Mutation associated with epilepsy
a technology of mutation and epilepsy, applied in the field of mutation associated with epilepsy, can solve the problems of varying degrees of involuntary muscle contraction, loss of consciousness, persistent increase in neuronal excitability, etc., to reduce the density of functional gabaa receptors, increase neuronal excitability and seizures, and reduce inhibitory responses to gaba
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Genotyping and Linkage Analysis
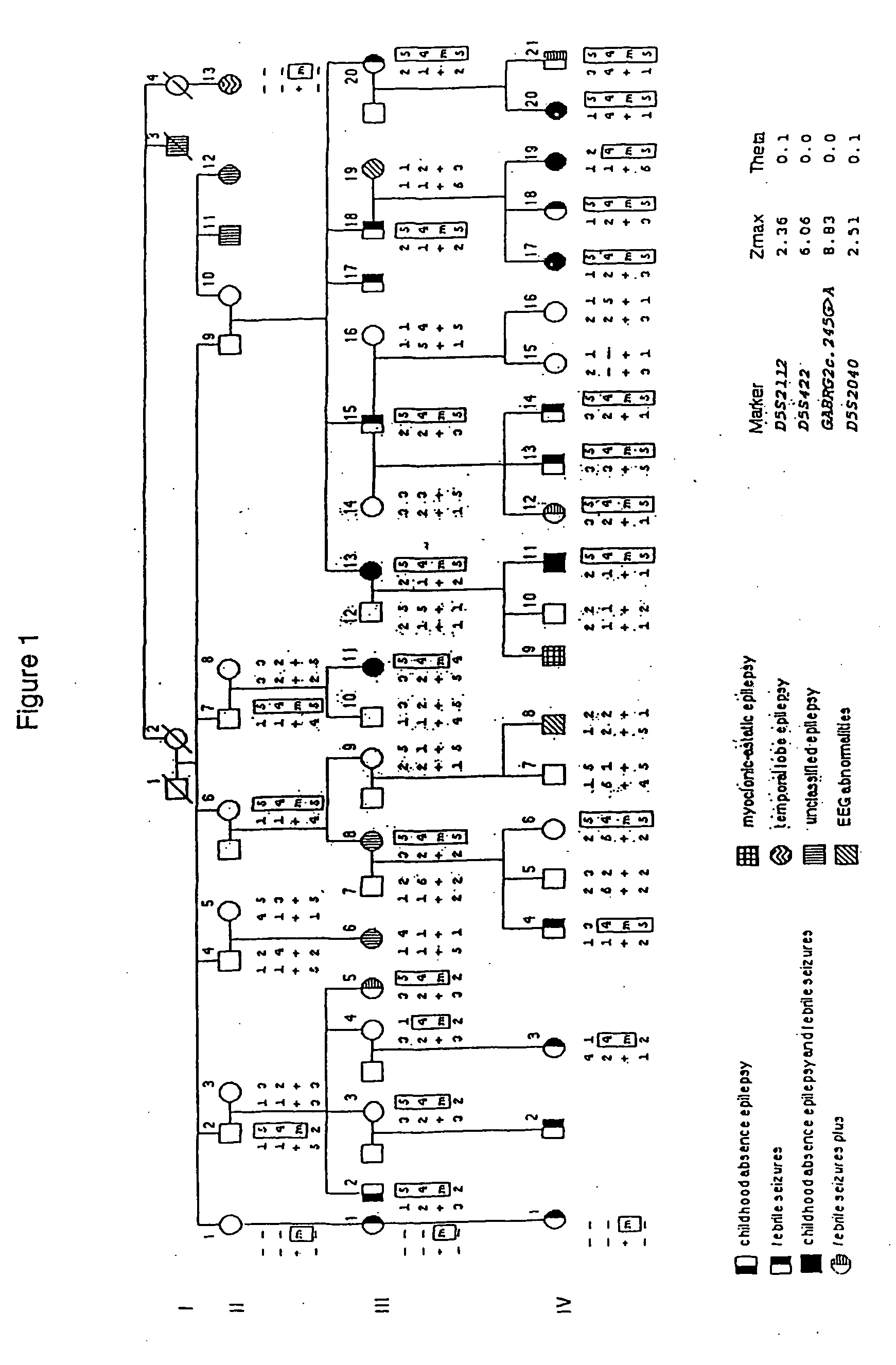
[0153] Automated genotyping of DNA samples obtained from Family 1 was carried out by the Australian Genome Research Facility. A genome-wide scan of 400 markers spread at an average genetic distance of 10 cM was performed. For the linkage analysis, all individuals with febrile seizures (FS), febrile seizures plus (FS+) or childhood absence epilepsy (CAE) were considered affected. Those individuals with unclassified epilepsy or abnormal electroencephalograms were assigned an unknown affection status. Lod scores were determined using FASTLINK v4.0P (Lathrop and Lalouel, 1984). Two point lod scores were calculated assuming autosomal dominant inheritance, 75% penetrance, a disease allele frequency of 0.0001 and equal marker allele frequencies.
