Solid-state image pickup device and method of resetting the same
a solid-state image and pickup device technology, applied in the field of solid-state image pickup devices, can solve the problems of low manufacturing yield, affecting the variance of manufacturing process, saturation charge qsub>sat/sub>or the depletion voltage vsub>dp /sub>, etc., to achieve effective photoelectric conversion, reduce residual charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
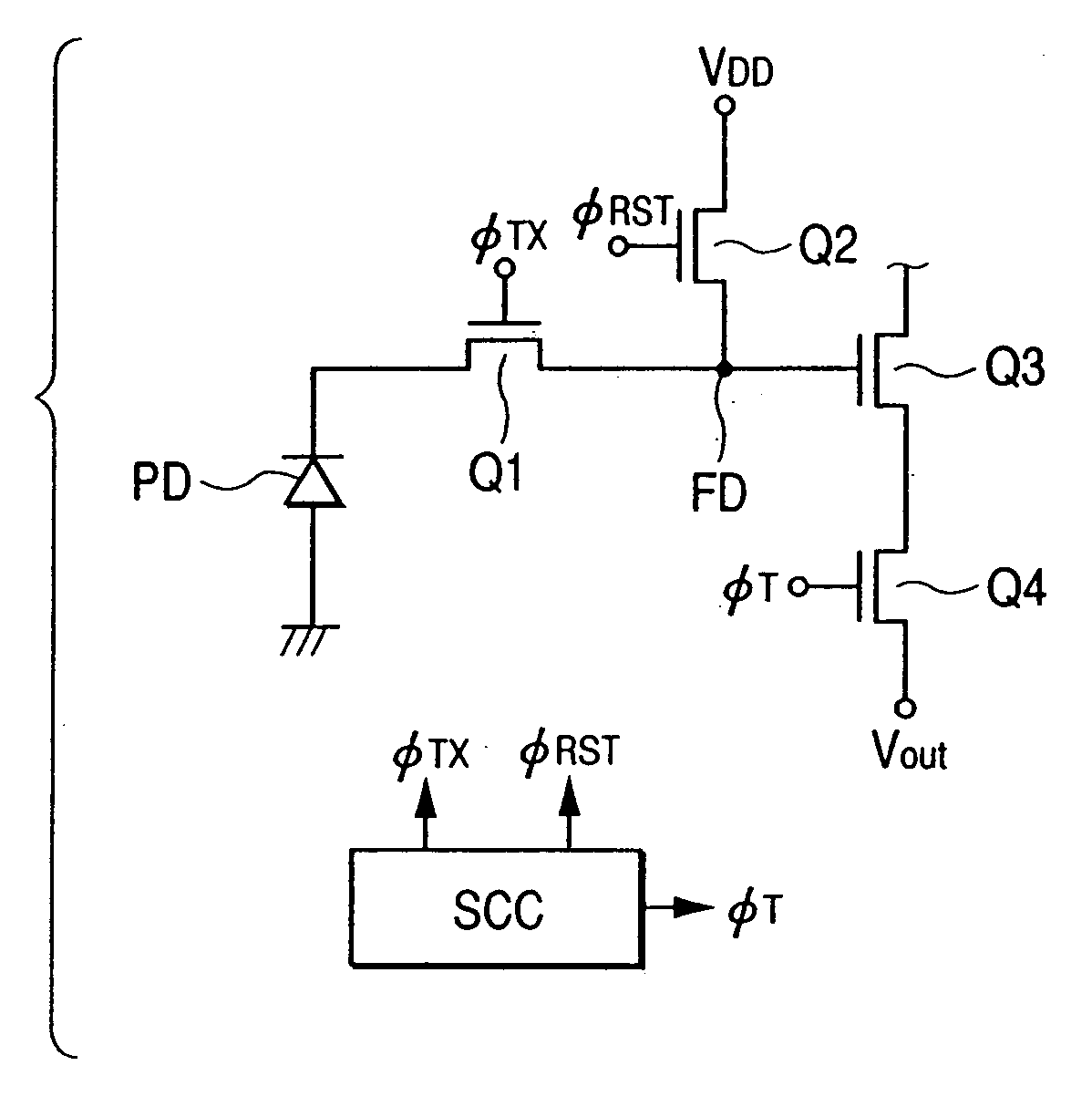
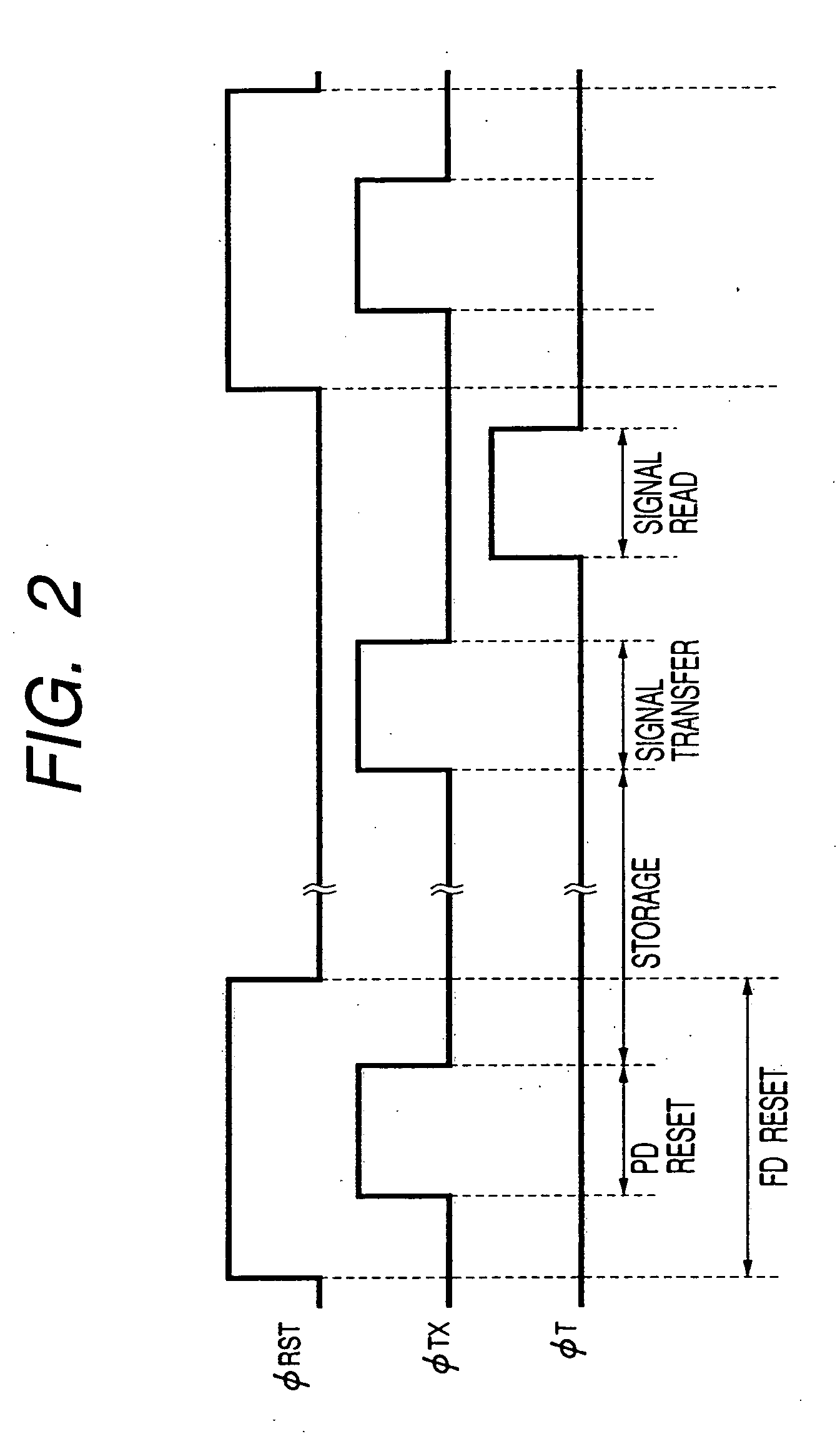
[0046]FIG. 1 is a schematic circuit diagram of a pixel of a preferred embodiment of solid-state image pickup device according to the invention and FIG. 2 is a drive timing chart illustrating the operation of the preferred embodiment of solid-state image pickup device according to the invention. Note that the basic configuration of this embodiment is commonly applicable to the remaining embodiments as will be described hereinafter.
[0047] The photoelectric converter PD typically comprises a photodiode having a PN junction or a PIN junction. One of the terminals of the photoelectric converter is held to a reference potential for applying a reverse bias voltage, while the other terminal thereof is connected to a transfer switch Q1. From FIG. 1, it will be seen that the cathode is connected to the transfer switch Q1 to transfer electrons.
[0048] In FIG. 1, Q2 denotes a reset switch having one of its terminals connected to reference voltage source VDD for applying a resetting voltage.
[0...
embodiment 2
[0071] Now, another embodiment of the present invention will be described by referring to FIGS. 6, 7 and 8.
