Dental releasing materials
a technology of releasing materials and dentures, applied in the field of dental releasing materials, can solve problems such as bulk fractures, and achieve the effect of enhancing the strength of composite materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
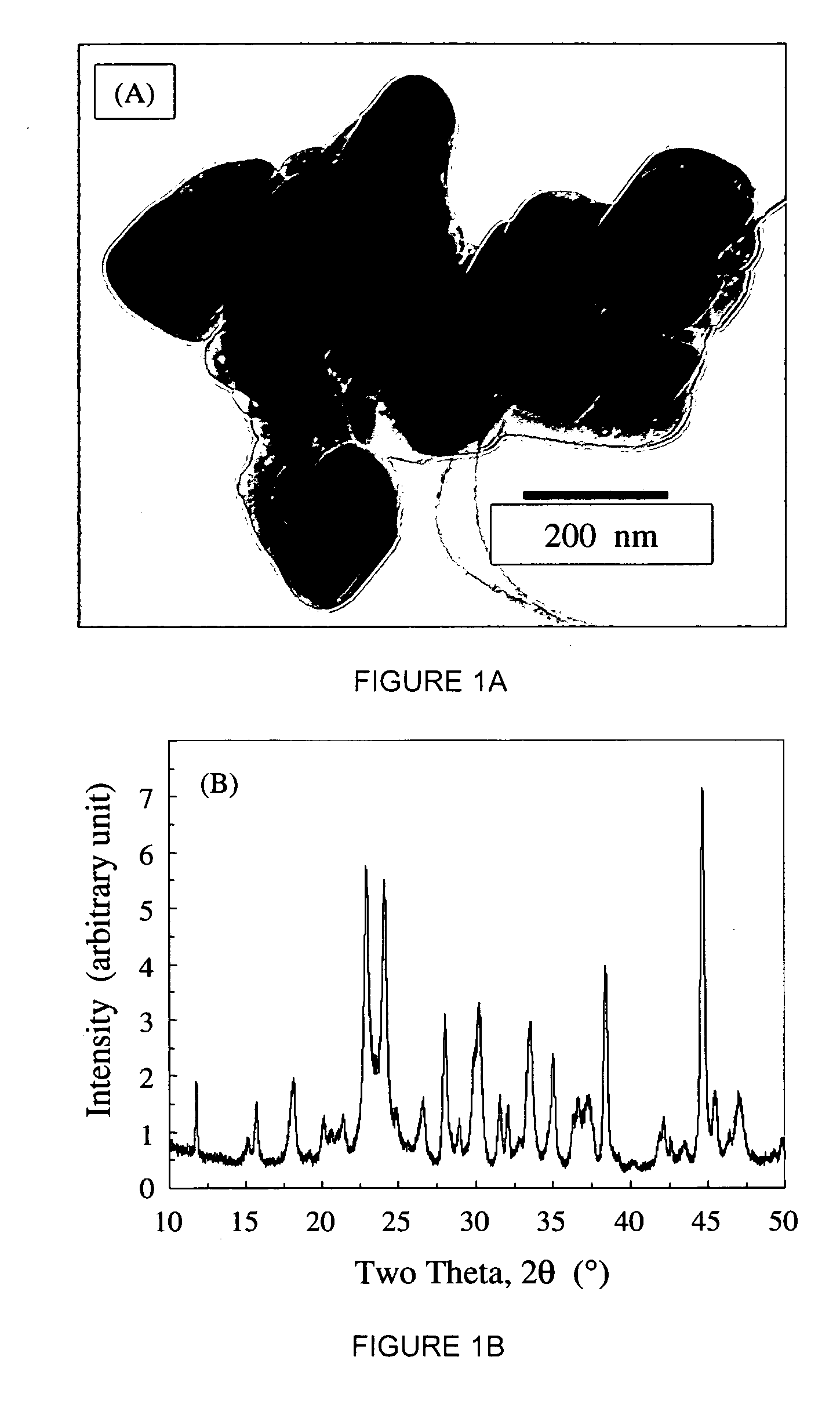
[0072] Nano MCPM particles. In this example, nano-sized MCPM (monocalcium phosphate monohydrate, Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O) particles are used as fillers to make dental releasing materials. The nano MCPM powder can be prepared by using a spray drying process or other suitable processes. The spray drying apparatus consists of a spray nozzle situated on the top of a glass column, which is heated with electrical heating tapes and thermally insulted. The water in the diluted Ca—P solution are evaporated into the dry, heated air in the column and expelled from the precipitator into a hood. The fine particles suspended in the flow are trapped in the precipitator and collected at the end of the process. The solution for making nano MCPM is prepared by dissolving CaCO3 in a H3PO4 diluted solution (8 mM Ca and 16 mM PO4). While this process serves as an example, nano MCPM from other processes can also be used as fillers for dental materials.
