Borrelia burgdorferi bacterin
a bacterin and borrelia technology, applied in the field of borrelia burgdorferi bacterin, can solve the problems of hampered establishment of protocols for effective chemical treatment of lyme disease, long-term infection, and difficulty in detecting spirochetes in affected tissues, so as to enhance the immunogenicity of inactivated borrelia burgdorferi, and enhance the immunogenicity of inactiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Borrelia Burgdorferi Bacterin
Equipment Needed:
[0062] Sterile: 20 ml tubes, 250 ml bottles and 10 liter jugs; 200, 500 or 3,000 liter fermenter; serological pipets; magnets; mixing and storage tanks; and centrifuge.
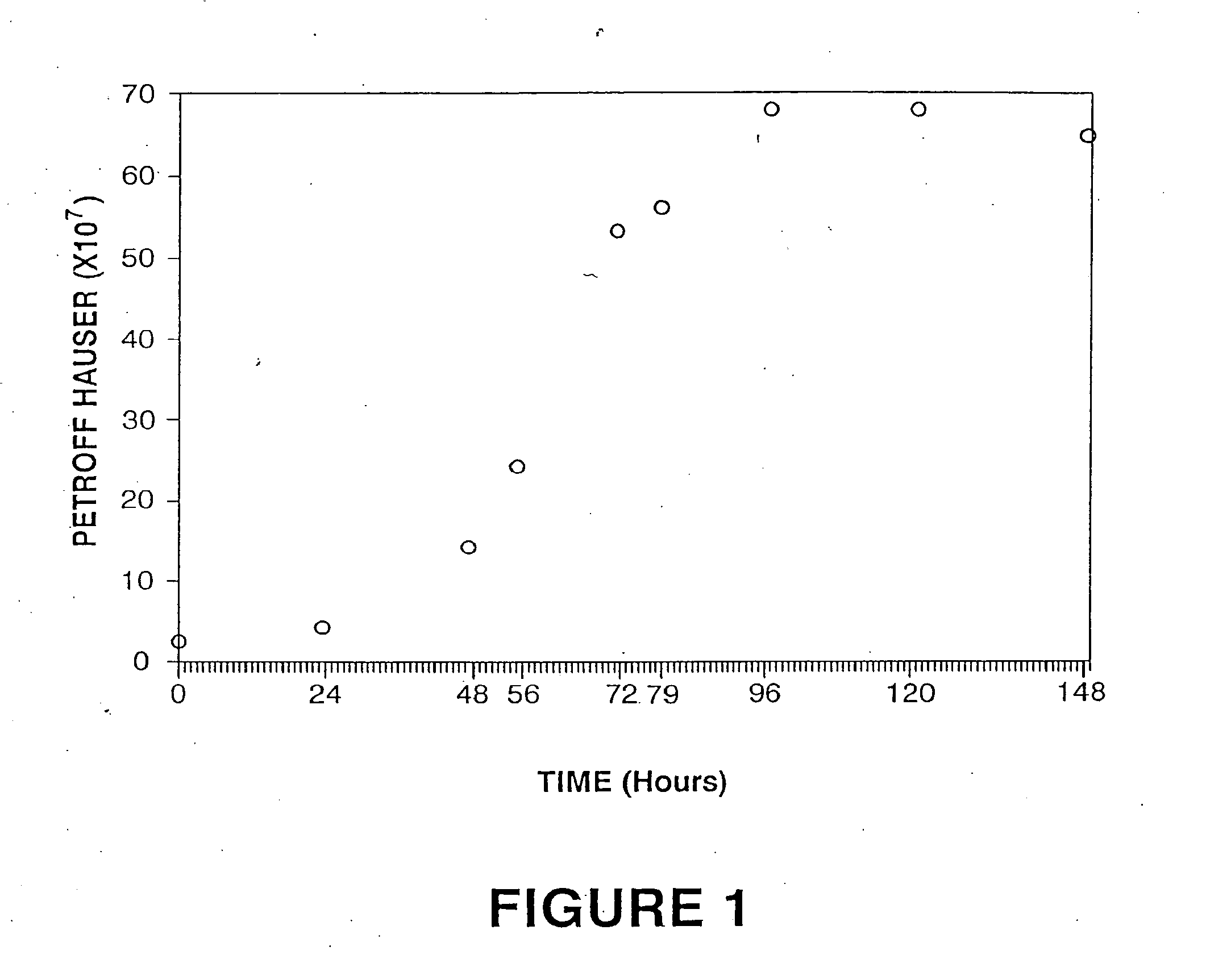
[0063] Nonsterile: magnetic stirring motors; pipet aids; peristaltic pumps; tubing and tubing clamps; Petroff / Hauser counting chamber; darkfield microscope; coveralls, gloves, hats, masks, shoe covers and face shields; micropipet and micropipet tips; saline solution blanks.
[0064] Microorganisms used: Two isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi are used in the preparation of the product, B. burgdorferi isolates C-1-11 and S-1-10 obtained from Dr. Steven M. Callister, Gundersen Medical Foundation, La Crosse, Wis. The bacterin will contain adjusted counts of each Borrelia isolate culture to satisfy potency standard requirements.