[0154] Additional microsatellite markers from chromosome 5 were manually genotyped as previously described by Phillips et al (1995). Briefly, PCR amplification was carried out on 100 ng of genomic DNA using [α-32P]dC...
example 3
Mutation Analysis of GABRG2 in Family 1
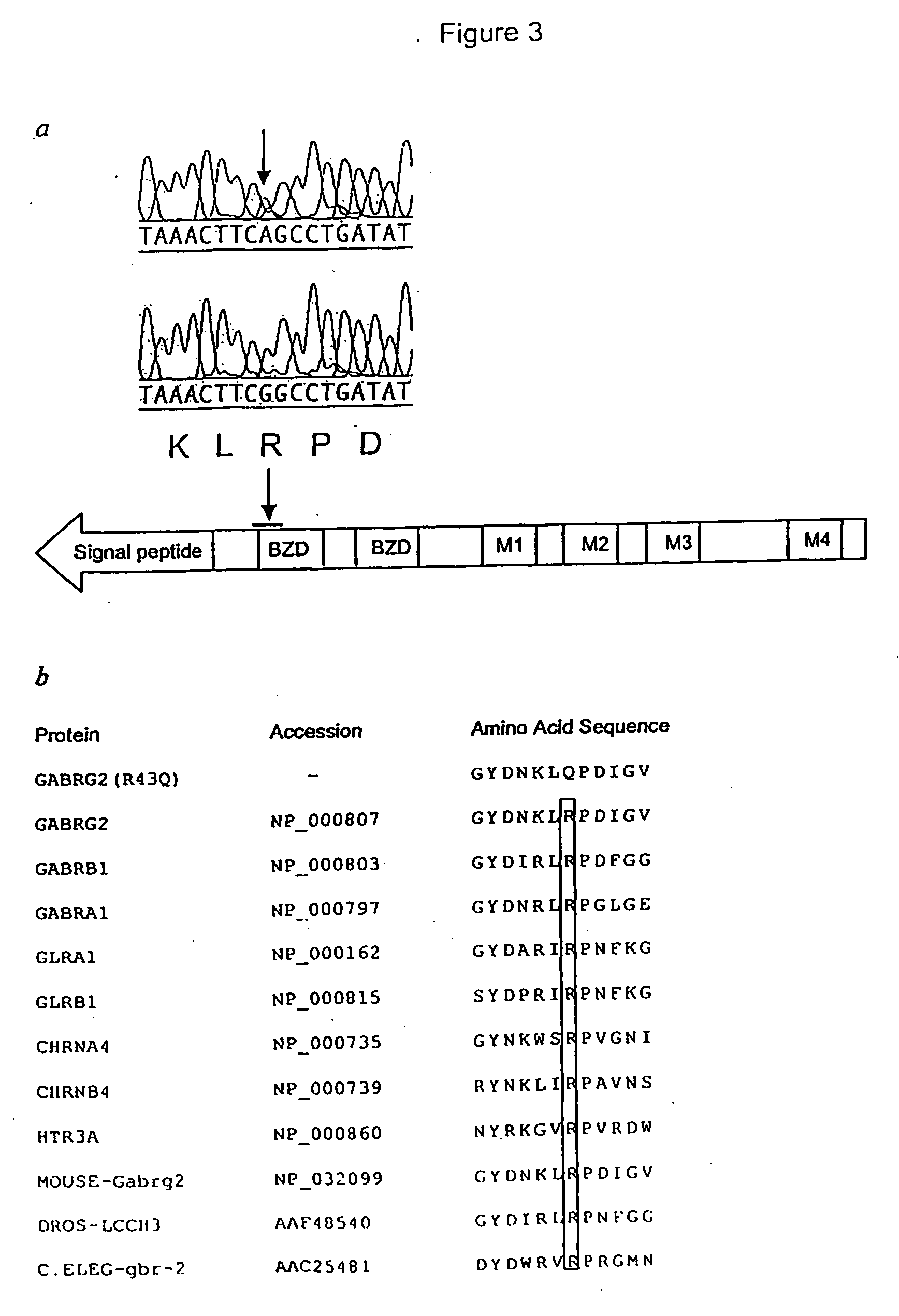
[0157] SSCP analysis of GABRG2 exons followed by sequencing of SSCP bandshifts was performed on individuals from Family 1 to identify disease causing mutations. The primers used to analyse Family 1 are shown in Table 2. The sequences of these primers are represented by SEQ ID Numbers:7-24.
