Heat sink
a heat sink and heat pipe technology, applied in the field of heat sinks, can solve problems such as degrading thermal exchange efficiency, and achieve the effects of reducing heat pipe size, and improving heat exchange or radiating efficiency of heat pipes within a limited spa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
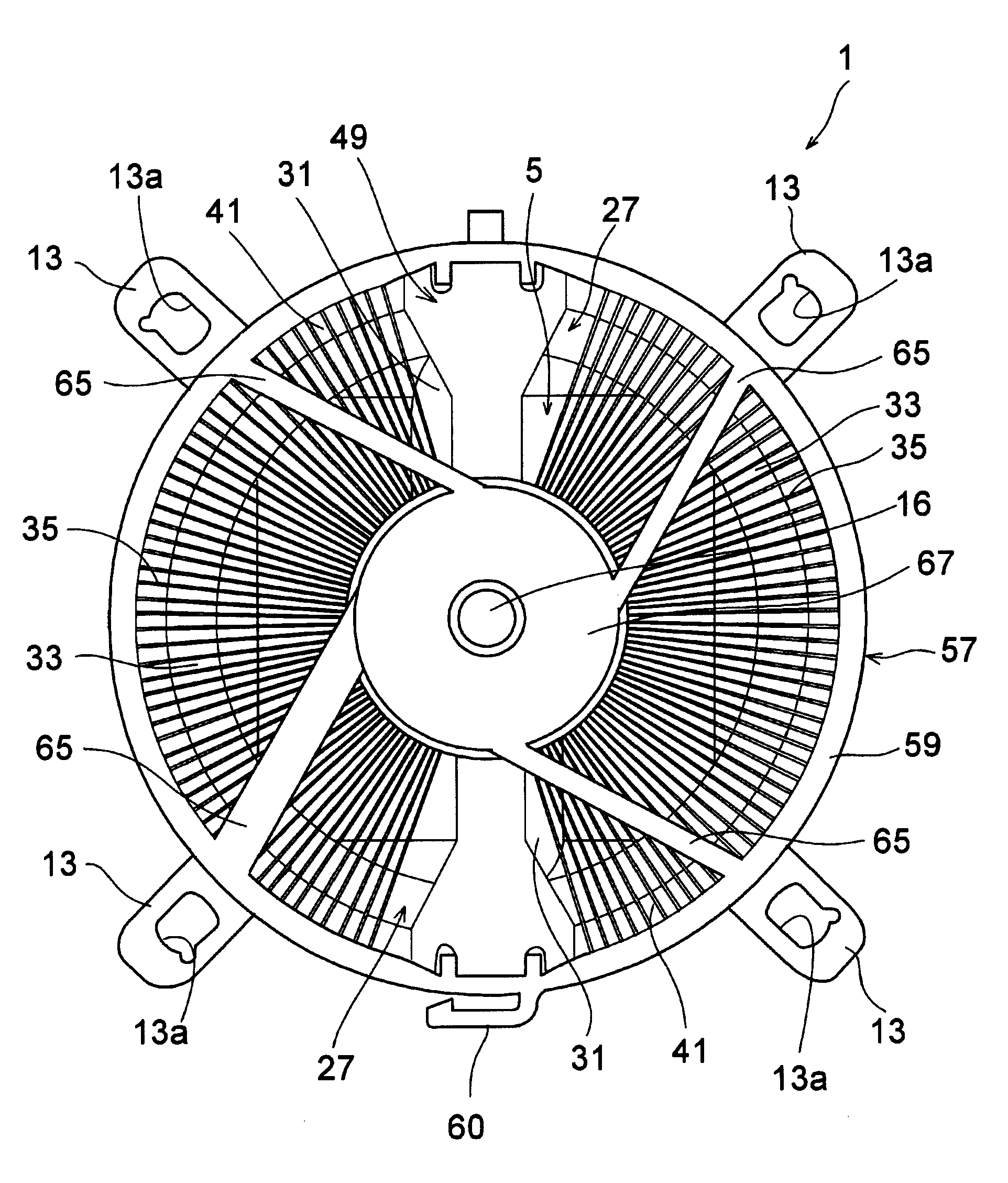
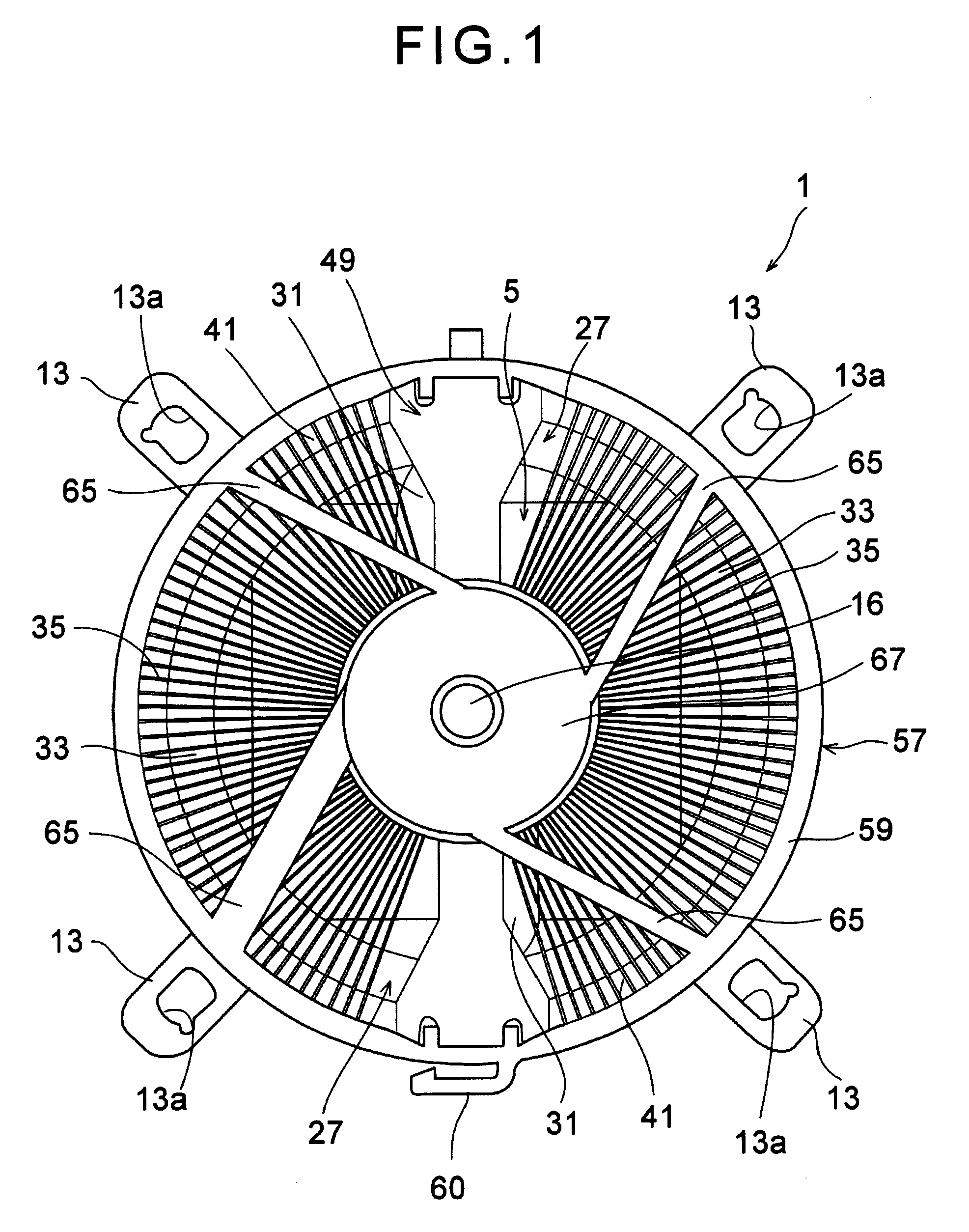
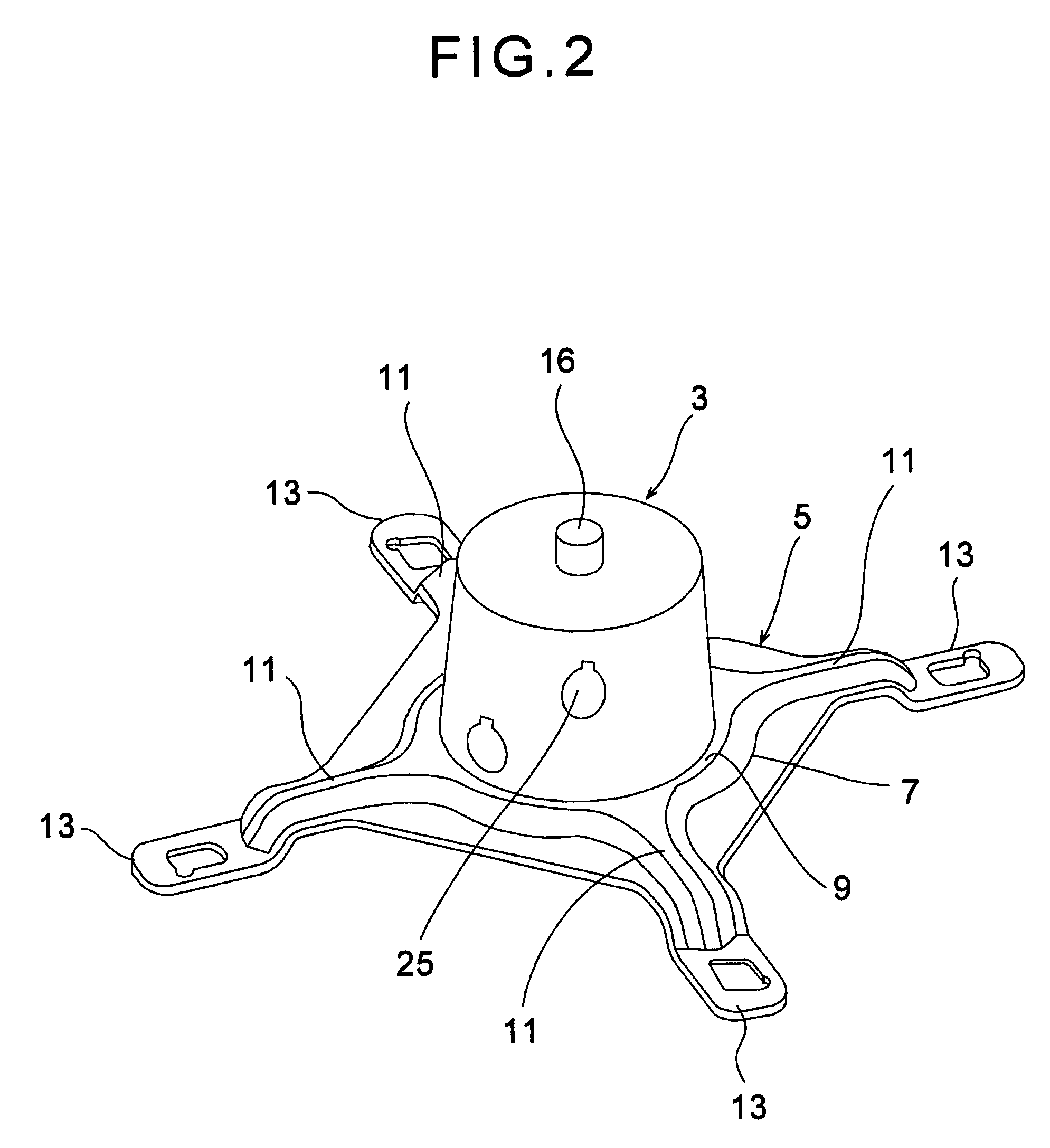
[0039]Here will be described a first exemplary embodiment of the invention. FIG. 1 is a top view showing a heat sink according to the invention. The heat sink 1 illustrated in FIG. 1 comprises an installation base 5. As illustrated in FIGS. 2 to 4, a heat receiving base 3 is mounted on a center of the installation base 5, and a bottom face of the heat receiving base 3 is aligned to be contacted with at least an upper face of a not-shown electron device as an exothermic element, e.g., a central processing unit.
[0040]As illustrated in FIG. 2, the installation base 5 comprises a base plate 7, a circular reinforcement frame 9, linear reinforcement frames 11 and clips 13. The circular reinforcement frame 9 is formed