Intramyocardial injection of autologous bone marrow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
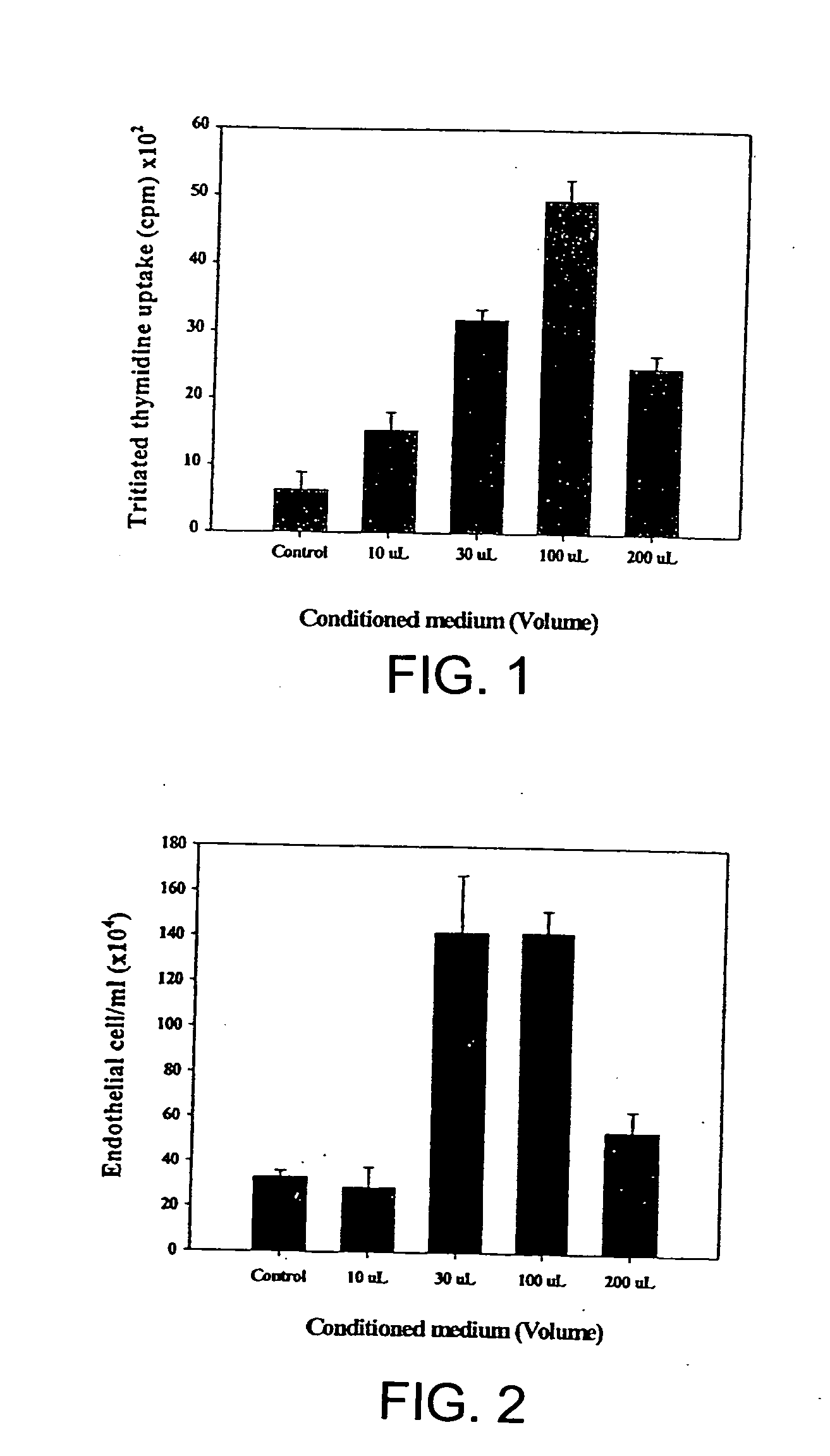
[0027] Effect of Bone Marrow Cultured Media on Endothelial Cell Proliferation
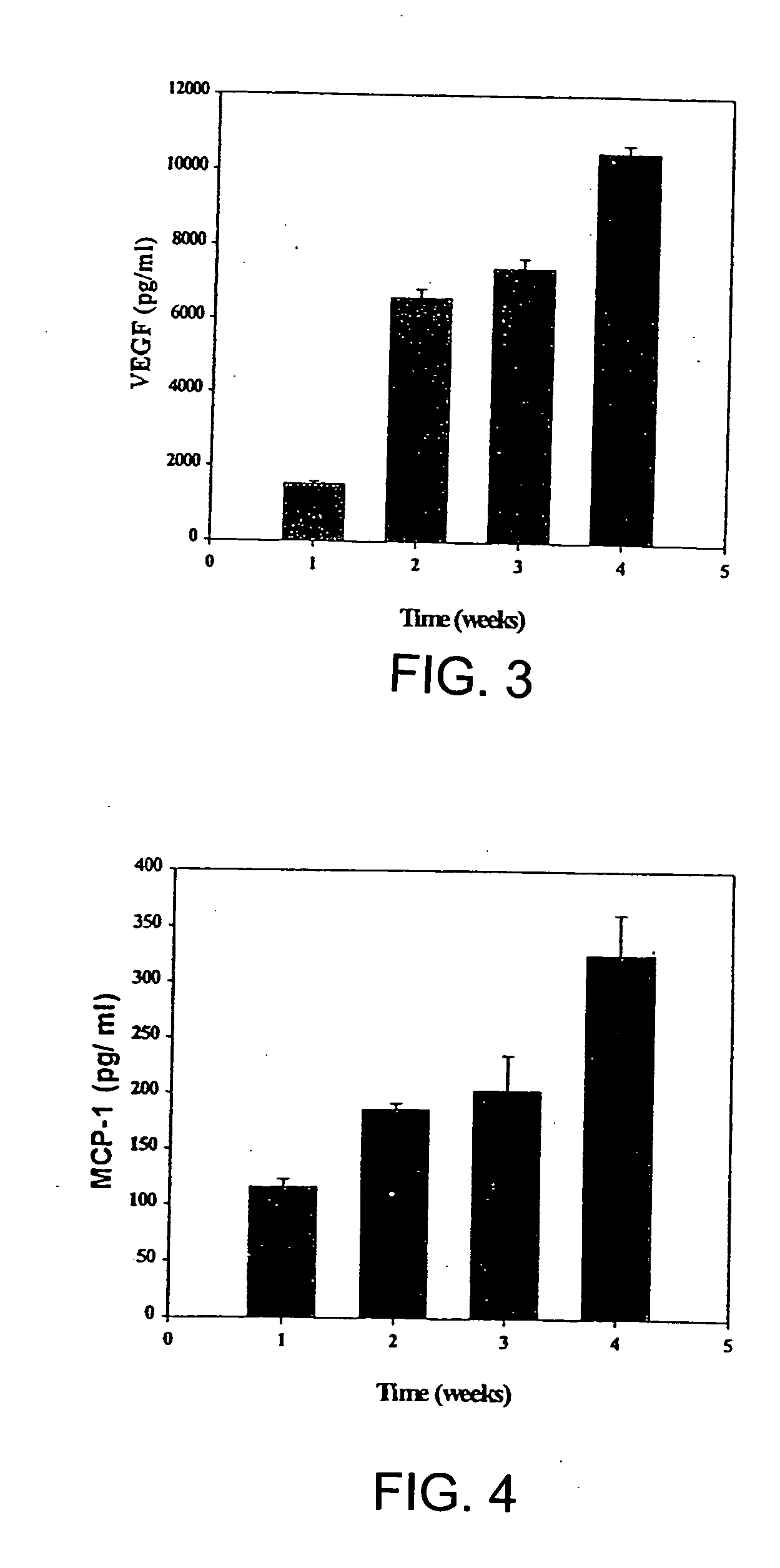
[0028] Studies were conducted to determine whether aspirated pig autologous bone marrow cells obtained secreted VEGF, a potent angiogenic factor, and MCP-1, which recently has been identified as an important angiogenic co-factor. Bone marrow was cultured in vitro for four weeks. The conditioned medium was added to cultured pig aortic endothelial cells (PAECs), and after four days proliferation was assessed. VEGF and MCP-1 levels in the conditioned medium were assayed using ELISA. During the four weeks in culture, BM cells secreted VEGF and MCP-1, such that their concentrations increased in a time-related manner. The resulting conditioned medium enhanced, in a dose-related manner, the proliferation of PAECs. The results indicate that BM cells are capable of secreting potent angiogenic cytokines such as VEGF and MCP-1 and of inducing proliferation of vascular endothelial cells.
[0029] Pig Bone Marrow Culture
[0...
example 2
[0045] Effects of Hypoxia on VEGF Secretion by Cultured Pig Bone Marrow Cells
