Method for evaluating effect of seriously-polluted lake dredging on bottom mud microbe ecological system structure and function
An ecosystem and heavy pollution technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to scientifically evaluate the risk of sediment dredging, scarcity of biomass, and decline in credibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
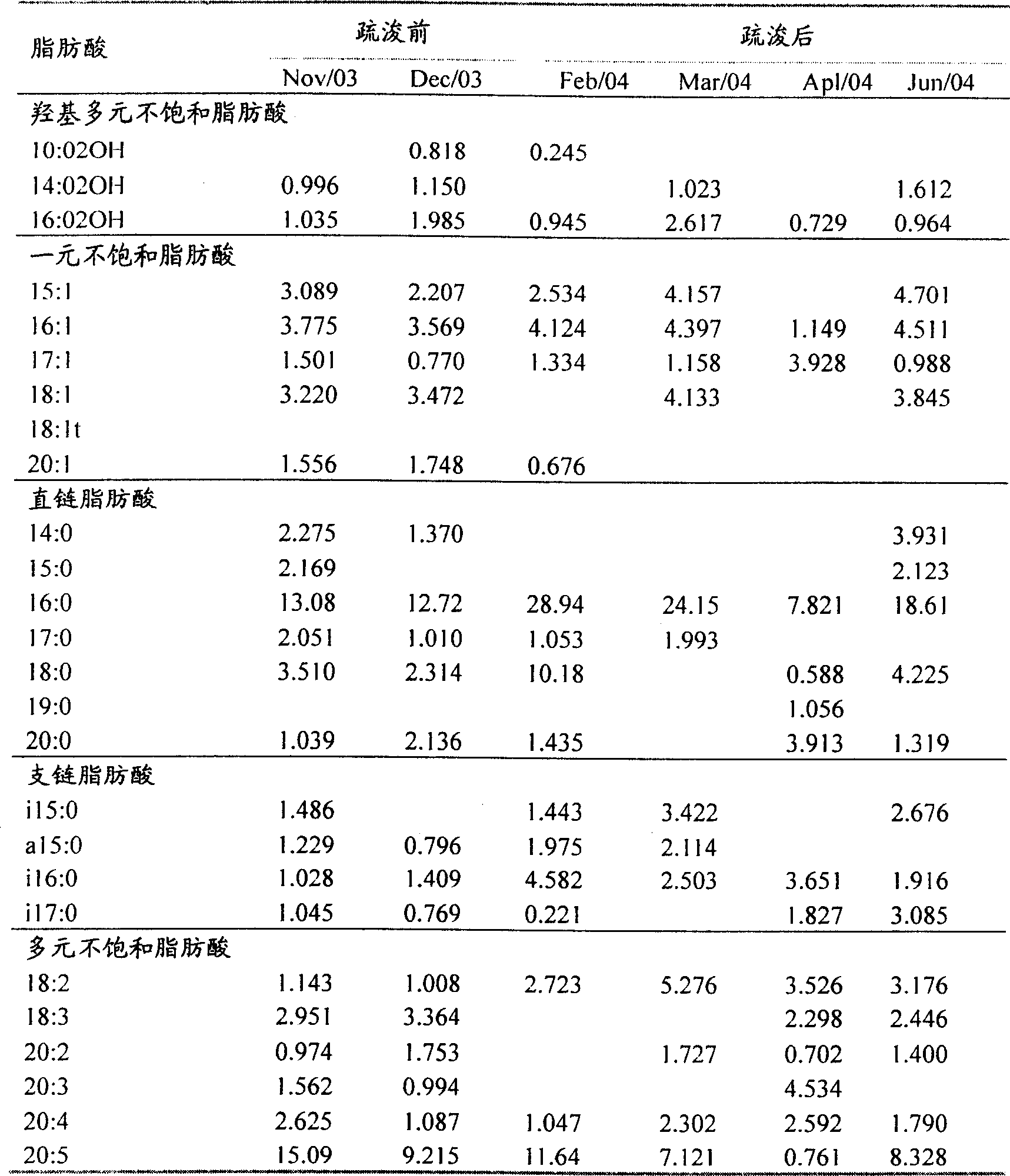
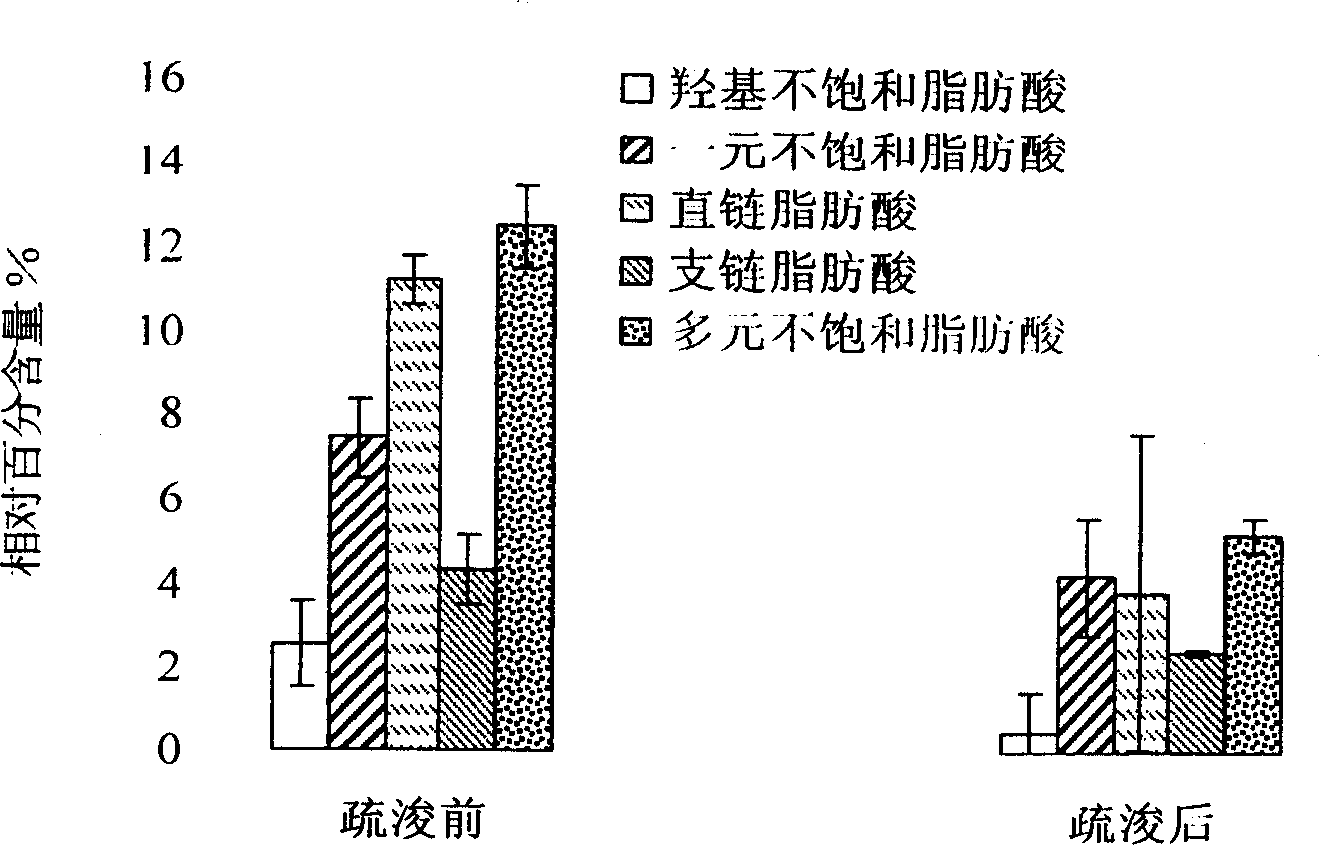
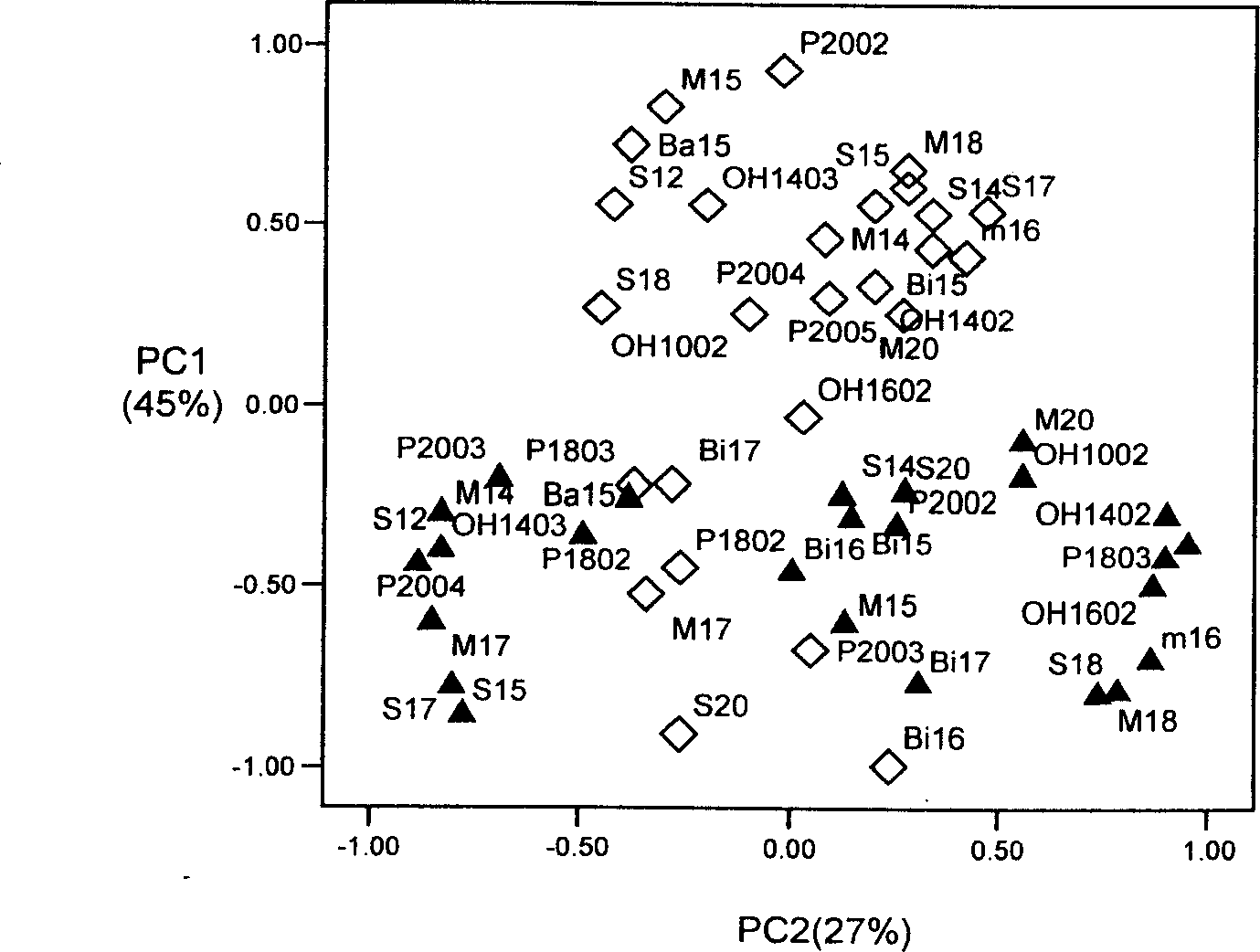
[0028] The present invention compares the influence of bottom mud dredging on the formation of benthic microbial communities in Wuli Lake by sampling and detecting fatty acid types in bottom mud samples before and after dredging in Wuxi Wuli Lake.
[0029](1) Use the fatty acid analysis method to evaluate the impact of dredging on the microbial community structure in the sediment: before dredging, it is necessary to collect 2-3 samples as the background value of the lake water quality and sediment; sampling 2-3 times during the dredging process times; sampling once a month after dredging, and the whole sampling process lasts for 1-2 years. Use a columnar sediment sampler (7 cm in diameter) to collect 1 kg of sediment samples from the surface layer (1-5 cm). Three mud samples were collected at each point for parallel processing. The samples were sealed in plastic bags, transported back to the room under refrigerated conditions in an incubator, and stored at 4°C until analysis....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com