Treatment of ischemic brain injuries with brain targeted antioxidant compounds
a brain injury and antioxidant compound technology, applied in the direction of anti-neurotoxic agents, peptide/protein ingredients, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of generating more toxic free radicals, accumulation of oxidation damage, cell death,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
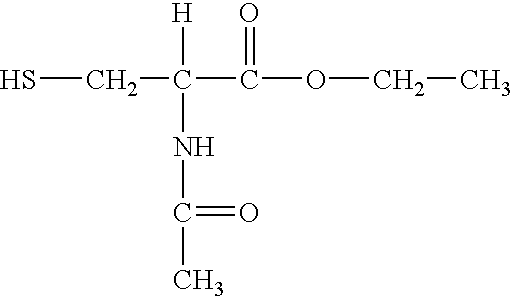
Synthesis of N-Acetyl Cysteine Ethyl Ester (Compound A)
[0103] N-acetyl cysteine (4.6 mmol) was added in portions to a cooled (e.g., 2-8.degree. C.) solution of 2 ml thionyl chloride and 10 ml absolute ethanol. The resulting mixture was refluxed at 40.degree. C. for 1 hour and then the volatiles were removed in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 10 ml of water and was extracted twice with 20 ml of methylene chloride. The extract was dried under vacuo. The title compound was crystallized from petroleum ether (fraction 40-60.degree.) in 55% yield.
[0104] The resulting product has the following characteristics:
[0105] (a) Melting point of 90.degree. C.
[0106] (b) Anal. calculated for C.sub.7H.sub.11NO.sub.3S:
1 Calculated: C, 43.9 H, 6.8 Found: C, 42.5 H, 6.0
[0107] (c) Thin layer chromatography in n-butanol / acetic acid / water (4 / 1 / 4) was carried out and the Rf value was Rf=0.91. The Rf value of the reactant, N-acetyl cysteine is 0.78.
[0108] (d) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) in deutarated...
example 2
Synthesis of N-Acetyl .beta.,.beta.-Dimethyl Cysteine Ethyl Ester or N-Acetyl-Penicillamine Ethyl Ester (Compound B)
[0116] N-acetyl .beta.,.beta.-dimethyl cysteine (2.6 mmol) was added in portions to a cooled (2-8.degree. C.) solution of 2 ml thionyl chloride and 10 ml absolute ethanol. The resulting mixture was refluxed at 40.degree. C. for 1 hour and then the volatiles were removed in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 10 ml of water and was extracted twice with 20 ml of methylene chloride. The extract was dried under vacuo. The title compound was crystallized from a methanol-water solution ({fraction (1 / 100)}, fraction 40-60.degree.) in 25% yield.
[0117] The resulting product has the following characteristics:
[0118] (a) Melting point of 180.degree. C.
[0119] (b) Thin layer chromatography in n-butanol / acetic acid / water (4 / 1 / 4) was carried out and the Rf value was Rf=0.66. The Rf value of the reactant, N-acetyl .beta.,.beta.-dimethyl cysteine is 0.88.
[0120] (c) Nuclear Magnetic Reso...
example 3
Synthesis of N-Acetyl Glutathione Amide (Compound I)
[0127] Ammonia gas was bubbled through absolute dry ethanol at -70.degree. C. (dry ice with acetone), for 10 minutes. N-acetyl glutathione ethyl ester (compound G), 350 mg (1 mmol) was added to the cooled ethanol / ammonia solution and ammonia was continued to bubble through the solution for additional 10 minutes. Then, the solution was corked and was left at room temperature. After 16 hours, the flask was opened and access of ammonia and the ethanol were evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was lyophilized. The yield was 84%.
[0128] The resulting product has the following characteristics:
[0129] (a) Thin layer chromatography in n-butanol / acetic acid / water (4 / 1 / 4) was carried out and the Rf value was Rf=0.71.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| infarct size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com