Multimedia system for mobile client platforms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
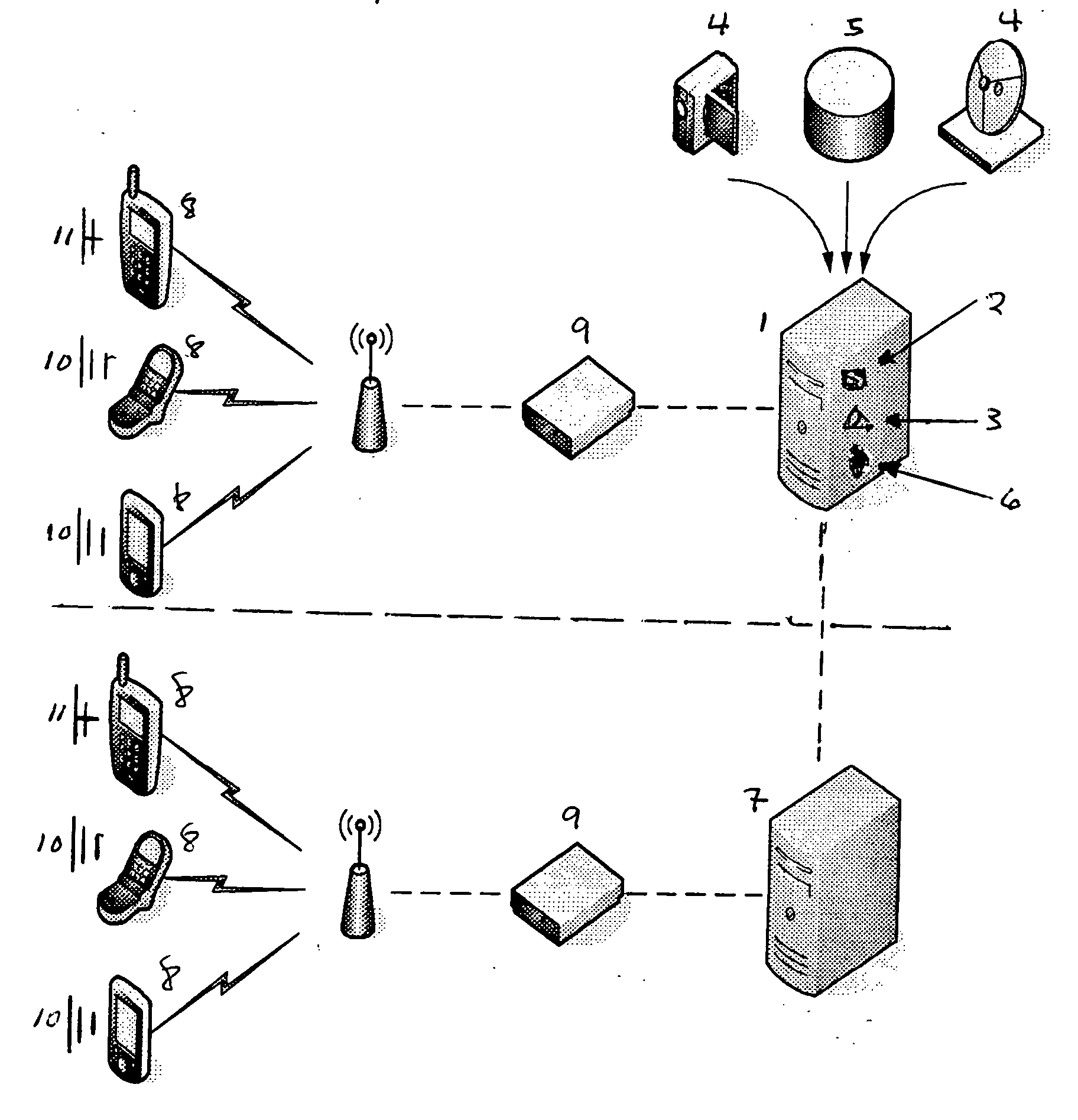
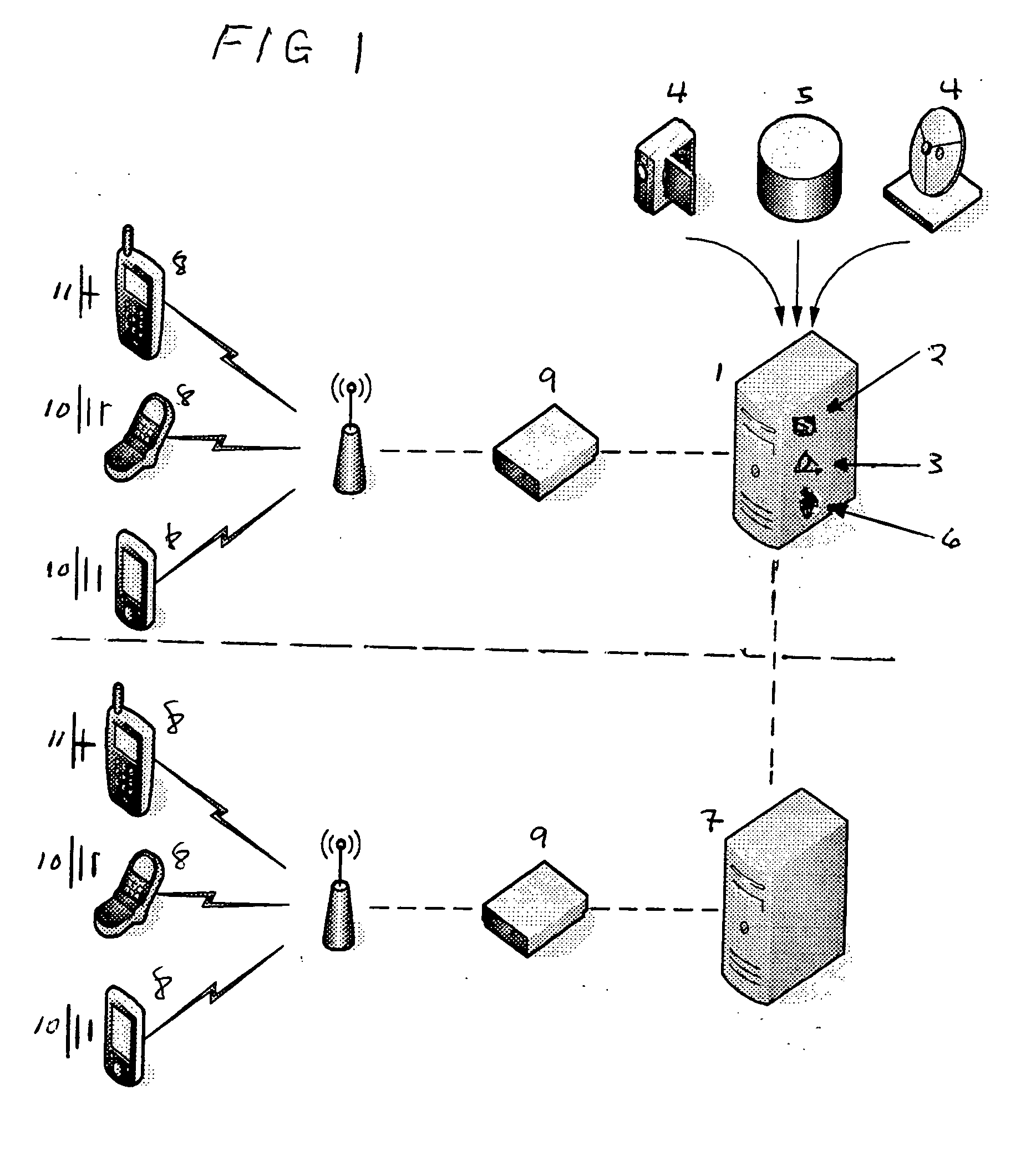
[0047]FIG. 1 illustrates a centralized content server system 1, utilizing a transcoder 2 and a multimedia object creator 3 to create multimedia objects from a live broadcast 4 or to transcode and create multimedia objects from archived multimedia files 5. The central server includes an indexing host system 6 to deploy created multimedia objects to relevant content servers 7 through the wired Internet and to verify all geographically dispersed wireless clients 8. The system includes the potential use of proxy cellular network http servers 9, which can cache large numbers of small multimedia objects to support large numbers of concurrent wireless clients 8 running multimedia object java applets 10 or embedded or downloaded non-java multimedia players 11.