[0073] Examples of nano MCPM particles thus produced are show...
example 2
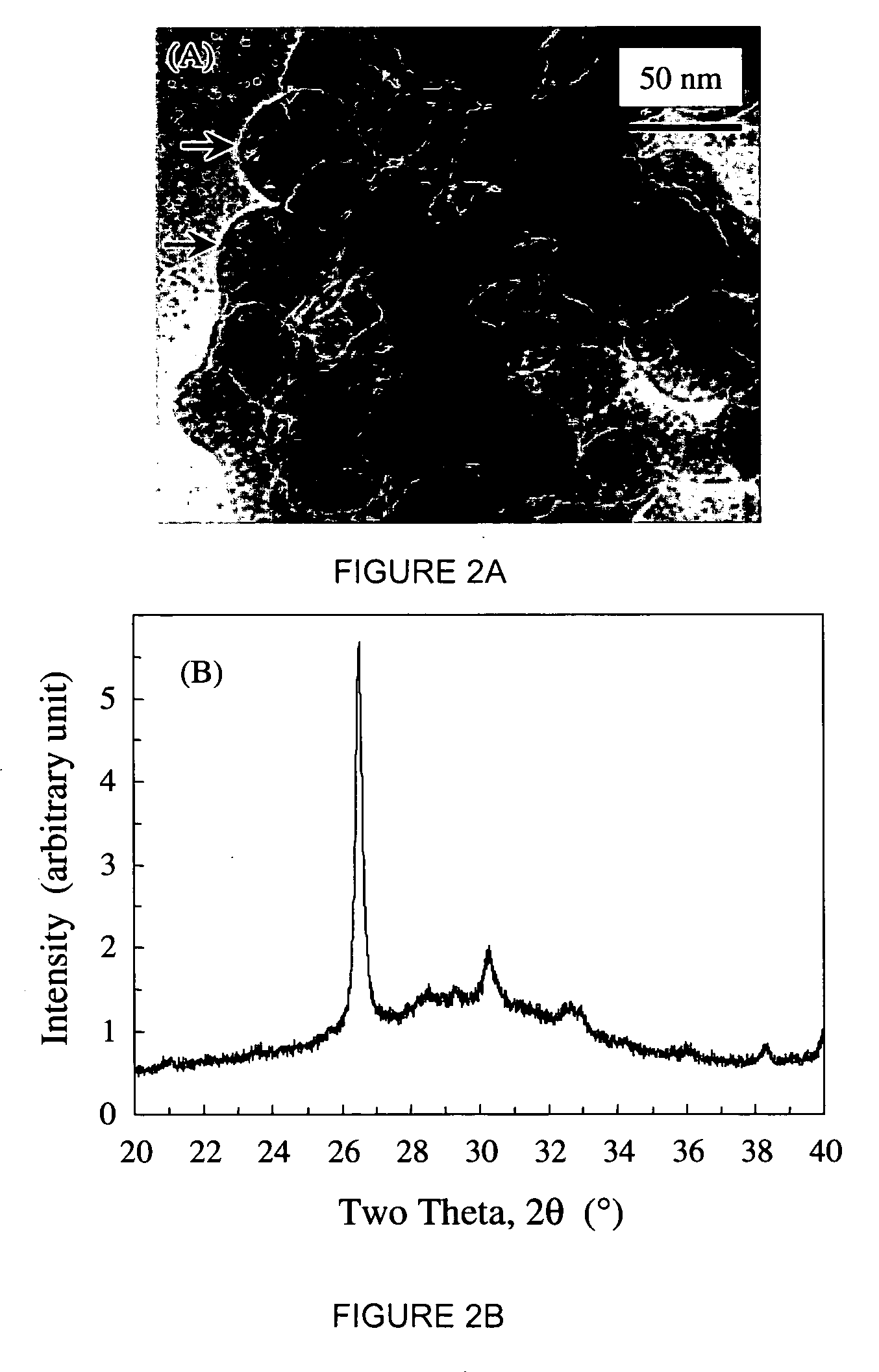
[0074] Nano DCPA particles. In this example, nano-sized DCPA (dicalcium phosphate anhydrous, CaHPO4) particles are used as fillers in dental materials. Nano DCPA can be made by using a method similar to that described in Example 1 as well as by other suitable methods. For nano DCPA, the solution being sprayed contains an acid component to solubilize the calcium phosphate compound. The DCPA-saturated solution that is used in the spray drying process is prepared by dissolving commercial DCPA in a dilute acetic acid (16 mmol / L) solution (8 mM Ca and PO4). While this process serves as an example, nano DCPA from other processes can also be used as fillers for dental materials.
