Connecting material, method for manufacturing connecting material, and semiconductor device
a technology of connecting material and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, soldering apparatus, and semiconductor/solid-state device details, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient wetness, inability to suppress temperature cycle, and breakage of semiconductor elements due to thermal stress at the cooling time of connection or after connection cooling, etc., to improve connection reliability, reduce the process of manufacturing material, and improve the wetness at the time of connection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment
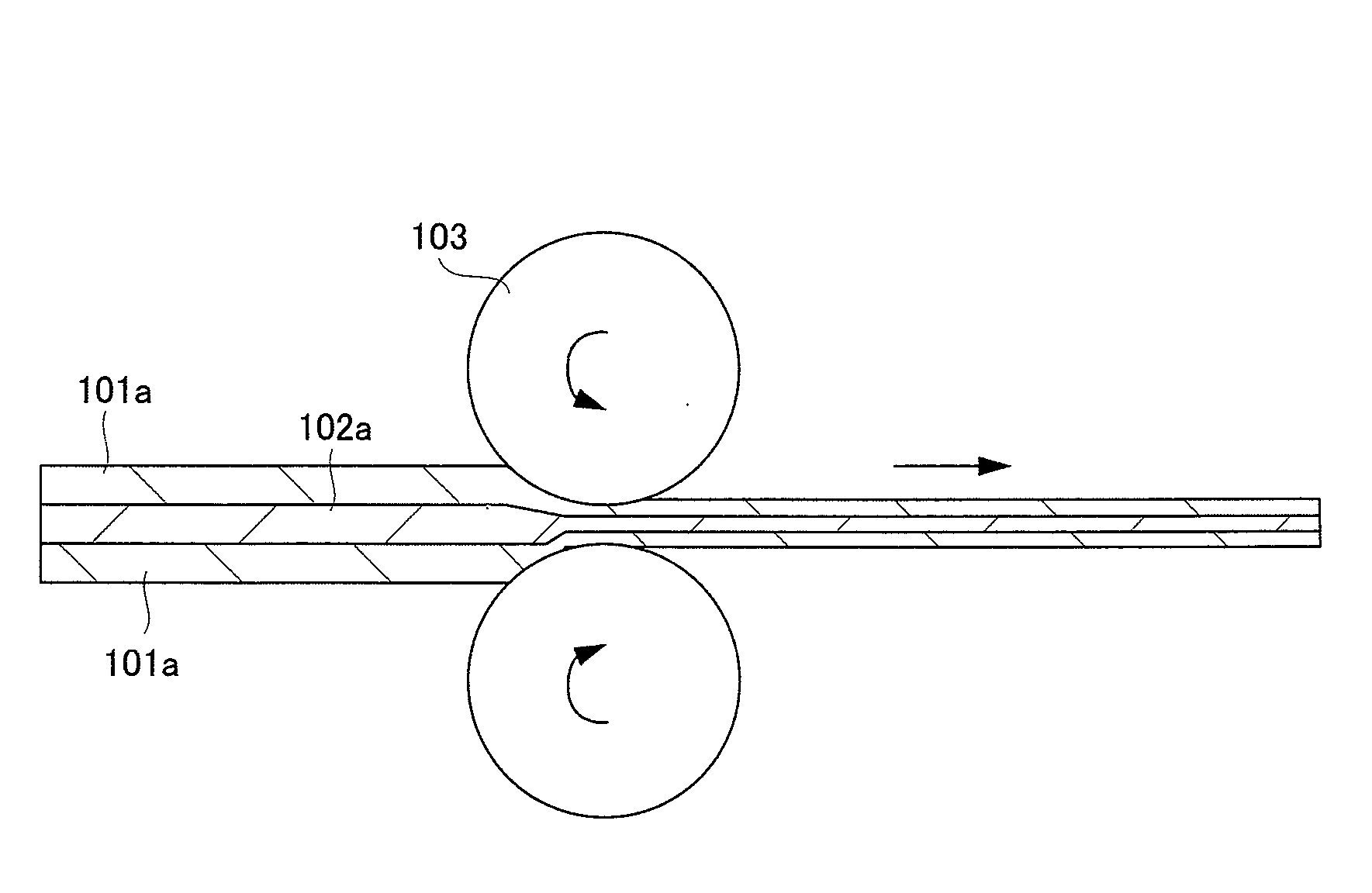
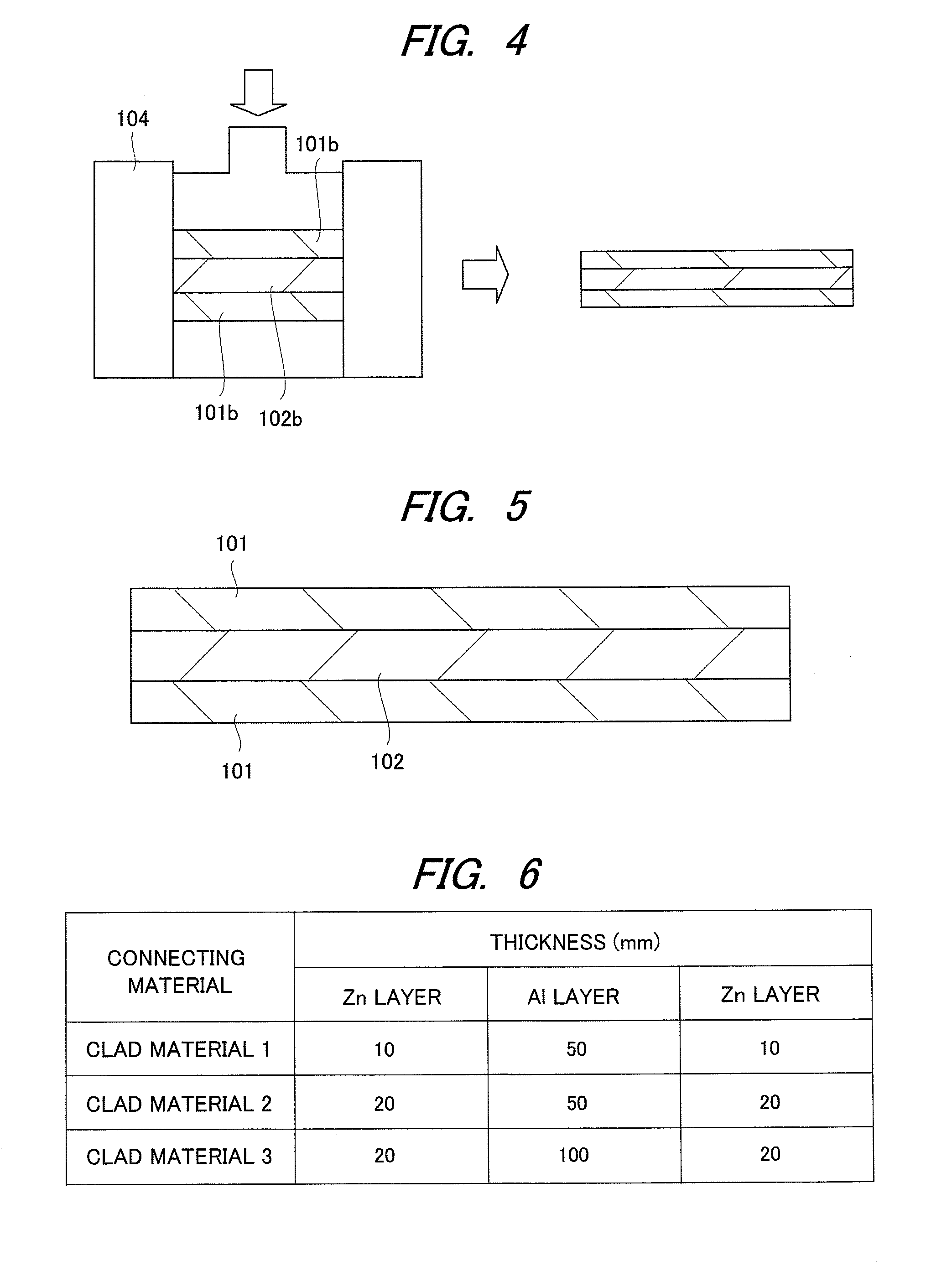
[0038]FIG. 5 shows a cross section of a connecting material according to the embodiment of the present invention. In the connecting material according to the present embodiment, a Zn series alloy layer (simply referred to as Zn layer or Zn) 101 as a lower layer, an Al series alloy layer (simply referred to as Al layer or Al) 102 as an intermediate layer and a Zn series alloy layer (simply referred to as Zn layer or Zn) 101 as an upper layer are formed. As shown in FIG. 3 described above, this connecting material is manufactured by stacking the Zn series alloy layer 101a, the Al series alloy layer 102a and the Zn series alloy layer 101a and then performing the rolling process, that is, the clad rolling.
[0039]FIG. 6 shows all the connecting materials (referred to as clad material) thus manufactured. In the clad material 1, the thicknesses of the Zn layer, the Al layer and the Zn layer are 10, 50 and 10 μm, respectively. In the clad material 2, the thicknesses thereof are 20, 50 and 20...
