Molded fiber manufacturing
a technology of molded fibers and molded bodies, applied in the field of molded fiber manufacturing, can solve the problems of reducing the adhesion of the molded fiber shaped body to the thermo-, and the ineffective vacuum dewatering, so as to reduce the amount of water, reduce the energy consumption of manufacturing, and reduce the effect of thermal energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
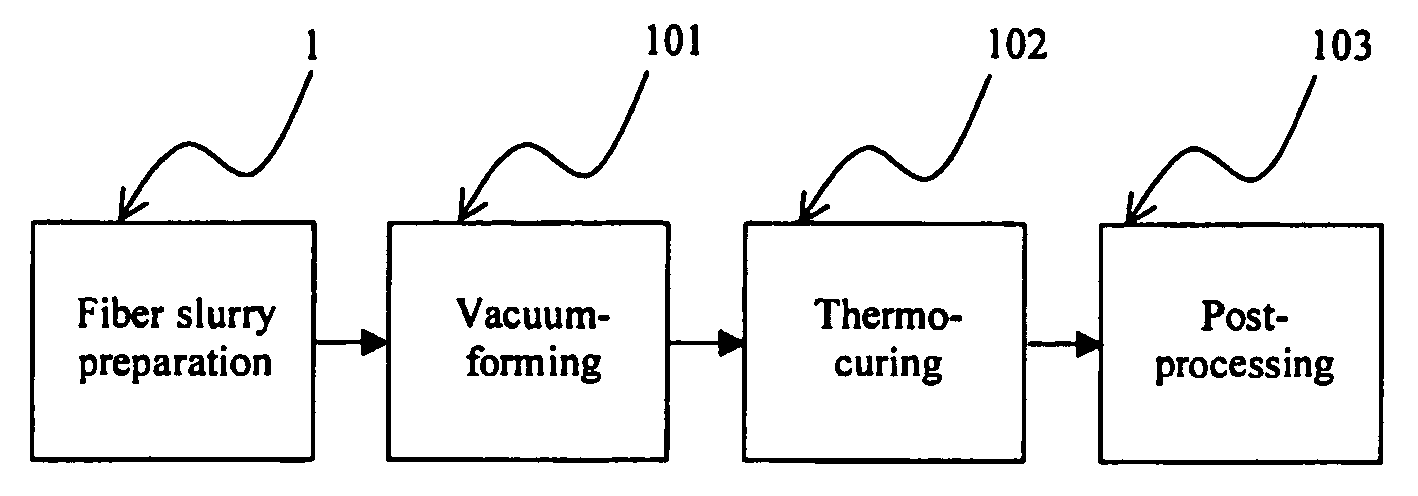
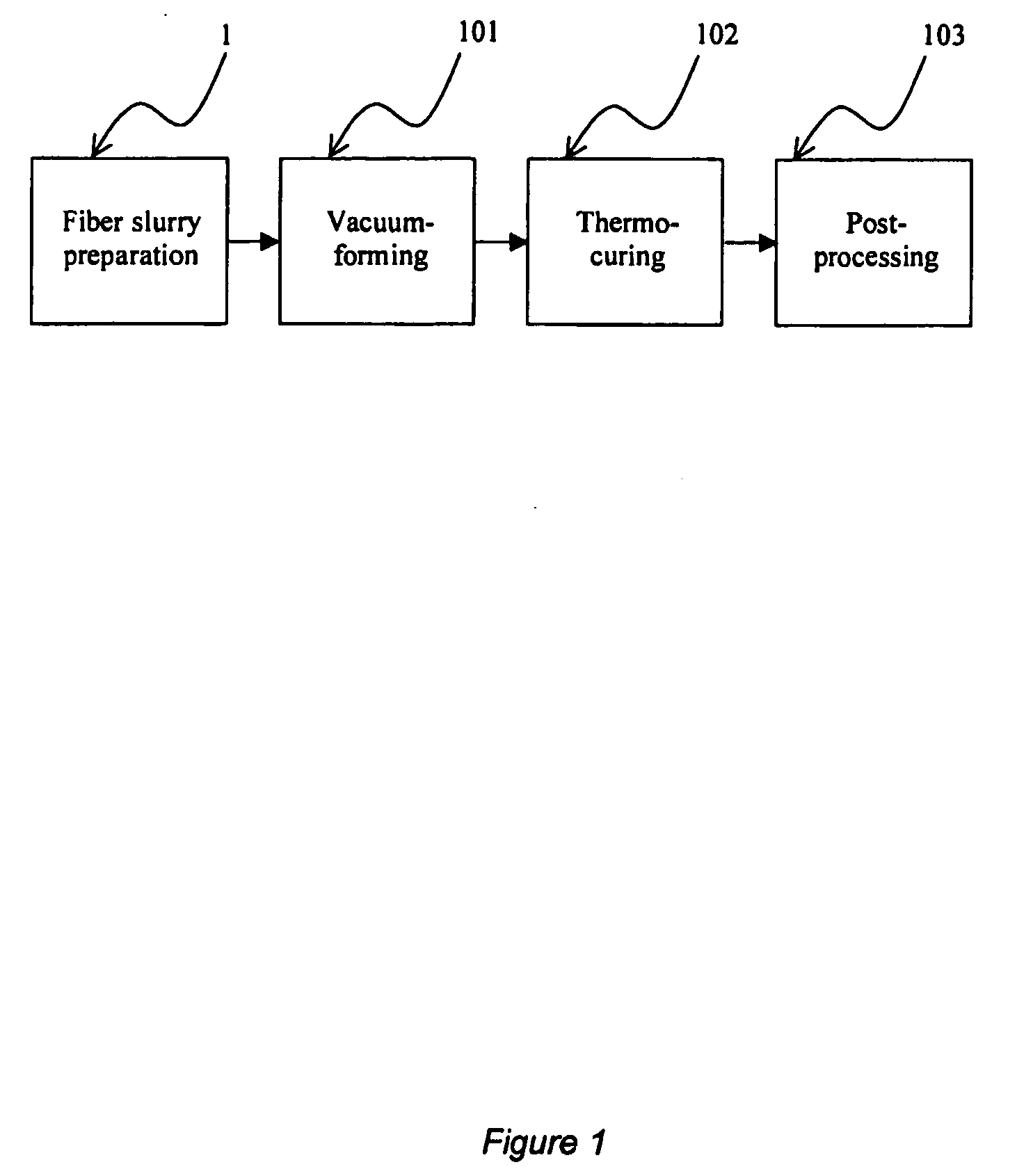
[0025] The improved molded fiber shaped body manufacturing process consists of four major steps. These are (1) fiber slurry preparation; (2) vacuum-forming and (3) thermo-curing and (4) post-processing.
