Peptide mediated synthesis of metallic and magnetic materials
a technology peptides, applied in the field of organic materials, can solve the problems of inconvenient large-scale and/or volume production, inconvenient synthesis of metallic and magnetic materials, and high cost of traditional synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles, and achieve the effect of improving control and reducing the size of features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
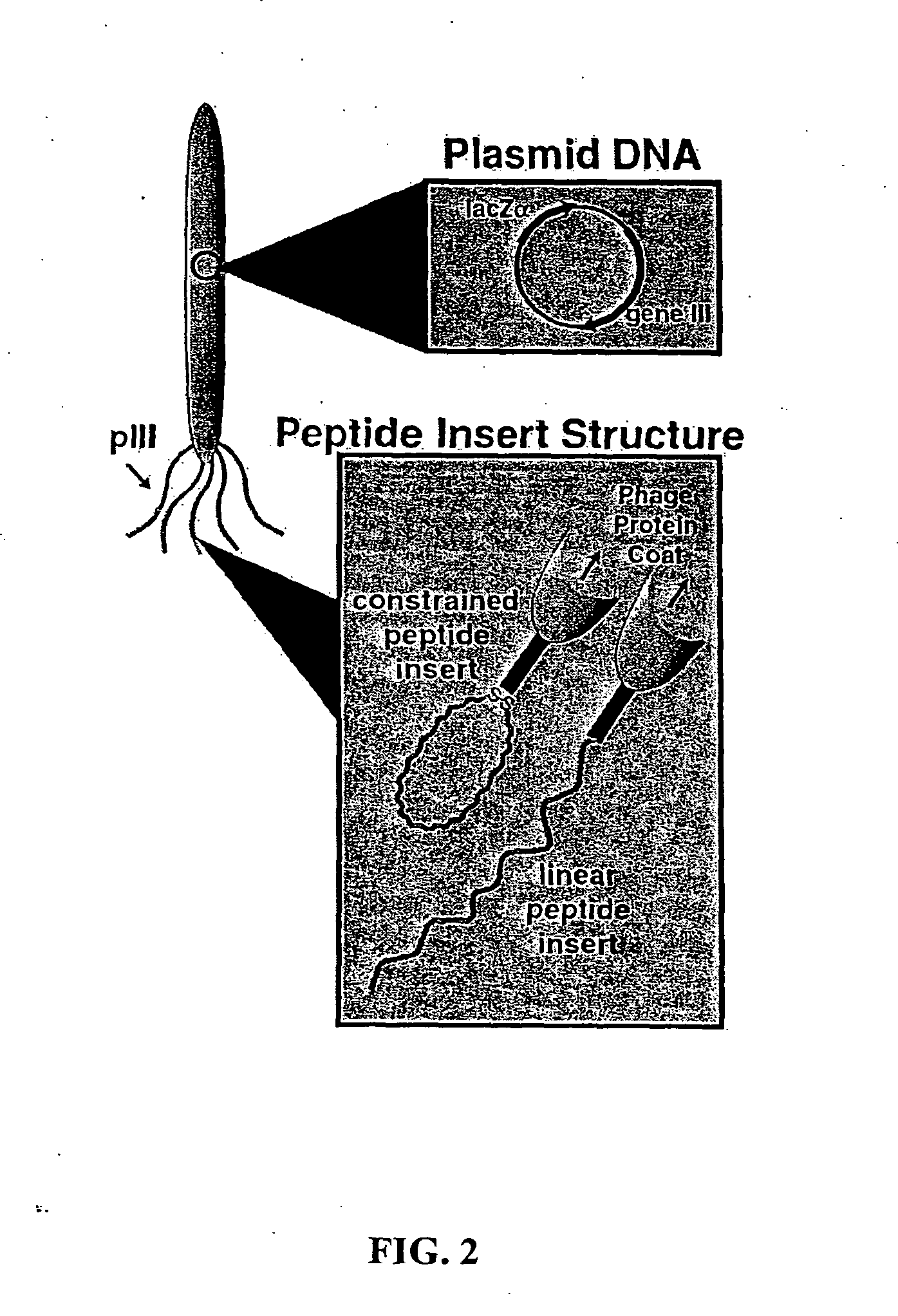
Peptide Preparation, Isolation, Selection and Characterization
[0073] Peptide selection. The phage display or peptide library was contacted with the semiconductor, or other, crystals in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 0.1% TWEEN-20, to reduce phage-phage interactions on the surface. After rocking for 1 hour at room temperature, the surfaces were washed with 10 exposures to Tris-buffered saline, pH 7.5, and increasing TWEEN-20 concentrations from 0.1% to 0.5%(v / v). The phage were eluted from the surface by the addition of glycine-HCl (pH 2.2) 10 minute, transferred to a fresh tube and then neutralized with Tris-HCl (pH 9.1). The eluted phage were titered and binding efficiency was compared.
