Process for preducing mixed electrolyzed water
a technology of electrolyzed water and process, which is applied in the direction of water/sewage treatment by electrochemical methods, instruments, water treatment water, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating reducing power, too low dissociation ratio, and inability to use ascorbic acid as electrolytic aid, etc., to achieve effective mixing, and improve the ability to dismutate superoxide radical
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
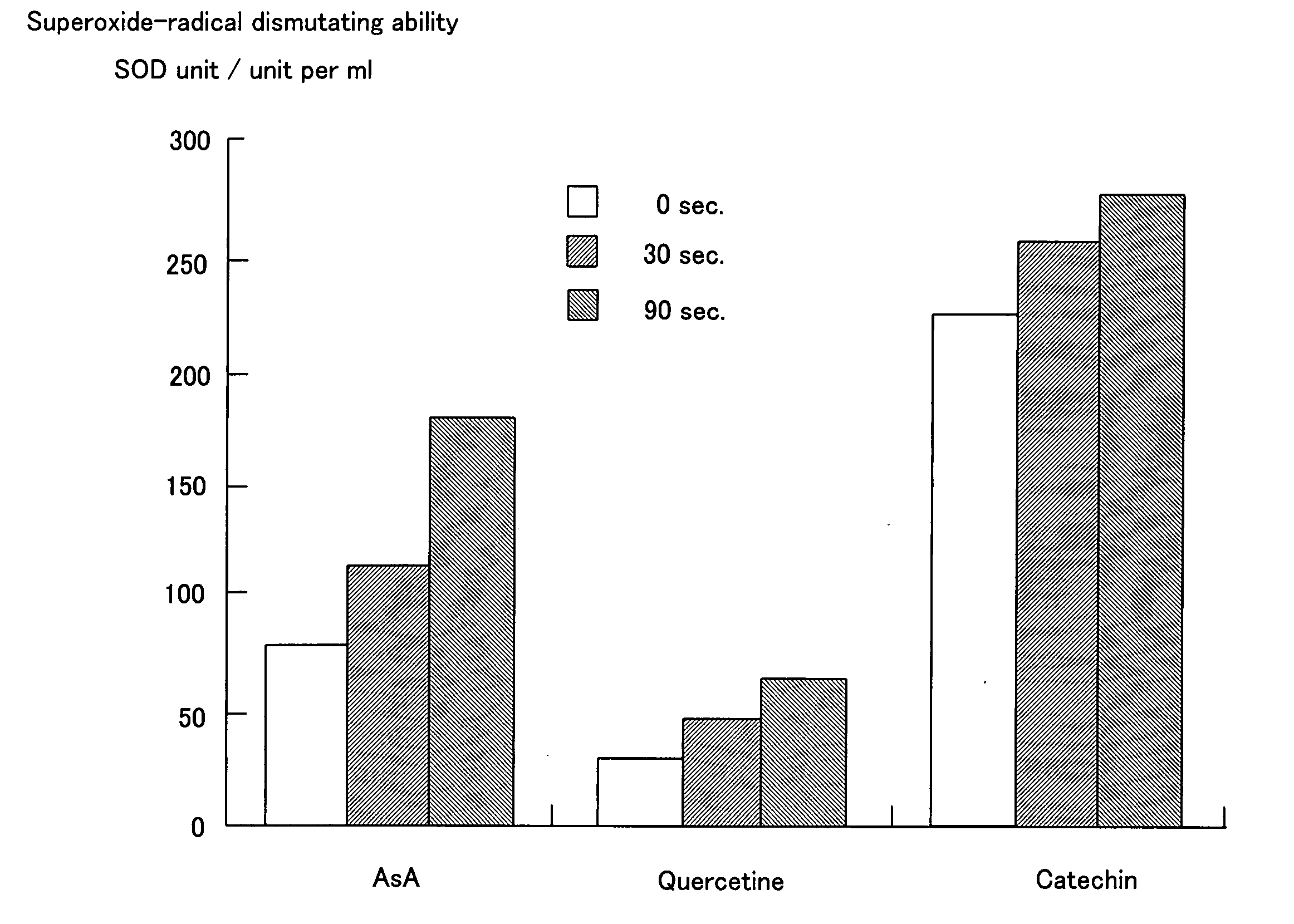
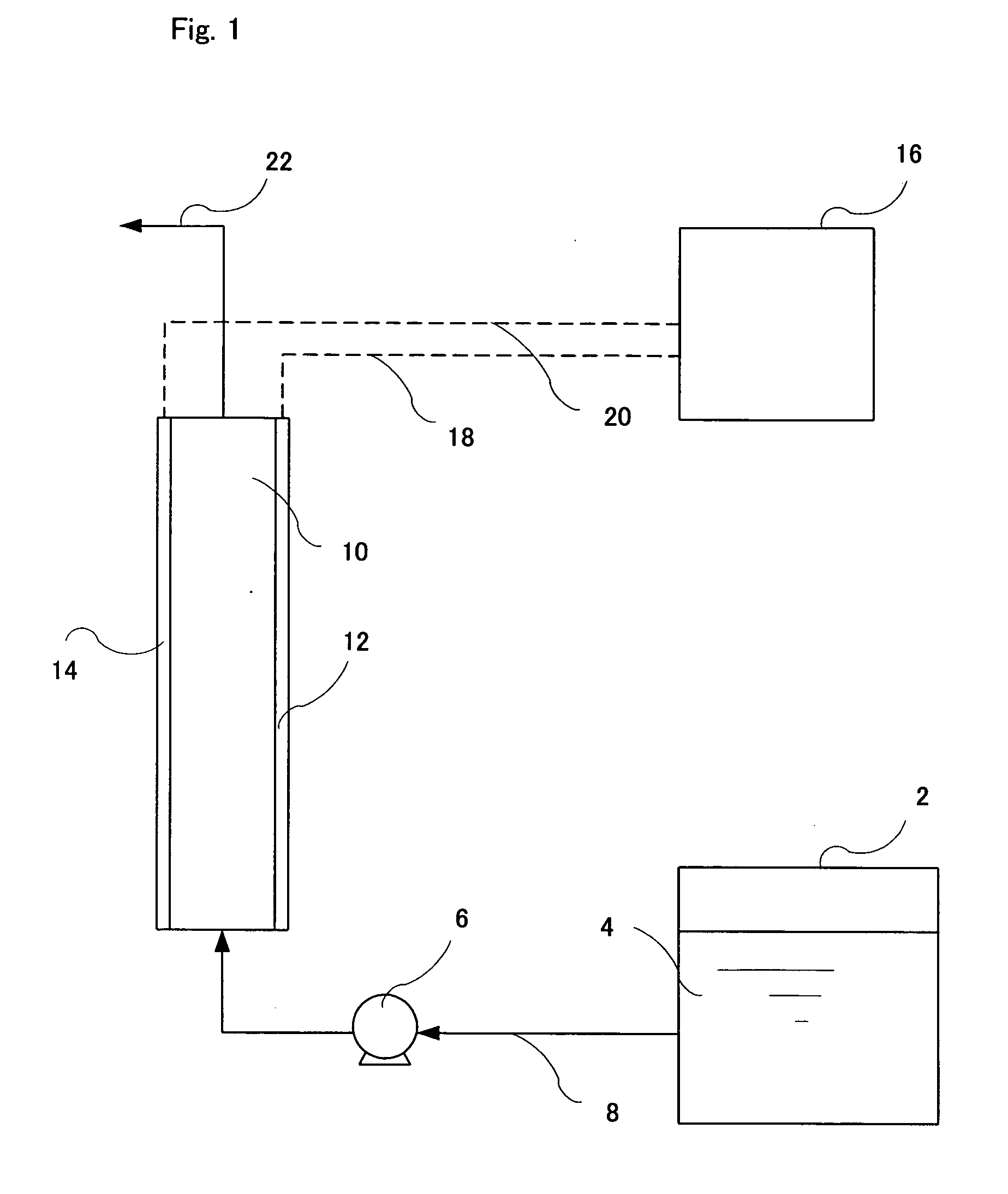
