Hip/pap polypeptide compositions for use in liver regeneration and for the prevention of liver failure
a technology of liver failure and composition, applied in the field of human hepatocarcinomaintestinepancreas/pancreaticassociated protein, can solve the problems of liver failure risk of patients subject to inborn metabolism errors, severe damage to body's entire metabolism, and metabolic instability, so as to improve liver function and liver function, and confirm liver cell transplantation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Characterization of Human HIP / PAP Transgenic Mice
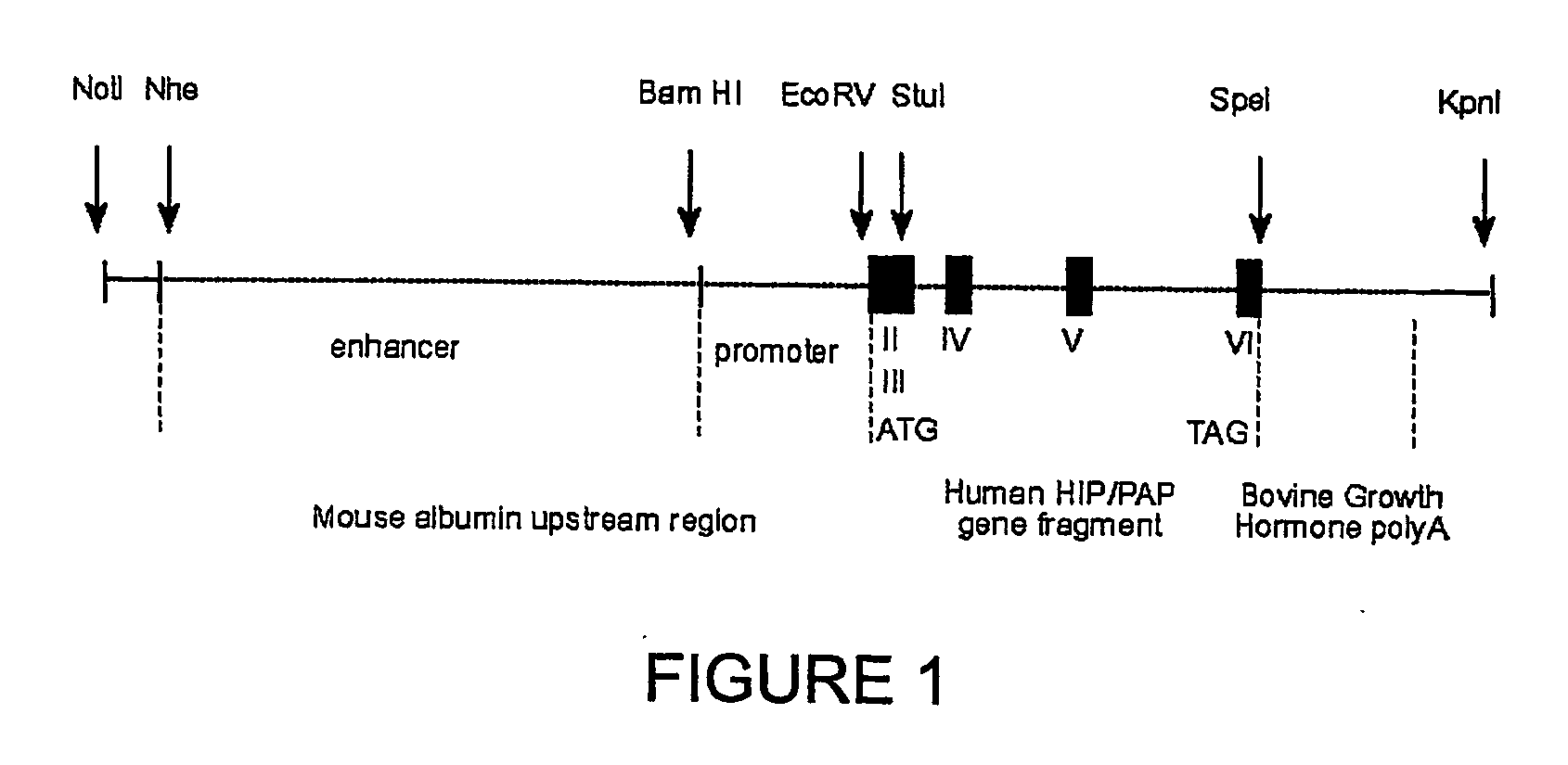
[0218] The HIP / PAP transgene was specifically expressed in the liver, and HIP / PAP-expressing mice did not develop livers tumours, after a two year following. Immunohistolocalization analysis detected HIP / PAP protein in the liver of transgenic mice as diffuse intra-hepatocyte immunostaining, occupying most of the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes (FIGS. 2A, 1 and 2). Staining was heterogenous and positive regions were located either in centrolobular or portal areas of the liver acinus. This heterogeneous distribution likely reflects HIP / PAP secretion, thus hepatocytes could be either positive or negative before or after HIP / PAP secretion respectively. HIP / PAP protein was secreted into the serum (250 ng / ml to 700 ng / ml) in homozygote transgenic lines 24 and 27, and into the culture medium of primary hepatocytes (30 to 120 ng / ml per 2.105 cells). No difference in morphology and ploïdy was detected between HIP / PAP-expressing and control hepat...
example 2
Liver Regeneration is Stimulated in Mice Expressing the Human HIP / PAP Gene
[0219] To test in vivo the HIP / PAP effect on liver cell proliferation, liver regeneration induced by partial hepatectomy was examined. Low magnification (×20) views for times 24, 36, 46 and 55 hours post partial hepatectomy are presented FIG. 3A. At the indicated times, percentages of positive BrdU cells were higher in HIP / PAP transgenic than in wild-type livers, despite the low overall frequency of nuclei which had incorporated BrdU in both groups. The percentages of nuclei incorporating BrdU were significantly higher in HIP / PAP transgenic mice (median 33%; range 20-42%) compared to wild-type (median 18%; range 11-27%) (P=0.0014), 46 hours after partial hepatectomy (FIG. 3 B). To reinforce the hypothesis that HIP / PAP protein may act as Growth Factor during liver regeneration, the time-course of the hepatic mass restoration in wild-type and transgenic mice was established, after hepatectomy (FIG. 3C). Animal ...
example 3
HIP / PAP Mitogenic Effect in Primary Culture Hepatocytes
[0220] In order to further investigate the enhanced liver regeneration observed in vivo after hepatectomy in HIP / PAP transgenic mice, primary cultures of hepatocytes were used to evaluate a HIP / PAP mitogenic effect. Hepatocytes derived from HIP / PAP transgenic and wild-type mice exhibited two peaks DNA synthesis, 60 and 84 hours after plating, when stimulated by EGF (FIGS. 4 A and B). At 60 hours, mean percentages of BrdU-positive hepatocytes were 31±7% (n=19) and 16±4% (n=20) in transgenic and wild-type mice, respectively (p−1) was added to wild-type hepatocytes, EGF-induced DNA synthesis increased from 16±4% to 24±7% (p=0.0168; n=8; FIG. 4C). These results showed that HIP / PAP was a mitogenic factor for hepatocytes in primary culture. The mitogenic effect of HIP / PAP on hepatocyte proliferation was thus demonstrated both in vivo and in vitro.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com