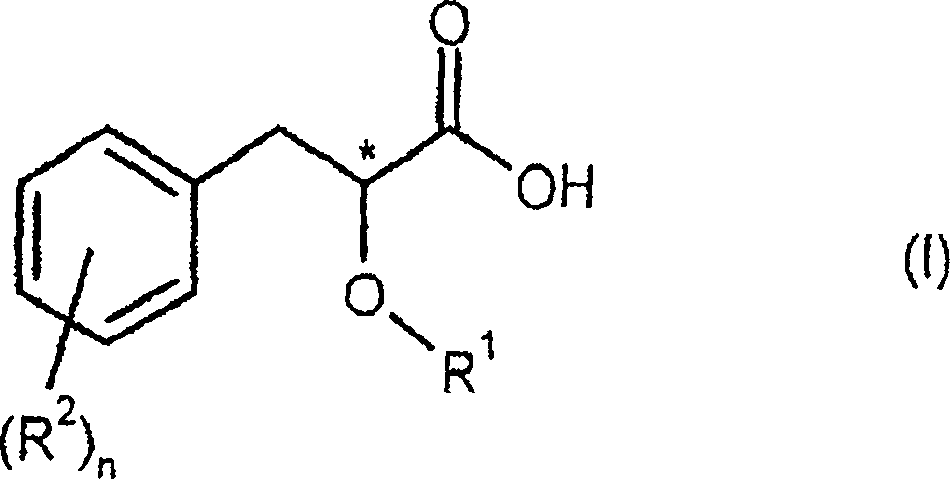
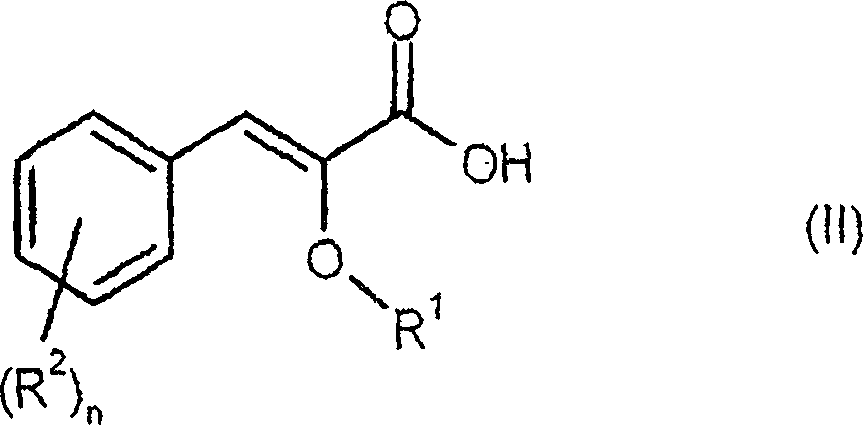
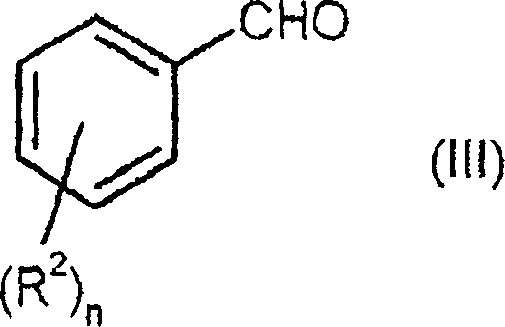
Process for preparing enantiomerically enriched 2-alkoxy-3-phenylpropionic acids
An enantiomer-enriched, enantiomer-selective technology applied in the field of 2-alkoxy-3-phenylpropionic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Preparation of Z-4'-hydroxy-2-methoxycinnamic acid:
[0077]
[0078] A solution of 150 g (1.20 mol) of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 316 g (3.00 mol) of methyl methoxyacetate in 1.018 l (5.39 mol) of 30% sodium methoxide in methanol was heated under reflux for 6 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled to 40° C. and mixed with 1 1 of water. 760 ml of methanol were distilled off from the reaction mixture, and the mixture was cooled to room temperature again. The reaction solution was adjusted to pH 2 with 410 ml of 37% aqueous hydrochloric acid, and the product was precipitated from the solution. The product suspension was stirred at room temperature for another 2 hours, filtered, and the filtered residue was dried under reduced pressure at 40°C overnight. 212.2 g of pure Z product (content: 92.4%, 83.8% of theory) were obtained as a yellowish solid.
[0079] 1 H NMR (400MHz, d 6 -DMSO): δ = 3.67 (s, 3H, O-CH 3 ); 6.79(d, 2H, Ar-H); 6.85(s, 1H, Ar-CH=); 7.61(d...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Preparation of Sodium (S)-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-methoxypropionate by Hydrogenation Using Ruthenium Catalyst Salt
[0083]
[0084] 62.5mg (1.0mmol) [RuCl 2 (p-cymene)] 2 and 139.6mg (2.1mmol) of 2,2'-dichloro-3,3'-dimethoxy-6,6'-bis(diphenylphosphino)biphenyl were suspended in 150ml of degassed methanol and refluxing Lower heat for 1 hour. The resulting solution was then cooled to room temperature and added to a solution of 40.46 g (200 mmol) of Z-4'-hydroxy-2-methoxycinnamic acid in 150 ml of degassed methanol. Subsequently, the mixture was transferred to an autoclave and hydrogenated at 70° C. and a hydrogen pressure of 85 bar for 16 hours. The mixture was then cooled, depressurized and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was taken up with 650 ml of isopropyl acetate, washed with 200 ml of 1N HCl and 100 ml of saturated NaCl solution, concentrated to a volume of 500 ml and mixed with a solution of 19.7 g of sodium acetate in 163 ml o...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Preparation of (S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methoxypropionic acid sodium salt by hydrogenation with rhodium catalyst:
[0089]
[0090] 6.3mg (0.0154mmol) Rh(COD) 2 BF 4 and 6.8 mg (0.0154 mmol) of (S,S)-2,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)pentane were dissolved in 1 ml of degassed methanol and added to 100 mg (0.51 mmol) of Z-4'-hydroxy - a solution of 2-methoxycinnamic acid in 3 ml of degassed methanol. Then, the mixture was transferred to an autoclave and hydrogenated at 50° C. and 3 bar hydrogen pressure for 16 hours. The mixture was then cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and under reduced pressure. (S)-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-methoxypropanoic acid was obtained as an oil in 80% enantiomeric excess (100% conversion of substrate).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com