[0074] The phage eluted after third-round substrate exposure were mixed with their Escherichia coli (E. coli) ER2537 host and plated on LB XGal / IPTG plates. Since the library phage were derived from the vector M13mp19, which carries the lacZα gene, phage plaques were blue in color when plate...
example ii
Biofilms
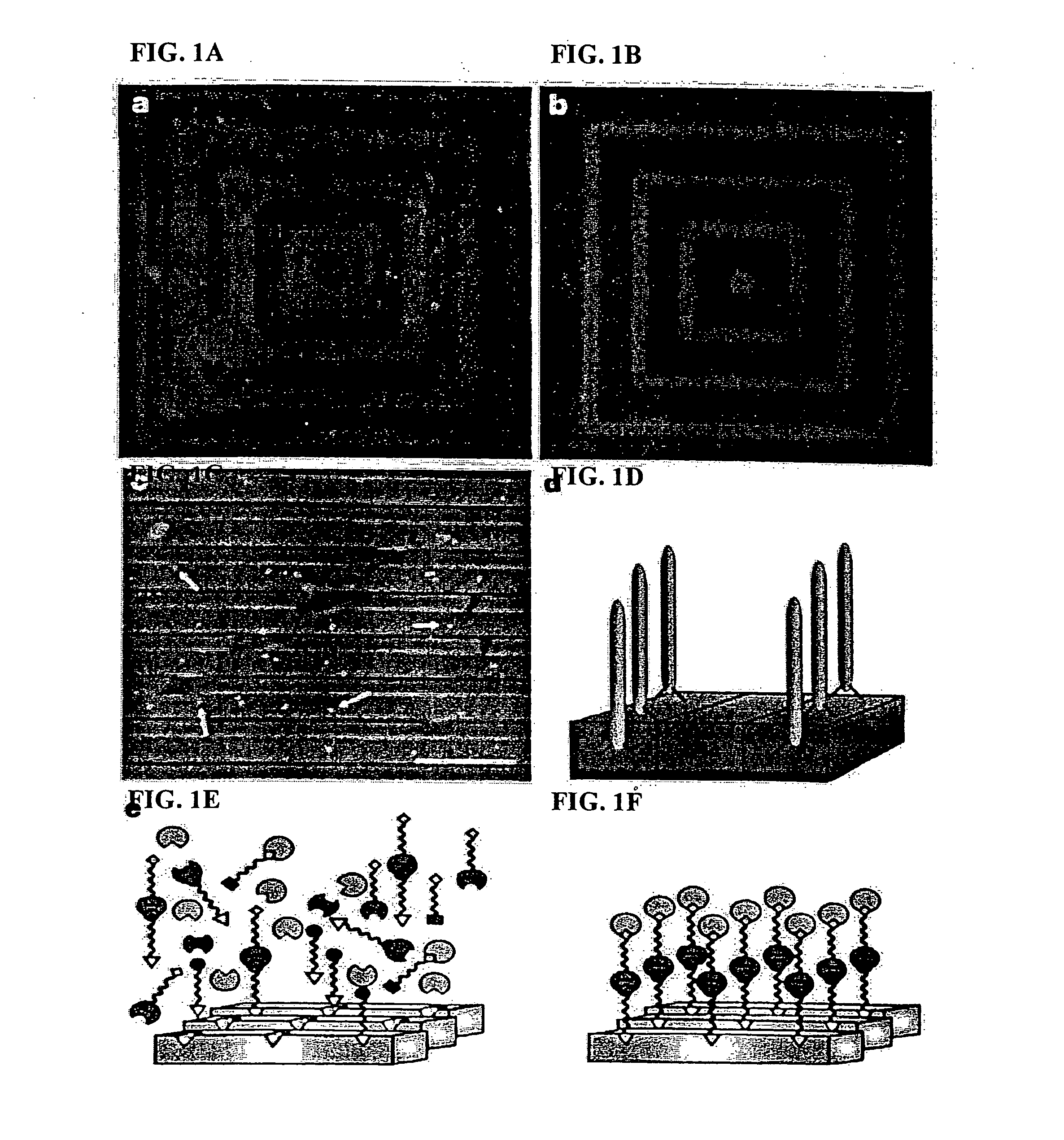
[0083] The present inventors have recognized that organic-inorganic hybrid materials offer new routes for novel materials and devices. Size controlled nanostructures give optically and electrically tunable properties of semiconductor materials and organic additives modify the inorganic morphology, phase, and nucleation direction. The monodispersed nature of biological materials makes the system compatible for highly ordered smectic-ordering structure. Using the methods of the present invention, highly ordered nanometer scale as well as multi-length scale alignment of II-VI semiconductor material using genetically engineered, self-assembling, biological molecules, e.g., M13 bacteriophage that have a recognition moiety of specific semiconductor surfaces were created.
[0084] Using the compositions and methods of the present invention nano- and multi-length scale alignment of semiconductor materials was achieved using the recognition and self-ordering system described herein. T...
example iii
Formation of Metallic and Magnetic Materials
[0107] A phage display technique was used to discover novel peptides that bind selectively to magnetic materials. In these particular studies, films of the magnetic materials were prepared by first synthesizing colloidal dispersions of the magnetic materials. These colloidal solutions were then drop coated onto Si wafers and annealed under N2 to generate the desired crystal structure. Phage display was then performed on these films (ε-Co, CoPt, and FePt), and peptides were discovered that bind selectively to each substrate. These peptides were then used to nucleate unique nanoparticles by mixing the phage expressing the peptide of interest, the metal salt, and a reducing agent.
[0108] The synthesis of nanoparticles with controlled size and composition is of fundamental and technological interest. In the last few years there has been a flurry of papers describing the synthesis of nanoparticles composed of metals and semiconductors with rem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com