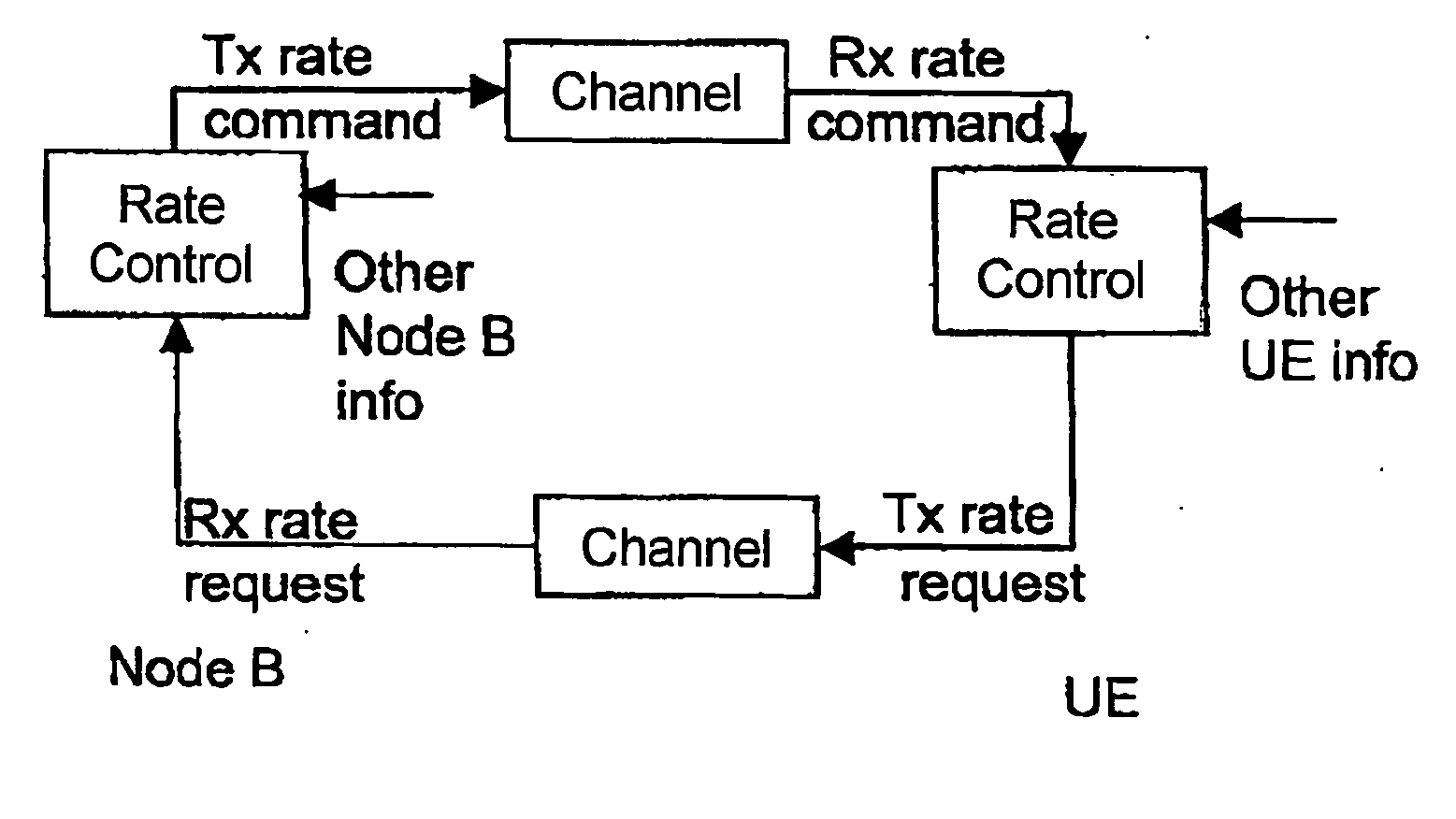
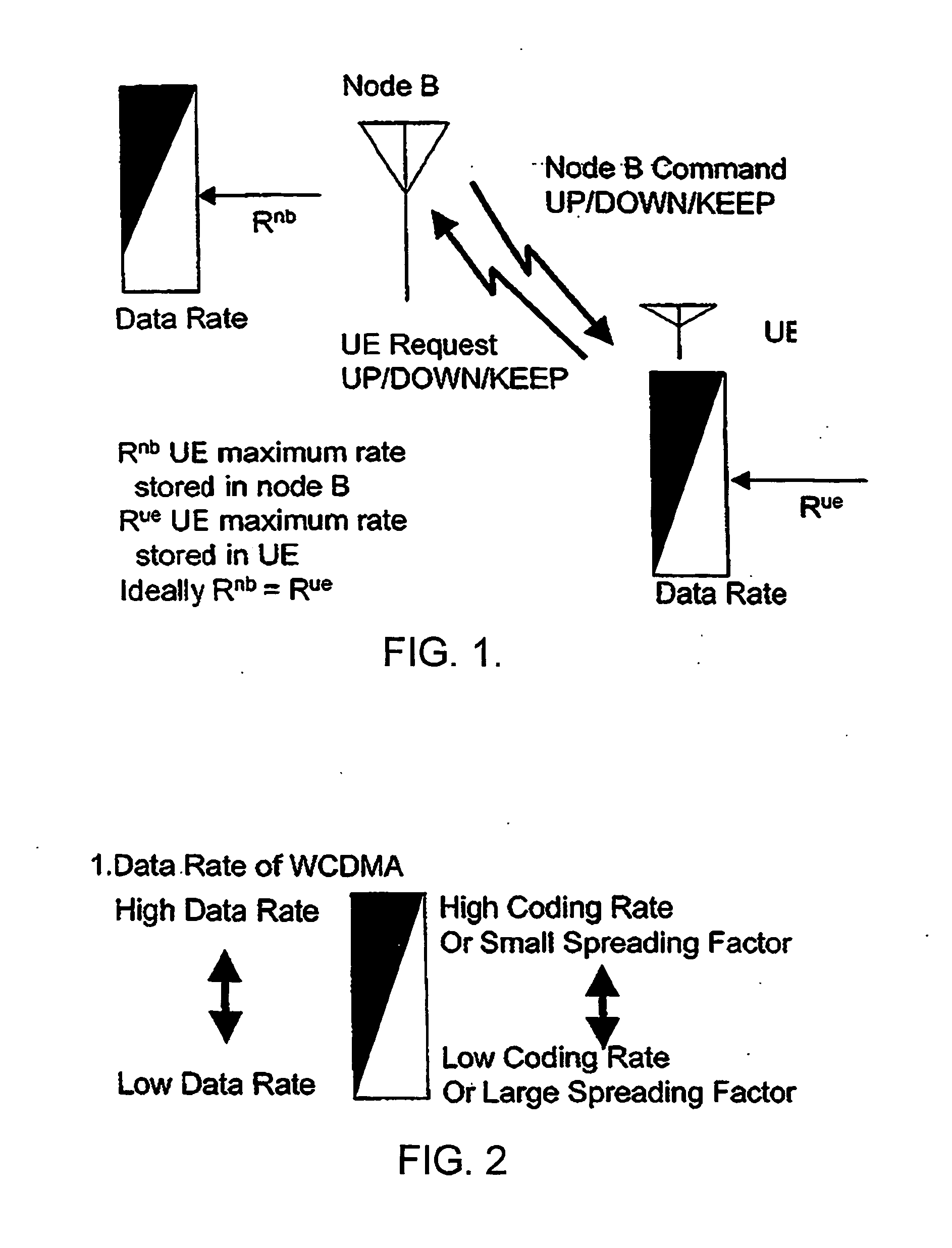
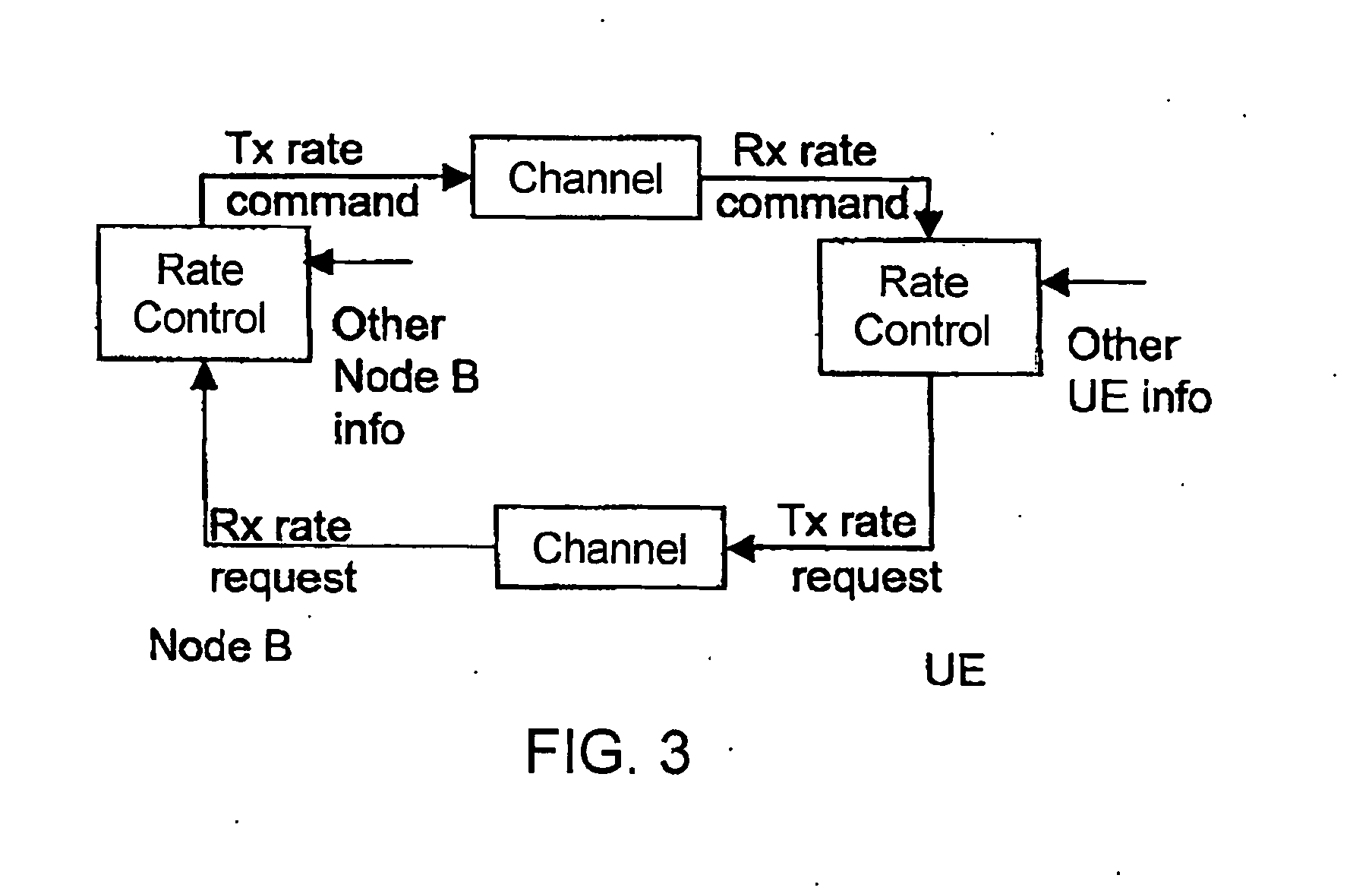
Rate control method and apparatus for data packet transmission
a data packet and rate control technology, applied in data switching networks, frequency-division multiplexes, wireless commuication services, etc., can solve the problems of inability to adapt to uplink rate control, and inability to transmit data packets with excessively high or excessively low transmission power, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing signalling errors and increasing system overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0261] The key concept in a first solution to the problem mentioned above is periodic reset-based synchronization. This involves the radio network controller (RNC) signalling a reset frequency Q and a reference data transmission rate Rref to both node B and the UE at radio-link establishment, and then after closed-loop rate control is initiated, node B and the UE periodically reset Rnb and Rue, respectively, to Rref. The time reference-of periodic reset is the Connection Frame Number (CFN) which is a common reference time between node B and the UE during radio link connection.
[0262] The benefit of this scheme is its simplicity. Also, this method is useful when the number of available uplink rates is small, although the periodic resetting will interrupt the fast closed-loop rate control. If the available uplink rate is large, significant jitter will cause severe interruption of closed-loop rate control.
[0263] A second solution to the problem mentioned above involves three “simultan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com