[0065] Identity of each microorganism and frequency of methods of identification: Identification is made on the basis of morphological a...
example 2
Preparation of the Product
[0081] Method of inactivation: The production growth is inactivated with binary ethyleneimine (BEI). Inactivation is conducted at 32° C.±2° C. The appropriate amount of BEI is prepared as a 0.344 M (7.05%) solution. A 7.05% BEI solution is prepared by dissolving 70.48 grams of 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide (molecular weight 204.89) and 8.00 grams NaOH (MW 40.00) in one liter of deionized water. The dissolved solution is incubated at 37° C. for two hours and then added to the culture at 30 ml per liter under constant agitation (slow stirring). The inactivation is conducted for no less than 24 hours at a pH of 7.3±0.2 with agitation (slow stirring). Upon completion of inactivation, the BEI is neutralized by the addition of sterile sodium thiosulfate. The appropriate amount of sterile sodium thiosulfate solution is prepared as a 3.015 M (47.7%) solution by dissolving 477.0 grams sodium thiosulfate in one liter of deionized water. This solution is filtered th...
example 3
Testing of the Bacterin
[0097] Purity: Each serial or subserial is tested for bacteria and fungi in accordance with 9 C.F.R. §113.26.
[0098] Safety: Safety testing is conducted on bulk or final containers in accordance with 9 C.F.R. §§ 113.38 and 113.40 wherein a dog safety test is conducted using a 2× (2 cc) dose given by IM injection.
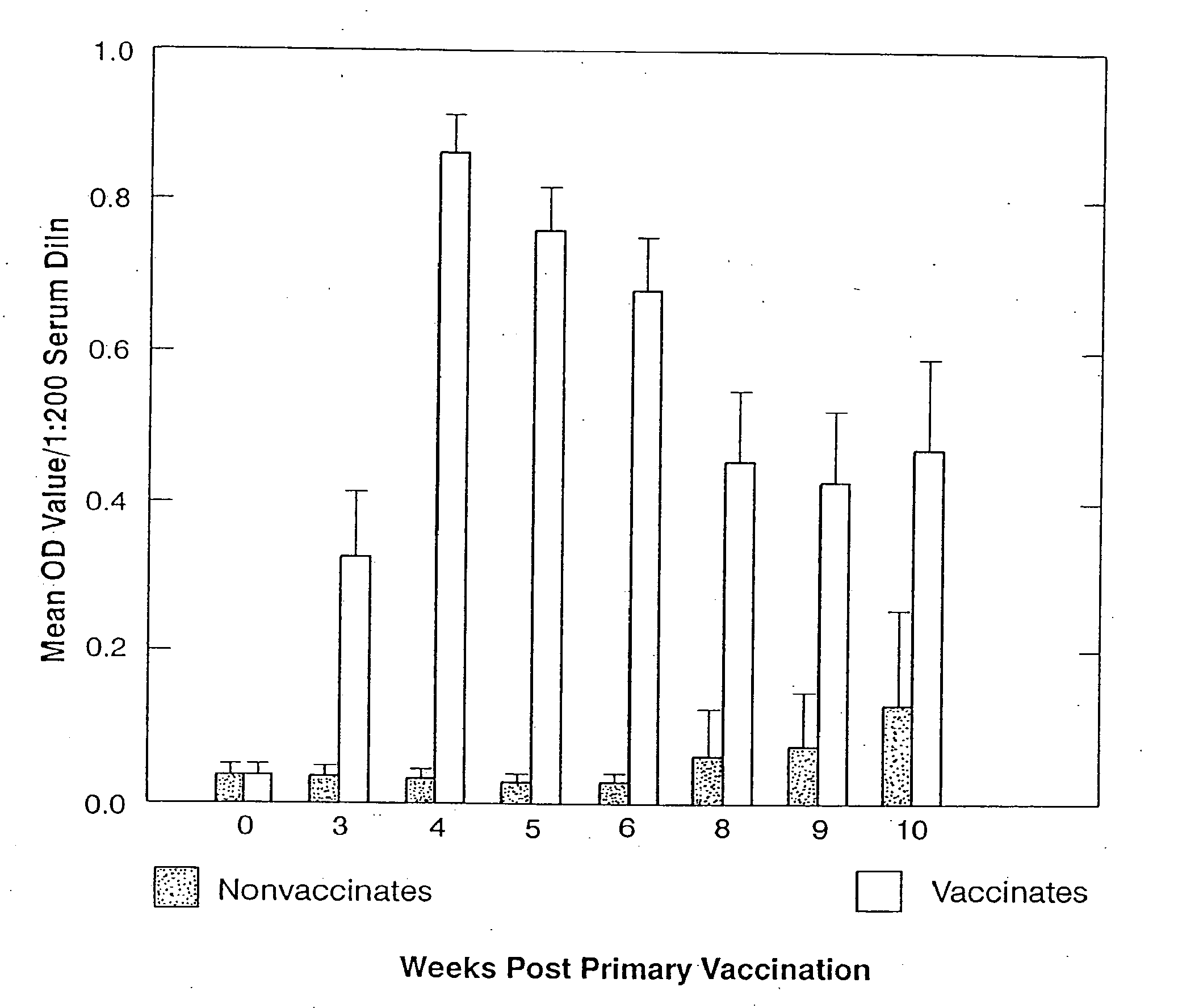
[0099] Potency: Potency testing is conducted on assembled bulk or final containers. Potency testing is conducted using an antigen capture ELISA. Satisfactory serials must have a relative potency of ≧1.0 as determine by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Veterinary Biologics Program's Relative Potency Calculations Software, Version 3.0.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com