[0072]FIG. 6 is a schematic cross sectional view of the second embodiment of solid-state image pickup device according to the invention. FIG. 7 is a schematic illustration of changes that can take place in the potential profiles of principal sections of the embodiment of solid-state image pickup device of FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is a drive timing chart illustrating the operation of the preferred embodiment of solid-state image pickup device of FIG. 6. Note that the embodiment of solid-state image pickup device of FIG. 6 has a basic circuit configuration same as the embodiment of FIG. 1.
[0073] Referring to FIG. 6, the photodiode of the photoelectric converter of this embodiment is a buried type photodiode comprising a P-type well 101 formed in the substrate surface, a N-type region 105 and a surface p-region 104. As described above, with a buried type photodiode, the dark current that ...
embodiment 3
[0082]FIG. 9 is an equivalent circuit diagram of a pixel of the solid-state image pickup device according to the invention. In FIG. 9, the photodiode PD is a buried type photodiode as in the case of the preceding embodiments. Otherwise, there are shown a MOS transistor Q1 operating as transfer switch for transferring a photoelectric charge to floating diffusion region FD, a MOS transistor Q2 operating as reset switch for resetting the floating diffusion region FD, an input MOS transistor Q3 of a source follower for outputting the voltage of the floating diffusion region FD and a MOS transistor Q4 operating as selection switch for selecting a pixel. The input MOS transistor Q3 of the source follower takes the role of a signal amplifier and the floating diffusion region FD operates as the input terminal of this signal amplifier.
[0083]FIG. 10 is a schematic circuit diagram of a solid-state image pickup device comprising a matrix of 2×2 pixels PX, each having a circuit configuration as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com