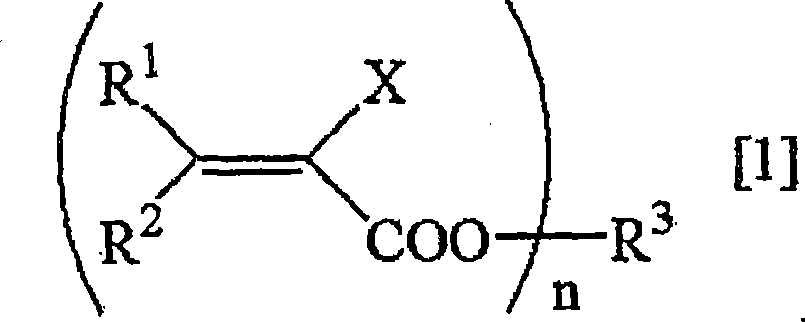
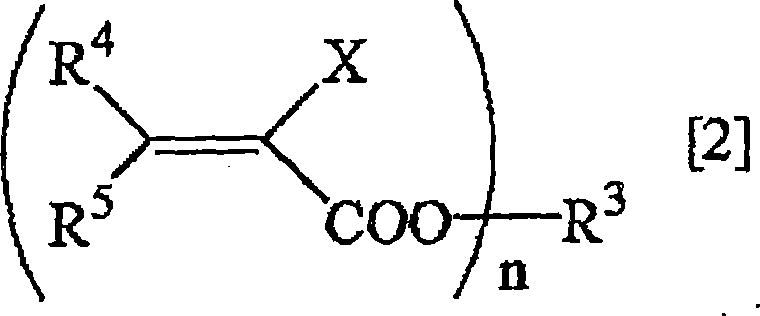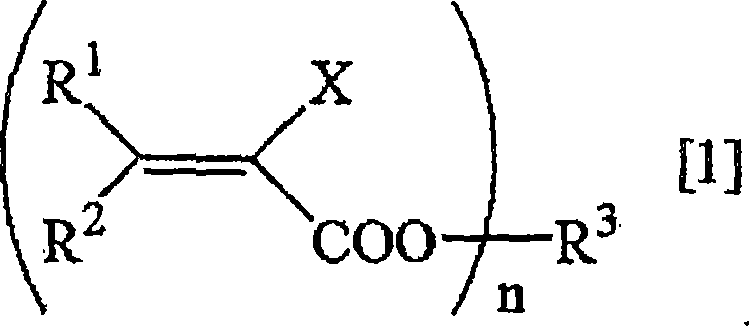Method for deuterating haloacrylic acid or its salt
A technology of deuterium and deuterium atoms, which is applied in the direction of organic chemistry methods, chemical instruments and methods, carboxylate preparation, etc. It can solve the problems of complex refining operations, difficulty in manufacturing, and low deuterium hydrogenation rate of hydrogen atoms, so as to improve operations environmental effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Deuterated hydrogenation of sodium 2-chloroacrylate (catalyst: Rh / C)
[0123] Suspend 500 mg of sodium 2-chloroacrylate and 100 mg of rhodium carbon (Rh 5%) in 17 mL of heavy water, replace the reaction system with nitrogen, and react in an oil bath at 160° C. for 24 hours. After the reaction was over, the reaction solution was filtered to remove the catalyst, and after evaporation under reduced pressure, the determination of the obtained compound was carried out. 1 H-NMR and 2 H-NMR and structural analysis showed that the isolated yield of sodium 2-chloroacrylate was 76%, and the deuterated hydrogenation rate was 95%. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2~3
[0125] Except using the inactive catalyst (mixed catalyst) shown in following Table 1, other is the same as embodiment 1, carries out heavy hydrogenation reaction to 2-chlorosodium acrylate. Table 1 also shows the separation yield and deuteration rate of the obtained product.
[0126] [Table 1]
[0127] Example
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com