examples 1 to 12
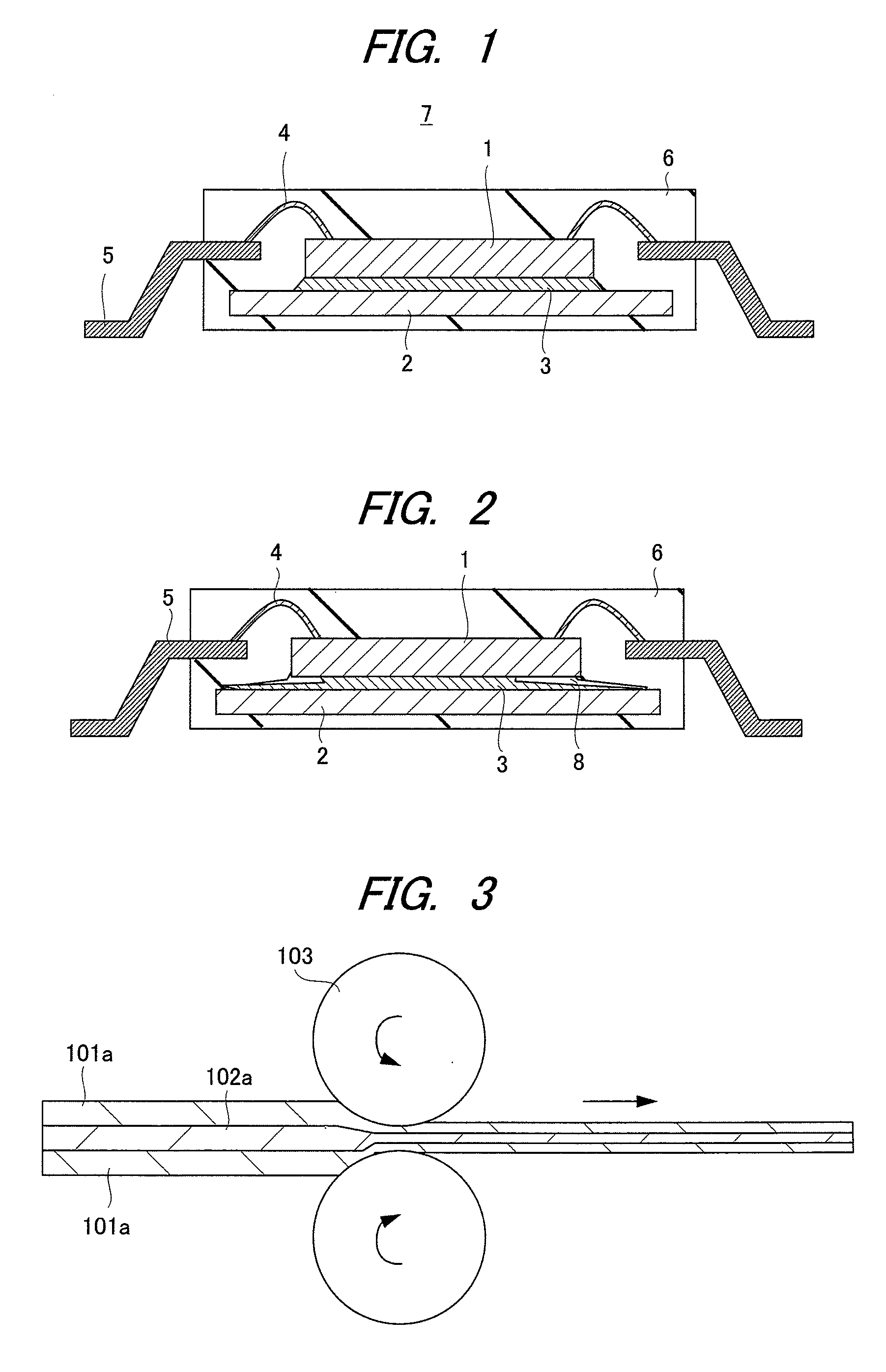
[0040]In the examples 1 to 12, as shown in FIG. 7, the connecting material 10 is used for the die bonding of the semiconductor device 11. This semiconductor device 11 includes a semiconductor element 1, a frame 2 connecting the semiconductor element 1, a lead 5 whose one end functions as an external terminal, a wire 4 connecting the other end of the lead 5 and an electrode of the semiconductor element 1, and a sealing resin 6 which seals the semiconductor element 1 and the wire 4, and the semiconductor element 1 and the frame 2 are connected by the connecting material 10.
[0041]In the manufacture of the semiconductor device 11, the connecting material 10 is supplied onto the frame 2 made of solid Cu or the frame 2 on which the Ni, Ni / Ag or Ni / Au plating is performed and the semiconductor element 1 is placed thereon, and thereafter, the heating is performed at 400° C. for 1 min. in an N2 atmosphere while applying pressure, whereby the semiconductor element 1 is die-bonded. FIG. 8 show...
examples 13 to 24
[0046]In the examples 13 to 24, as shown in FIG. 10, the connecting material 10a of the present invention is used as the sealing material of a semiconductor device 21 requiring the hermetic sealing. This semiconductor device 21 includes a semiconductor element 1, a module substrate 23 connecting the semiconductor element 1, a lead 5 whose one end functions as an external terminal, a wire 4 connecting the other end of the lead 5 and an electrode of the semiconductor element 1, and a metal cap 22 which hermetically seals the semiconductor element 1 and the wire 4 and is connected to the module substrate 23, and the module substrate 23 and the metal cap 22 are connected by the connecting material 10a. Note that, in the semiconductor device 21, chip components and others are also connected onto the module substrate 23.
[0047]In the manufacture of the semiconductor device 21, after the semiconductor element 1, the chip components and others are connected to the module substrate 23 by an S...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com