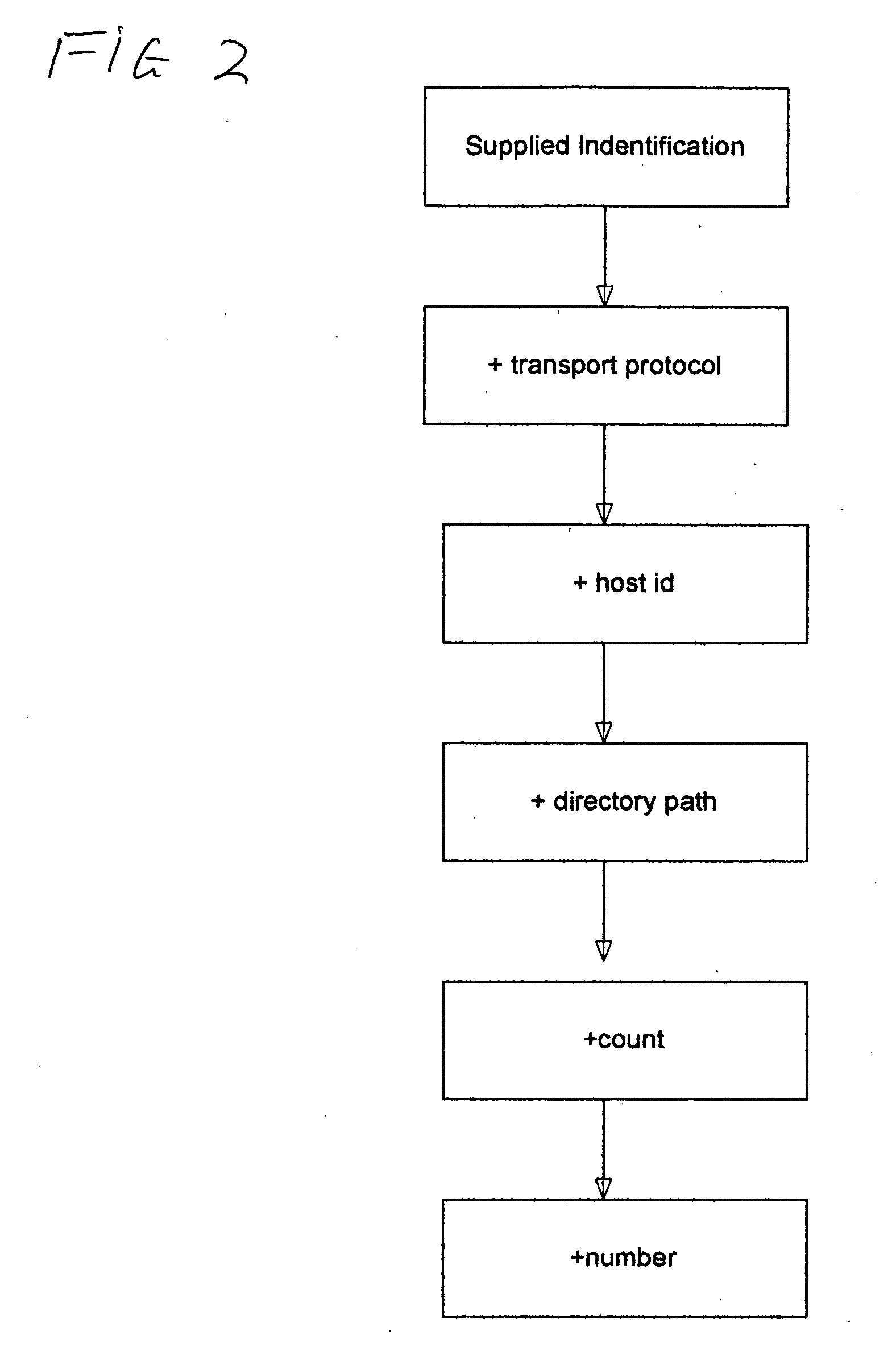
[0048]FIG. 2 is a flow diagram illustrating the process of multimedia object identification by the multimedia object creator 3. This process encodes a Supplied Identification to each multimedia object to identify the transport protoco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com