Production of super-macroporous intermediate-pressure-resisting spherical cellulose grain and adsorbent
A cellulose and ultra-large pore technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of wide distribution of pore size, slow solution mass transfer speed, difficult diffusion of macromolecular substances, etc., and achieve the effect of simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
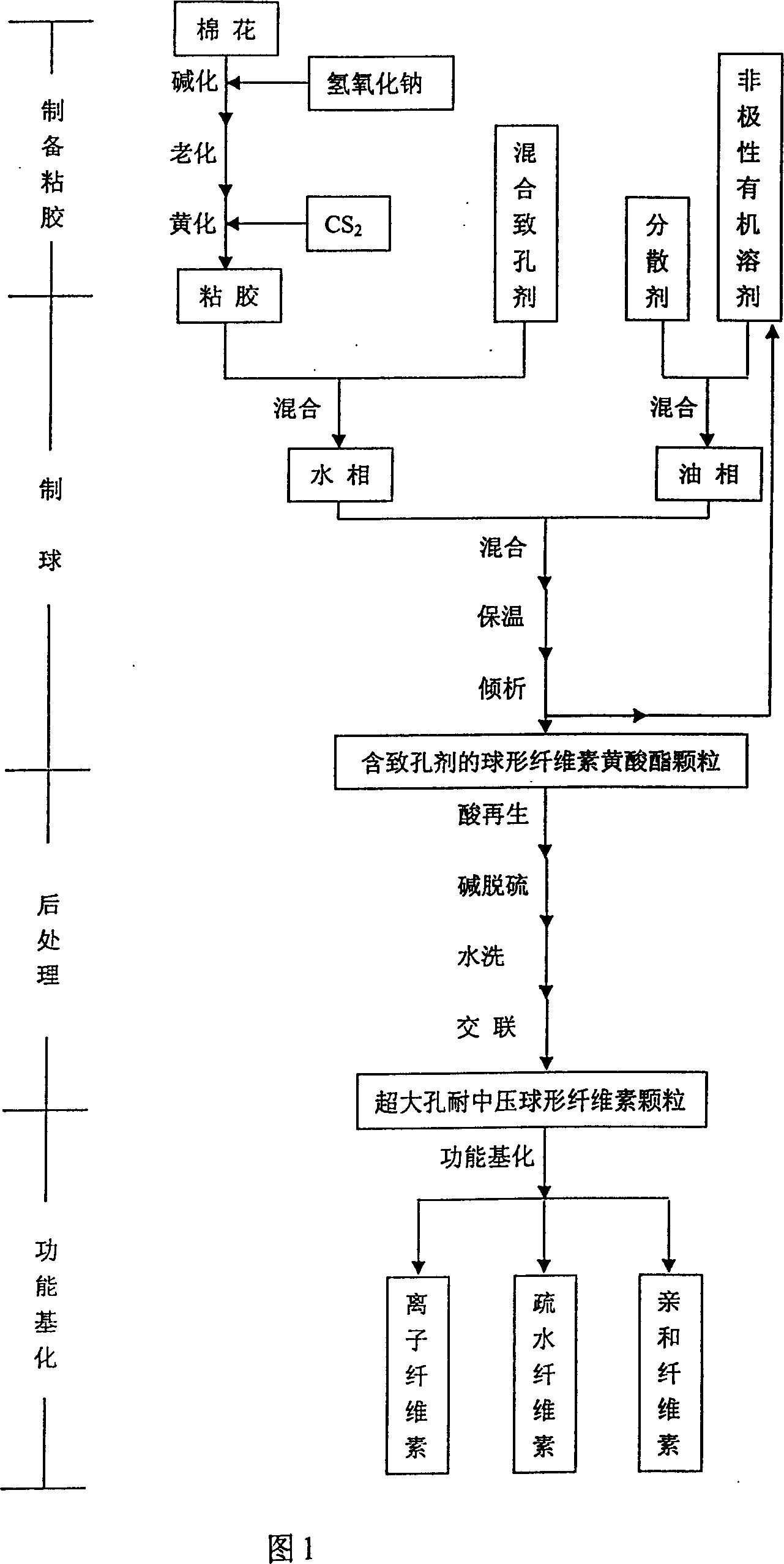
[0030] (1) Preparation of viscose
[0031] Soak 500g of ordinary cotton in 10kg of 18% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution for 2 hours, then take out the cotton, squeeze it dry, and age it for 3 days. Put in an airtight container, then add 250g CS 2 , shake at room temperature for 3 hours, put in an ice-water bath, add 5kg of 5.5% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and stir for 7 hours to obtain cellulose yellow acid viscose.
[0032] (2) "Hot sol phase inversion" ball making method
[0033] Mix oil phase 1500mL chlorobenzene with dispersant 37g (30g calcium carbonate, 2g potassium oleate and 5g span85), water phase 500g cellulose yellow acid viscose and mixed porogen 235g (20g benzene, 200g average molecular weight 10,000 polyphenylene Ethylene, 15g Tween80) were mixed evenly, and then the water phase was added to the oil phase, stirred at 200rpm for half an hour, rapidly heated to 70°C, and kept for half an hour. The oil phase was decanted to obtain spherical cellulose xant...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Preparation of viscose
[0040] Operate by the same operation steps as in Example 1.
