Methods and compositions to lower plasma cholesterol levels
a plasma cholesterol and composition technology, applied in the field of methods and compositions to lower plasma cholesterol levels, can solve the problems of narrowing of the vessel passages and ultimately hardening the vascular system, ischaemia or infarction, and large dosage, and achieve the effect of increasing the binding of lipoproteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
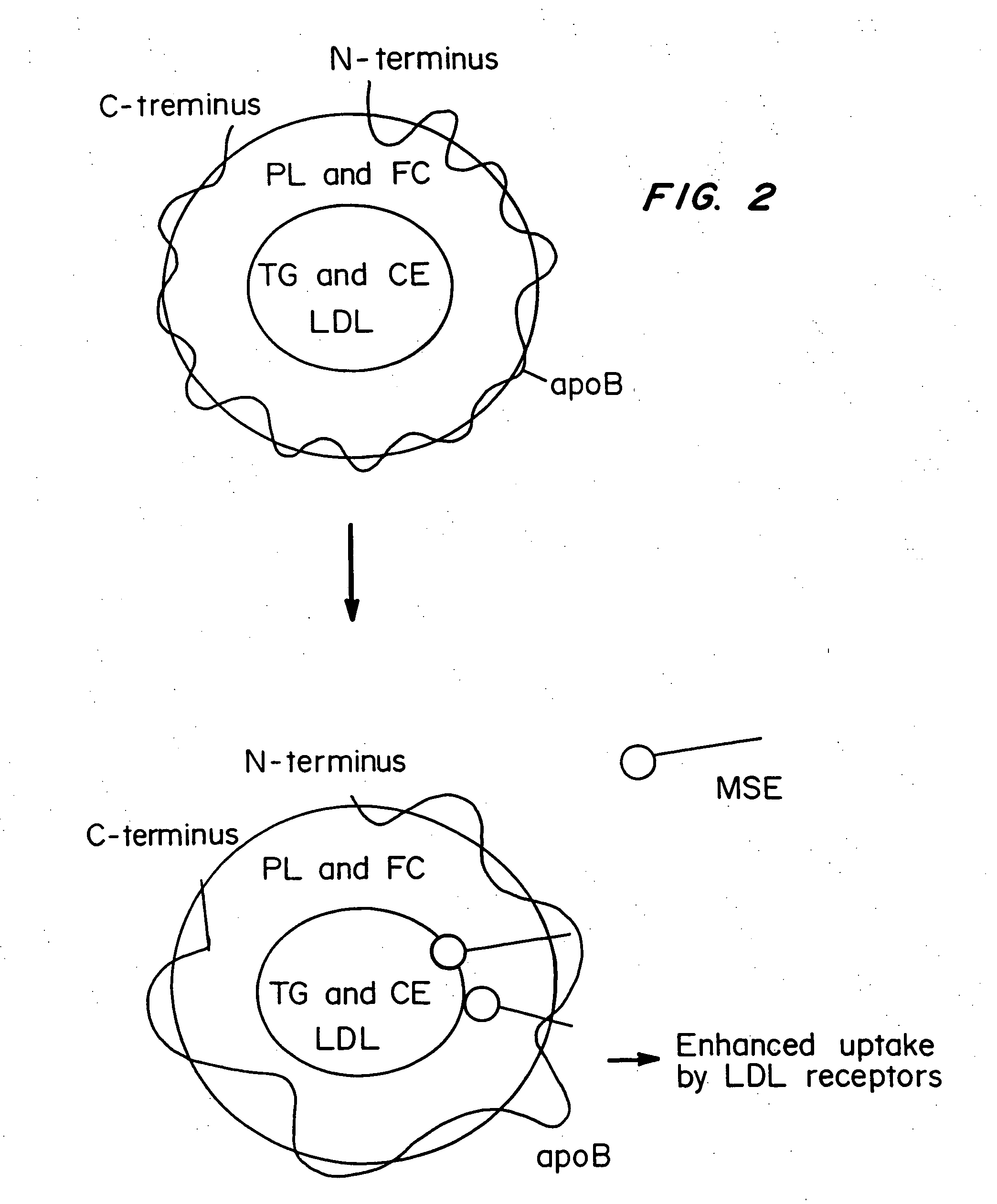
The Monosuccinic Acid Ester of Probucol Binds to VLDL and LDL In Vivo and In Vitro
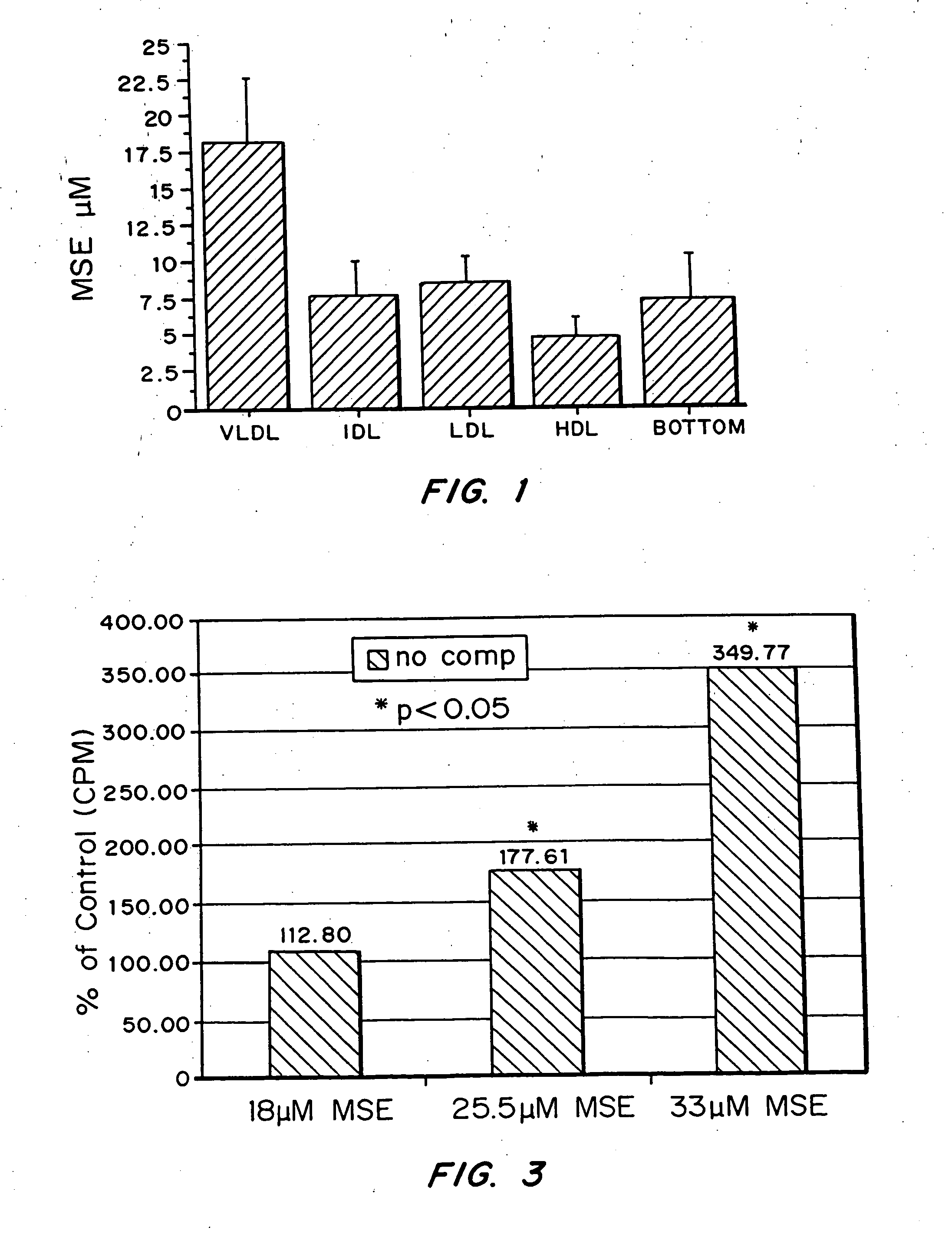
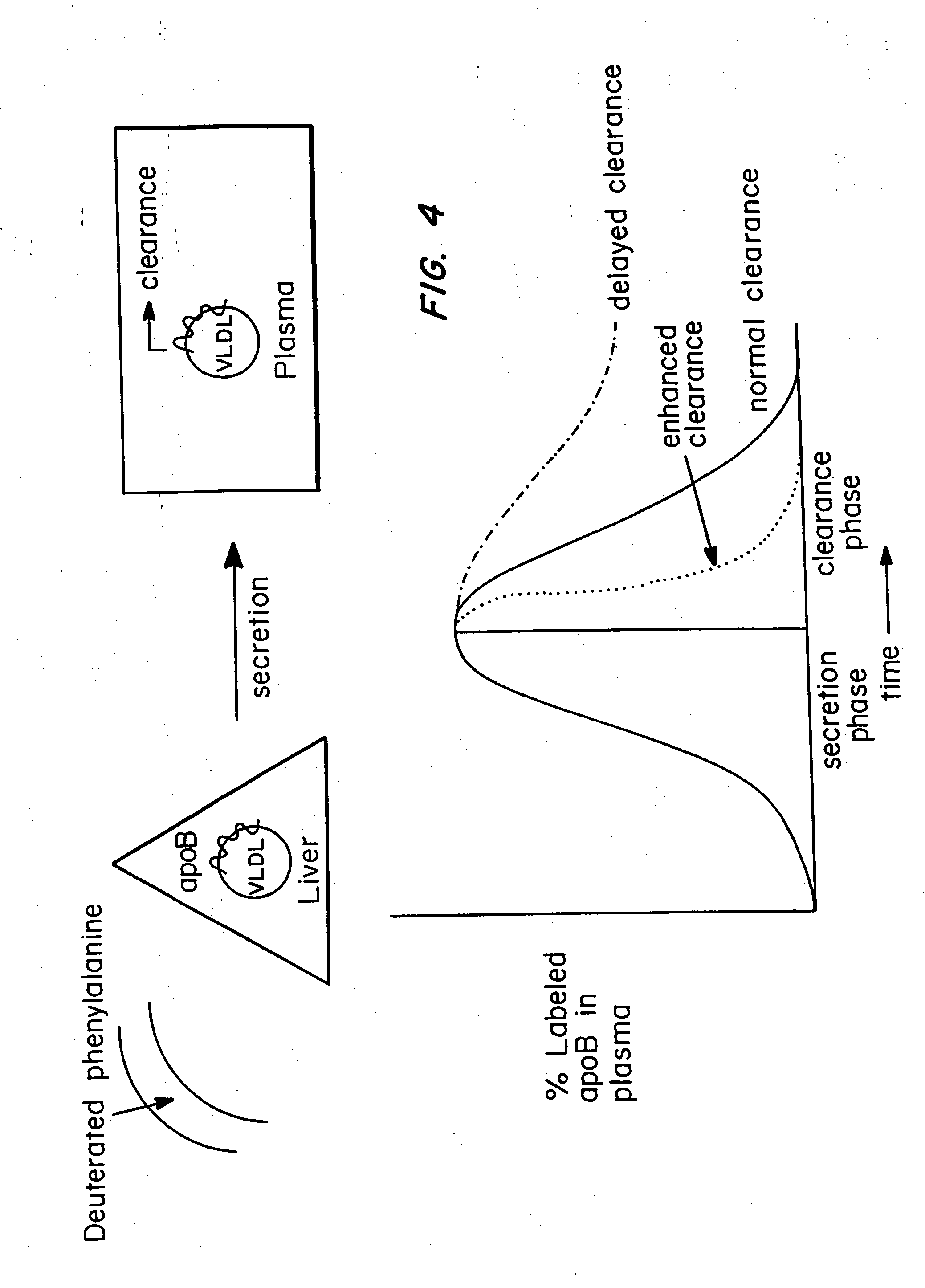
[0085] To examine if the monosuccinic acid ester of probucol partitions with plasma circulating lipoproteins, rabbits were fed a high-fat diet for six weeks and dosed with the compound at a dose of 150 mg / Kg per day orally. The animals were bled at six weeks and plasma lipoproteins isolated at high-speed using ultra-centrifugation.