[0046] It was demonstrated that hypoxia markedly increases the expression of VEGF by cultured bone marrow endothelial cells, results indicating that ex-vivo exposure to hypoxia, by increasing expression of hypoxia-inducible angiogenic factors, can further increase the collateral enhancing effect of bone marrow cells and its conditioned media to be injected in ischemic muscular tissue. Pig bone marrow was harvested and filtered sequentially using 300.mu. and 200.mu. stainless steel mesh filters. BMCs were then isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque gradient centrifugation and cultured at 33.degree. C. with 5% CO2 in T-75 culture flasks. When cells became confluent at about 7 days, they were split 1:3 by trypsinization. After 4 wks of culture, the BMCs were either exposed to hypoxic conditions placed in a chamber containing 1% oxygen) for 24 to 120 hrs, or maintained under normal conditions. The resulting conditioned med...
example 3
[0048] Effect of Bone Marrow Cultured Media on Endothelial Cell Tube Formation
[0049] It was demonstrated, using pig endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells co-culture technique, that the conditioned medium of bone marrow cells induced the formation of structural vascular tubes in vitro. No such effect on vascular tube formation was observed without exposure to bone marrow conditioned medium. The results suggest that bone marrow cells and their secreted factors exert pro-angiogenic effects.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell proliferation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com