a typical stainless steel material with approximately 20% cold work was chosen as a baseline for comparison. Two finite element models were created to examine the effect of mesh refinement on the accuracy of the solution. The number of degrees of freedom for the base model and the fine model were 44853 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic moduli | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic moduli | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com