[0086] Whole plasma was fractionated by fast phase liquid chromatography (FPLC) using a Superose 6HR 10 / 30 column. Elution was performed in a phosphate-buffered saline solution containing 0.01% EDTA and 0.02% NaN3 at a flow rate of 0.3 m / min. Approximately 0.6 ml was collected for each fraction and 20 fractions were available for analysis. The cholesterol content of the peaks corresponding to low density lipoprotein (LDL) and high density lipoprotein (HDL) were compared to CDC reference methods. VLDL corresponds to fractions 4-8 (elution volumes 7.2-9.6), LDL to fractions 9...
example 2
[0089] In order to demonstrate the binding of the monosuccinic acid ester of probucol to purified human LDL in vitro, agarose electrophoresis was employed. Agarose electrophoresis is a technique used to separate and study lipoproteins. The monosuccinic acid ester of probucol was added to purified human LDL and the mixture was run on agarose electrophoresis. Addition of the probucol derivative to LDL shifted the mobility of LDL, suggesting an interaction of the monosuccinic acid ester of probucol with LDL, most likely a physical association of the compound with the lipoprotein. In contrast, probucol did not shift the mobility of LDL.
example 3
The Monosuccinic Acid Ester of Probucol Binds to LDL and Changes the Epitope Expression of LDL-apoB-100
[0090] To determine if the binding of the monosuccinic acid ester to VLDL and LDL can cause a change in the structure of apoB-100, an immunoreactivity assay was designed. This is a sandwich ELISA assay which measures the expression of a specific epitope on apoB-100. Essentially the sandwich ELISA consists of a specific monoclonal antibody directed to that epitope on apoB-100 as a capture antibody laid on to a microtitre plate. LDL or VLDL added to the plate is bound to the antibody as a result of recognition of the specific epitope. A second polyclonal antibody is then used to quantify the amount of LDL captured.
[0091] The detailed immunoreactivity protocol is as follows. A nunc maxi-sorp microtiter plate is coated overnight at 4° C. with 100 μl of Anti-Human ApoB monoclonal antibody from Boehringer Mannheim (catalog # 1533 975) diluted 1:1000 in PBS pH 7.4. The compounds are dis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| binding affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| agarose electrophoresis | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrophoresis | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com