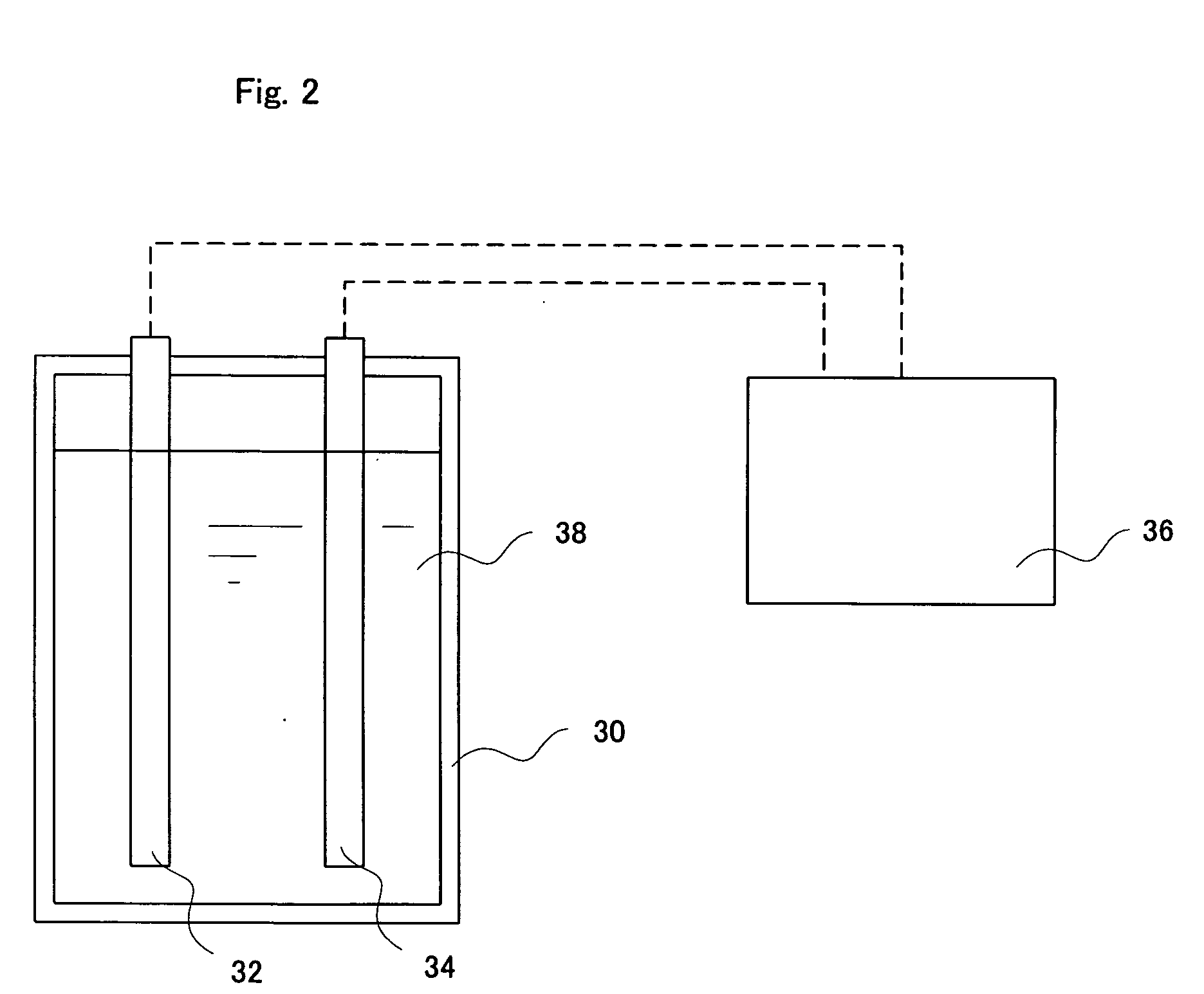
[0069] A raw electrolysis water containing ascorbic acid (AsA) was electrolyzed using an electrolysis apparatus shown in FIG. 2.
[0070] In an electrolytic bath was placed a pair of electrodes which are a 10×10 cm titanium plate coated with platinum. An inter-electrode distance was 2 mm. The electrolytic bath was a rectangular solid with a size of 11 cm (length)×5 cm (width)×12 cm (height). A 30 mM aqueous solution of AsA was prepared and 600 mL of the solution was charged in the electrolytic bath. While stirring the aqueous AsA solution, a current of 0.25 A was applied to the electrodes to conduct electrolysis. Electrolysis was conducted while alternating polarity at an interval of 30 sec after the initiation of electrolysis. Table 1 shows pH, a oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), a dissolved oxygen content (DO) and an electrical conductivity (EC) of the mixed electrolyzed water generated by electrolysis. Mixed electrolyzed water generated at various electrolysis times were netrali...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pKa | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pKa | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com