[0158] PCR reactions using exon specific primers contained 67 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8); 16.5 mM (NH4)2SO4; 6.5 μM EDTA; 1.5 mM MgCl2; 200 μM each DNTP; 10% DMSO; 0.17 mg / ml BSA; 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol; 15 μg / ml each primer; 200 μCi / ml [α-32P]dCTP; 100 U / ml Taq DNA polymerase, and 10 μg / ml genomic DNA. PCR reactions were performed using 10 cycles of 94° C. for 60 seconds, 60° C. for 90 seconds, and 72° C. for 90 seconds followed by 25 cycles of 94° C. for 60 seconds, 55° C. for 90 seconds, and 72° C. for 90 seconds. A final extension reaction for 10 minutes at 72° C. followed. Completed PCR reactions were subsequently mixed with an equal volume of formamide load...
example 4
Mutation Analysis of GABRG2 in Family 2
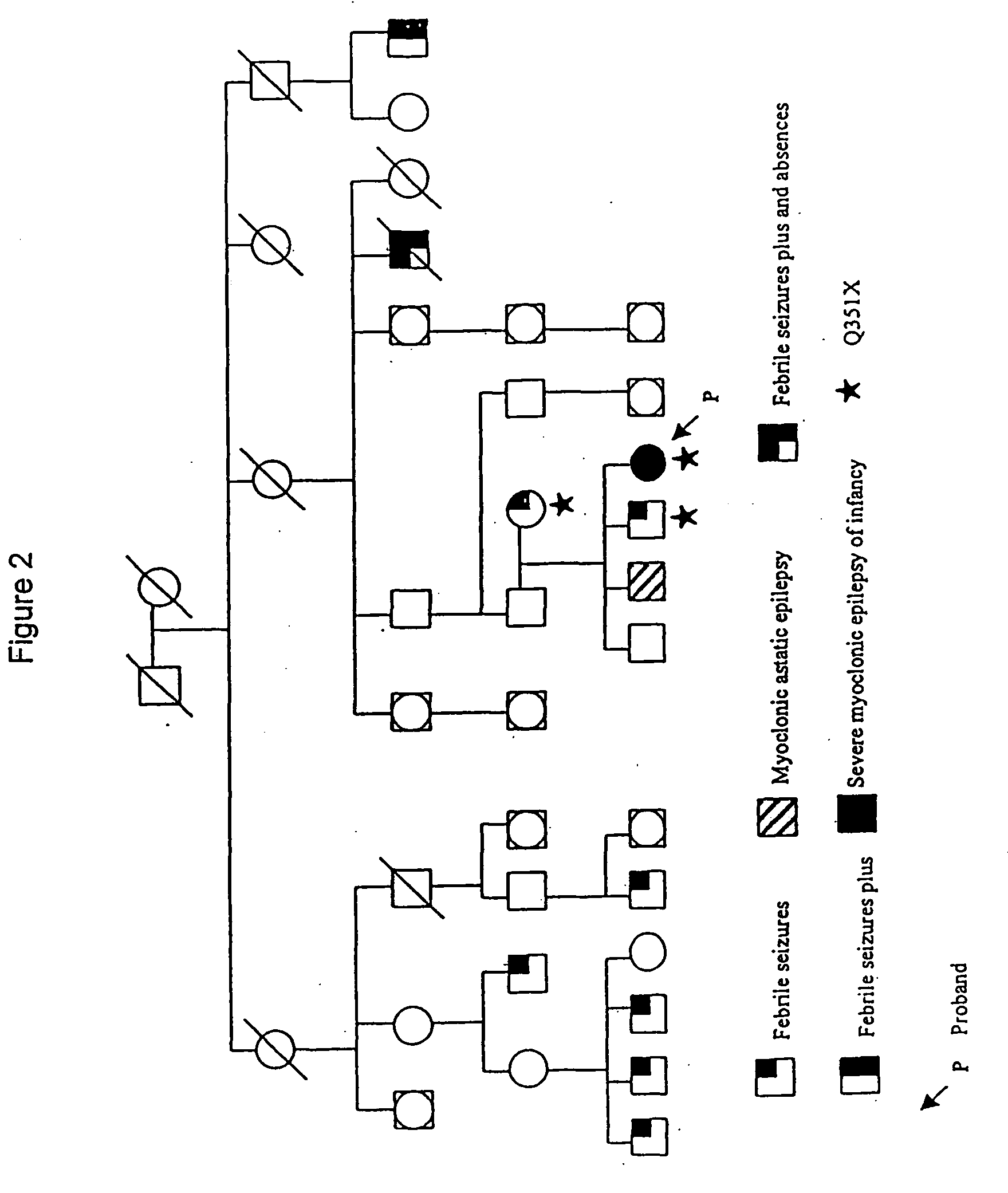
[0161] SSCP analysis of GABRG2 exons followed by sequencing of SSCP bandshifts was performed on individuals from Family 2 to identify disease causing mutations. The primers used to analyse Family 2 are shown in Table 3. The sequences of these primers are represented by SEQ ID Numbers:7-17, 19-24 and 25-29.
[0162] For the analysis of this family primers used for SSCP were labelled at their 5′ end with HEX. Typical PCR reactions were performed in a total volume of 10 μl using 30 ng of patient DNA. All PCR reactions contained 67 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8); 16.5 mM (NH4)2SO4; 6.5 μM EDTA; 1.5 mM MgCl2; 200 μM each dNTP; 10% DMSO; 0.17 mg / ml BSA; 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol; 5 μg / ml each primer and 100 U / ml Taq DNA polymerase. PCR reactions were performed using 10 cycles of 94° C. for 30 seconds, 60° C. for 30 seconds, and 72° C. for 30 seconds followed by 25 cycles of 94° C. for 30 seconds, 55° C. for 30 seconds, and 72° C. for 30 seconds. A final extension...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com