An adaptive method for extending, transforming and dithering modulation of watermarking
An adaptive and watermarking technology, applied in the fields of instruments, computing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as the impossibility of obtaining a large quantization step size, loss of STDM robustness, and non-compliance with the characteristics of perceptual systems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
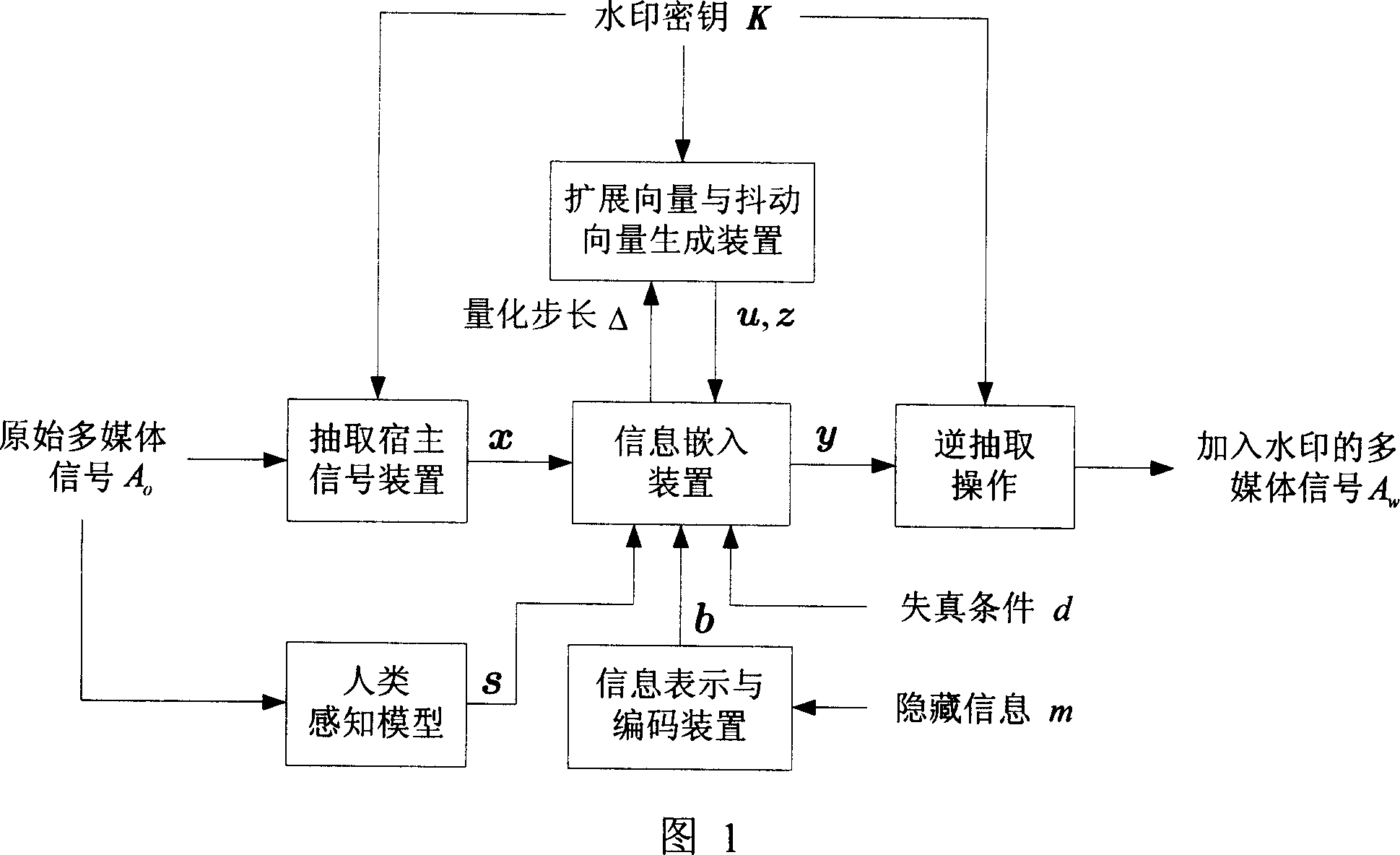
[0082] Watermark Carrier A o For an image signal, realize an adaptive STDM watermark embedding method, the whole process is as shown in Figure 1, including the following steps:
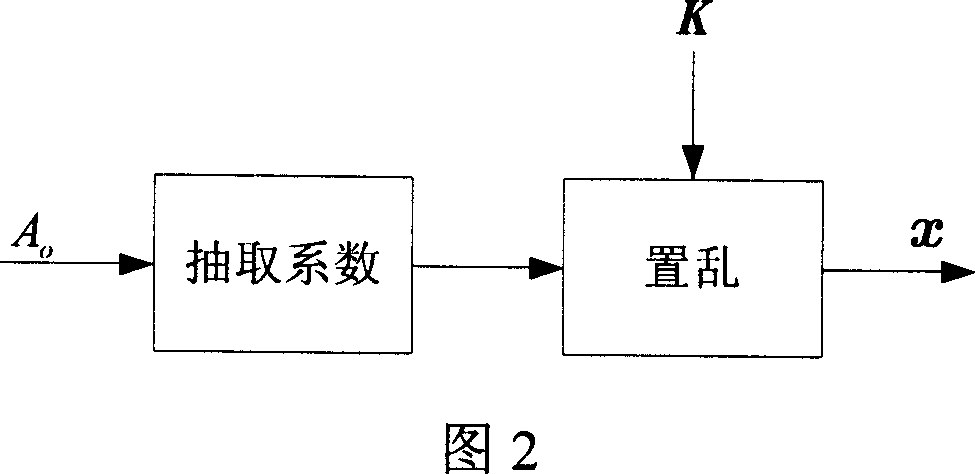
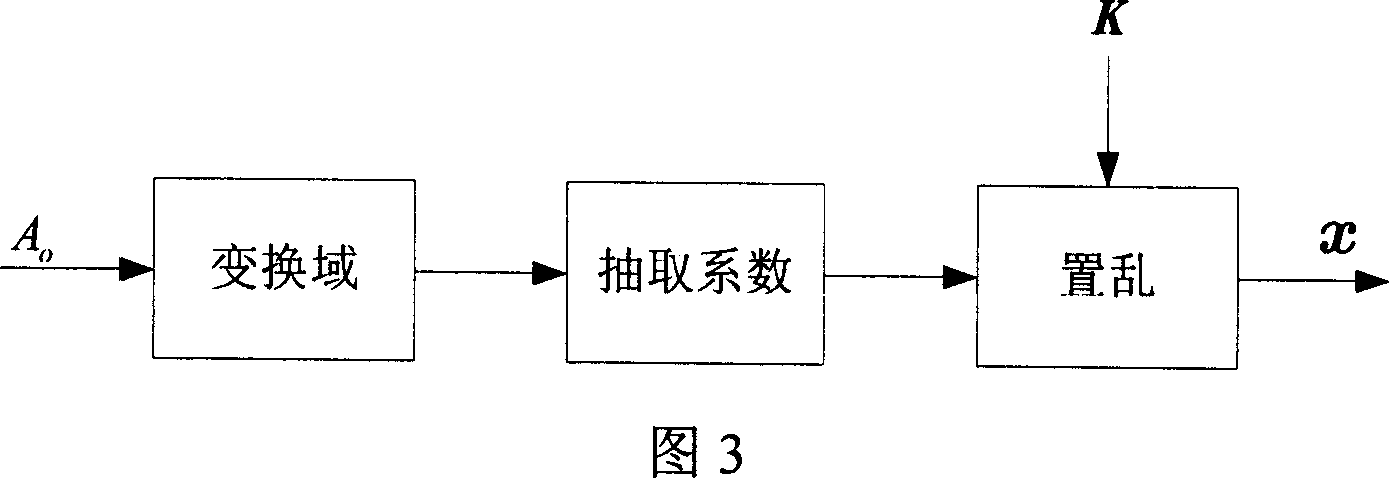
[0083] (1) From A o The block DCT (DCT: Discrete Cosine Transform) domain extracts the host signal x. A oDivide into multiple non-overlapping sub-blocks, each block contains 8×8 pixels, and then perform DCT transformation on each block. Perform zigzag sorting on the 64 DCT coefficients in each block, and select 62 DCT coefficients with ordinal numbers ranging from 3 to 64. Arrange all selected DCT coefficients into a large sequence as the host signal of the watermark. Then scramble the extracted host signal according to a certain random order. The generation of this random order depends on the watermark key K, and the final generated signal is recorded as x, and its length is N. This step is realized by extracting the host signal device, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 .
[0084] (2) In this e...
Embodiment 2
[0128] The difference from Example 1 is that the original signal A o It is an audio signal with a length of 10 seconds, and the time domain has a total of 4.4×10 4 sample, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0129] In step (1), from A o Extract the host signal x in the frequency domain of . Calculate A first o The short-time Fourier transform and energy spectrum, and then use the Garcia auditory model (R.A.Garcia.Digital watermarking of audio signals using a psychoacoustic auditory model and spread spectrum theory.Proc of 107 th AES Convention, New York, 1999, 1-42) calculates the maximum amplitude that the human ear cannot detect at each frequency point. In order to be consistent with the previous one, we also call it JND. Select the frequency points whose energy spectrum is smaller than the square of JND, count the number of these frequency points and generate a zero vector of equal length as the host signal x of the watermark, that is, x=θ.
[0130] In ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com