[0041] (2) "Hot sol phase inversion" ball making method
[0042] Mix the oil phase 1500mL vacuum pump oil with dispersant 47g (30g calcium carbonate, 2g potassium oleate and 15g span85) evenly, and then mix the water phase with 500g cellulose yellow acid viscose and 275g porogen (20g isopropanol , 250g of polyvinyl alcohol with an average molecular weight of 10,000, and 5g of Tween60) were evenly mixed and added to the oil phase, stirred at 200rpm for half an hour, rapidly heated to 70°C, and kept for half an hour. The oil phase was decanted to obtain spherical cellulose xanthate particles containing porogen.
[0043] (3) post-processing
[0044] Follow the same steps as in Example 1.
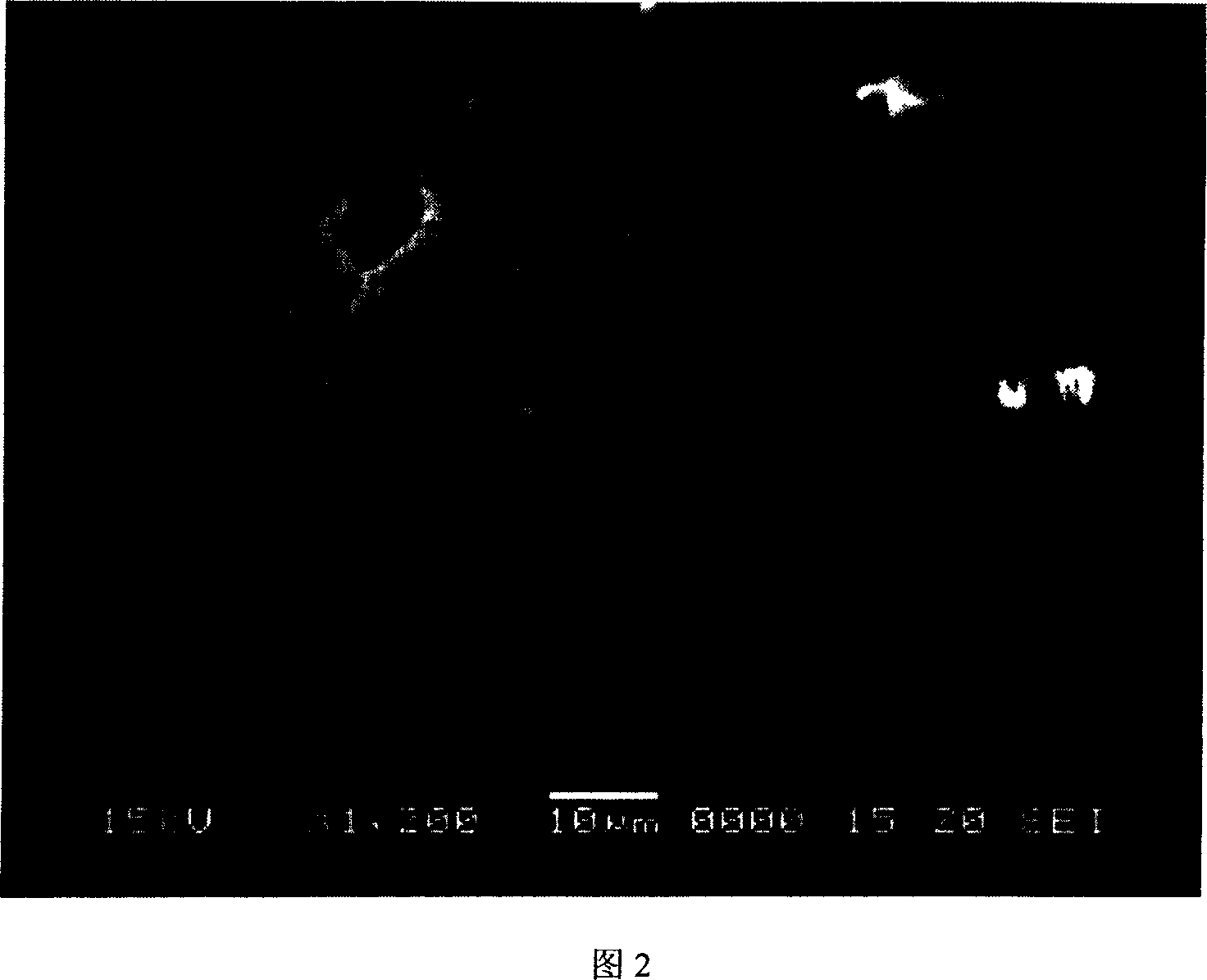
[0045] It has been determined that the ultra-large-porous medium-pressure-resistant spherical cellulose particles prepared by this method have a spherical or ellipsoidal appearance, 75% of whic...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Preparation of viscose
[0048] Follow the same steps as in Example 1.
[0049] (2) "Hot sol phase inversion" ball making method
[0050] Mix 1500mL transformer oil in the oil phase with 62g of dispersant (30g calcium carbonate, 2g potassium oleate and 30g span85), and then mix 500g of cellulose yellow acid viscose liquid in the water phase and 258g of mixed porogen (3g cyclohexylamine, 250g of polyoxyethylene with an average molecular weight of 10,000 and 5g of polyoxyethylene castor oil) were mixed evenly and added to the oil phase, stirred at 200rpm for half an hour, rapidly heated to 70°C, and kept for half an hour. The oil phase was decanted to obtain spherical cellulose xanthate particles containing porogen.
[0051] (3) post-processing
[0052] Follow the same steps as in Example 1.
[0053] It has been determined that the ultra-large-porous medium-pressure-resistant spherical cellulose particles prepared by this method have a spherical or ellipsoidal app...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com