[0075] Examples of nano DCPA particles thus produced are shown in the TEM micrograph in FIG. 2A. The particle sizes range from about 50 nm to 200 nm. Some nano particles appear to be connected to form a fibrous structure. The thickness of the fibrous structure is about 50 nm, and the length of the fibrous structure...
example 3
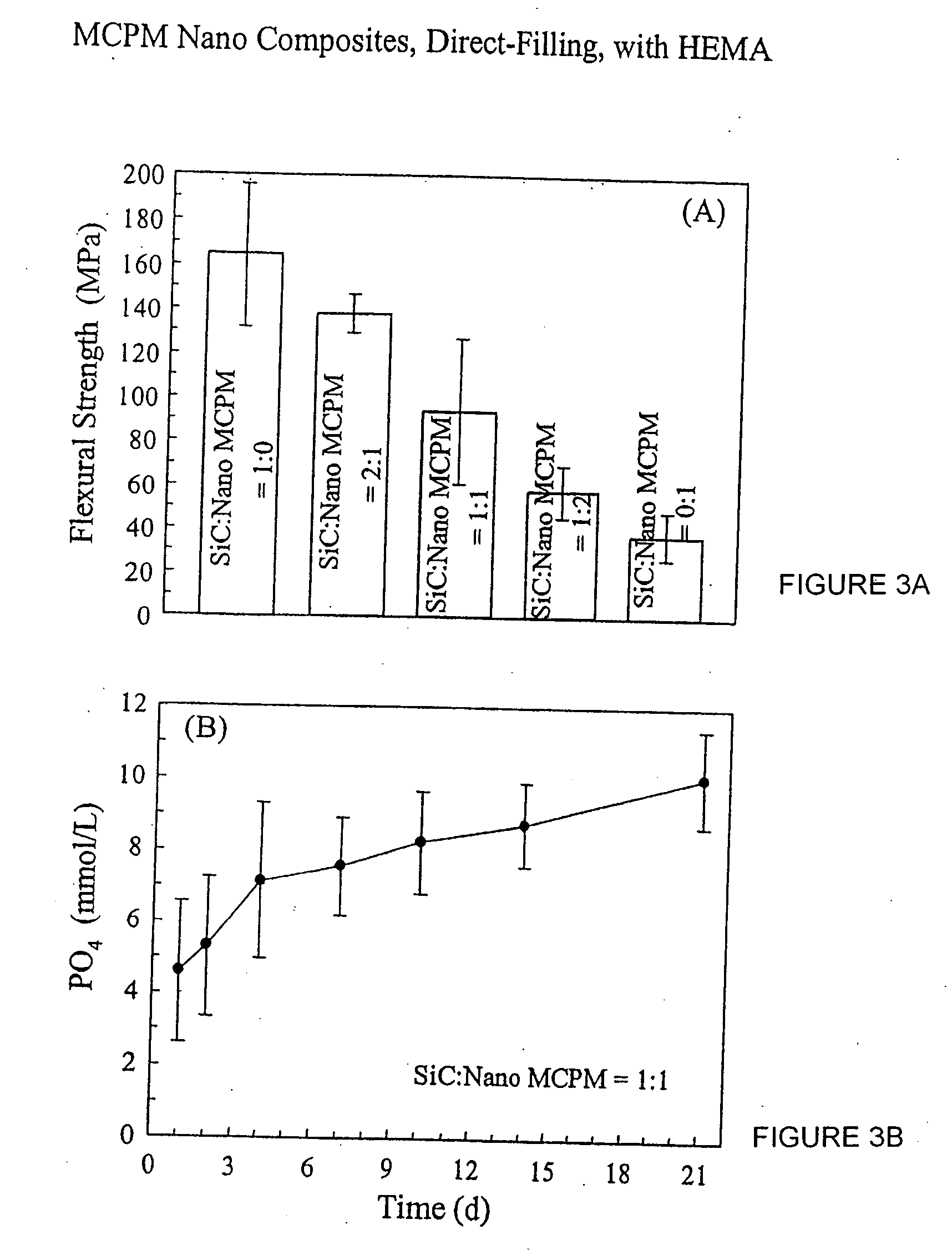
[0076] Direct-filling nano MCPM composites with HEMA. An example of manufacture of this invention comprises direct-filling composites containing nano MCPM and a strengthener. The strengthener can be glasses, ceramics, metals, polymers and mixtures thereof. They can be fibers, particulates or whiskers. As an example of using a strengthener, silicon carbide (SiC) fillers are used with an elongated shape having a diameter of 0.1-3 μm with a mean of 0.9 μm, and a length of 2-100 μm with a mean of 14 μm. SiC is mixed with silica (SiO2) having a particle size of 40-70 nm, at a SiC:silica mass ratio of 5:1, to serve as an example. The mixed powder is heat-treated at a temperature of 800° C. for 30 min. The powder is silanized as usual by mixing it with mass fractions of 4% 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS) and 2% n-propylamine in cyclohexane in a rotary evaporator. The silanized nano-silica-SiC fillers are referred to as SiC strengthener. The strengthener is mixed with nano MCPM...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com