on the base plate 7 at a predetermined height, and the heat receiving base 3 is mounted thereon. The linear reinforcement frames 11 extend from the circular reinforcement frame 9 radially to four corners of the base plate 7, and the end portion thereof is bent downwardly. At ...
second embodiment
[0067]Next, a heat sink 71 as the present invention will be explained with reference to FIGS. 12 to 14. FIG. 12 is a top view showing the heat sink 71.
[0068]Differences between the heat sink 71 of the second embodiment and the heat sink 1 of the first embodiment are configurations of a heat receiving base 73, heat radiation fins 81 and heat pipes 85. The remaining elements of the heat sink 71 illustrated in FIGS. 12 to 14 are similar to those of the heat sink 1, so further description will be omitted by allotting common reference numerals.
[0069]The heat receiving base 73 is made of a material whose heat conductivity is excellent such as a copper. As illustrated in FIG. 13, the heat receiving base 73 comprises a column shaped heat receiving body 75, and a cylindrical heat exhausting portion 77 which is formed integrally on a circumference of the heat receiving body 75. In heat receiving body 75, there are formed two vertical holes 79 into which an evaporating side of the after mentio...
third embodiment
[0078]Differences between the heat sink 91 of the third embodiment and the heat sink 1 and 71 are configurations of a heat receiving base 93, heat radiation fins 99a to 99n and heat pipes 97. The remaining elements of the heat sink 91 illustrated in FIGS. 15 to 17 are similar to those of the heat sinks 1 and 71, so further description will be omitted by allotting common reference numerals.
[0079]The heat receiving base 93 is made of a material whose heat conductivity is excellent such as a copper. As illustrated in FIG. 16, the heat receiving base 93 also has a column-shaped main body, and comprises vertical holes 93 into which an evaporation side of the after mentioned heat pipes 97 are buried tightly. The heat receiving base 93 further comprises a plurality of protrusions 93b, which are formed around outer circumference at regular intervals, and to which heat radiating fins 99a are contacted.
[0080]As illustrated in FIGS. 15 and 16, the heat pipes 97 in which the evaporation side is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com