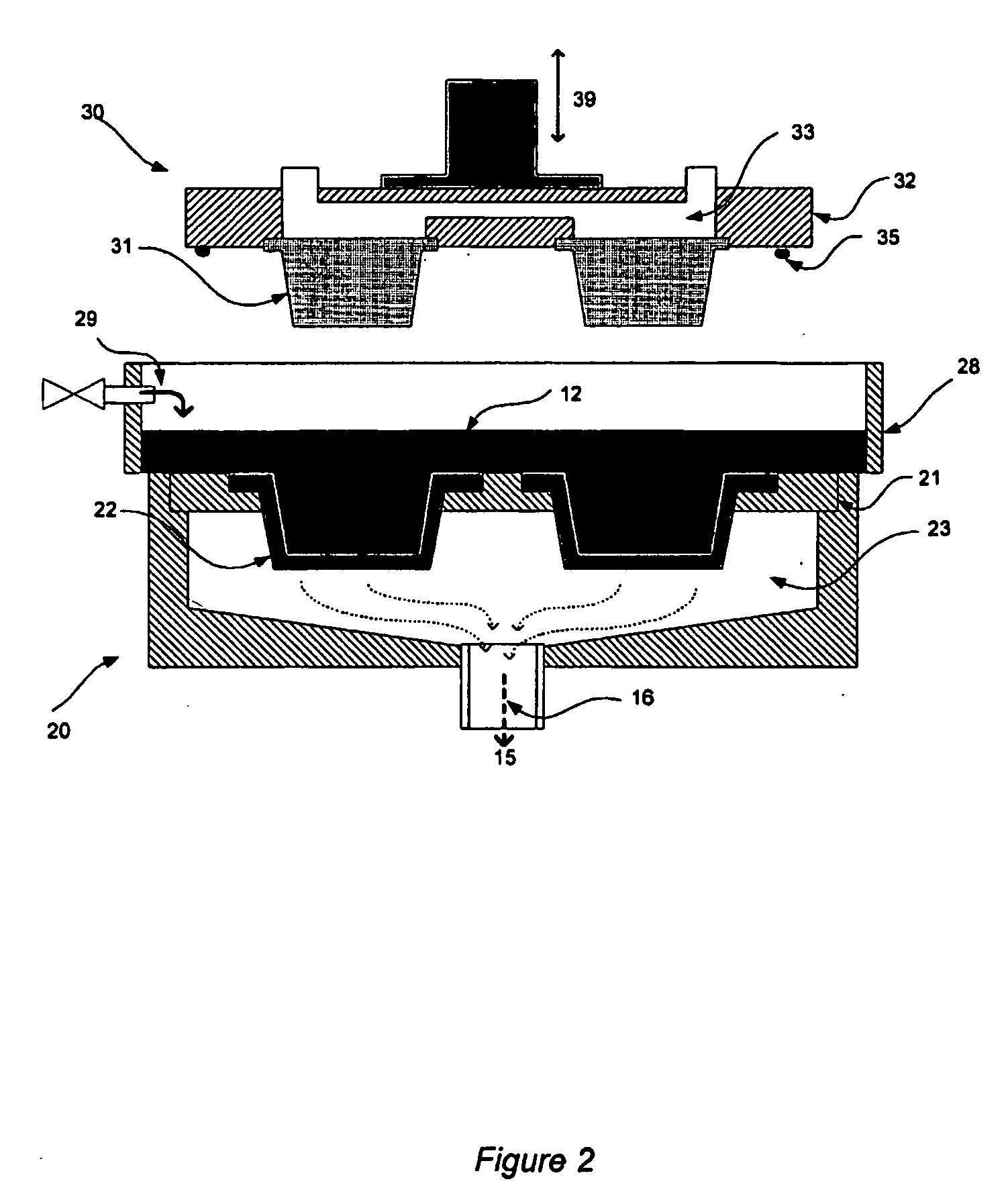
[0026] The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of fiber slurry. Sufficiently refined plant fibers such as fibers obtained from palm oil, coconut coir, hemp, kenaf and other fibrous plants are added to a mixer tank. The mixer tank can be pre-filled with water or water can be added simultaneously with the fiber. The amount of fiber is 0.1 to 5 percent (wt) with respect to 99.9 to 95 percent (wt) of water. The fibers are agitated by an agitator such as an impeller to disperse them in the water. The low consistency fiber mixture is sufficiently agitated until a homogenous slurry is obtained. Water based adhesive binder is then added to the mixer tank and the entire mixture is continuously agitated. The agitation action causes the adhesive binder to attach to the fiber. Func...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com