Migration-proof light-emitting semiconductor device and method of fabrication
A technology for light-emitting components and semiconductors, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, and electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problem that light-emitting semiconductor regions do not effectively utilize light extraction, and achieve the effects of preventing short circuits and suppressing leakage currents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
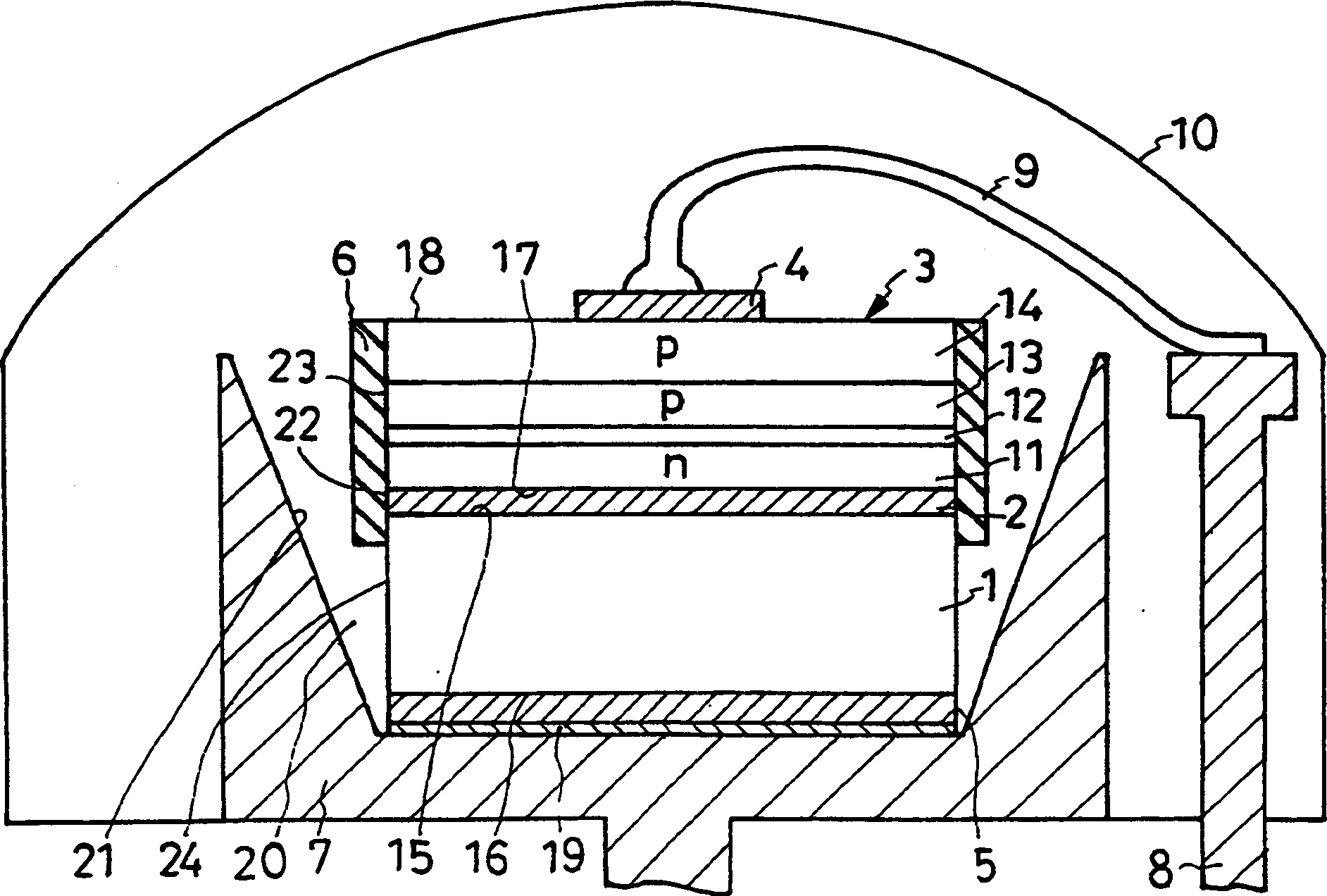
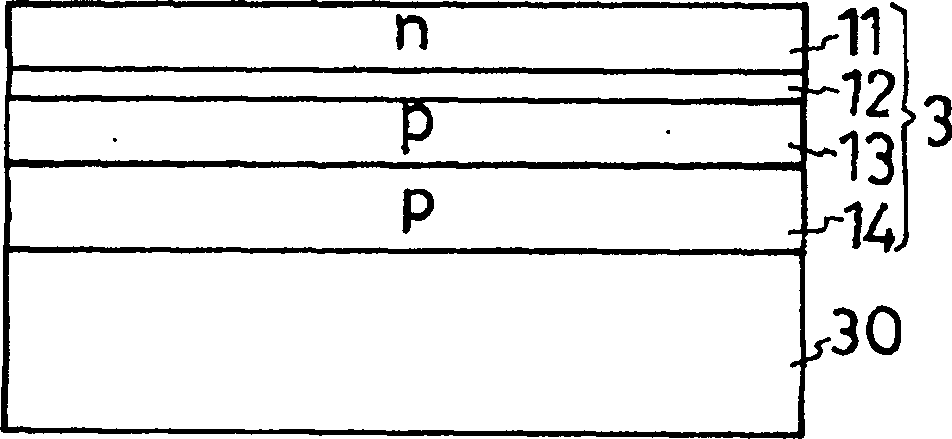
[0042] figure 1The light-emitting diode shown as the semiconductor light-emitting element of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is generally composed of the following parts: a conductive support substrate 1, a light reflection layer 2 made of a conductor layer, and a semiconductor region 3 with a light-emitting function. , the first electrode 4 , the second electrode 5 , the protective layer 6 , the mount 7 , the lead member 8 , the wire 9 and the resin enclosure 10 . In order to form a light-emitting diode with a double heterojunction structure, the semiconductor region 3 includes an n-type semiconductor layer 11 generally called an n-type cladding layer, an active layer 12, a p-type semiconductor layer 13 generally called a p-type cladding layer, and a p-type auxiliary layer. semiconductor layer 14 . The semiconductor region 3 will be described in detail later.
[0043] The support substrate 1 is composed of a conductive silicon semiconductor including one main surface ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Below, explain Figure 8 The semiconductor light-emitting element of Example 2 is shown. but, Figure 8 and represent Examples 3 to 8 described later Figure 9 to Figure 14 basically with figure 1 The same symbols are used for the same parts, and descriptions thereof are omitted. and also, Figure 8 ~ Figure 14 The semiconductor light-emitting element shown is also provided with figure 1 The mounting seat 24, the lead terminal 8, the wire 9 and the same part of the enclosure 10, but in order to simplify Figure 8 ~ Figure 14 The illustration is omitted.
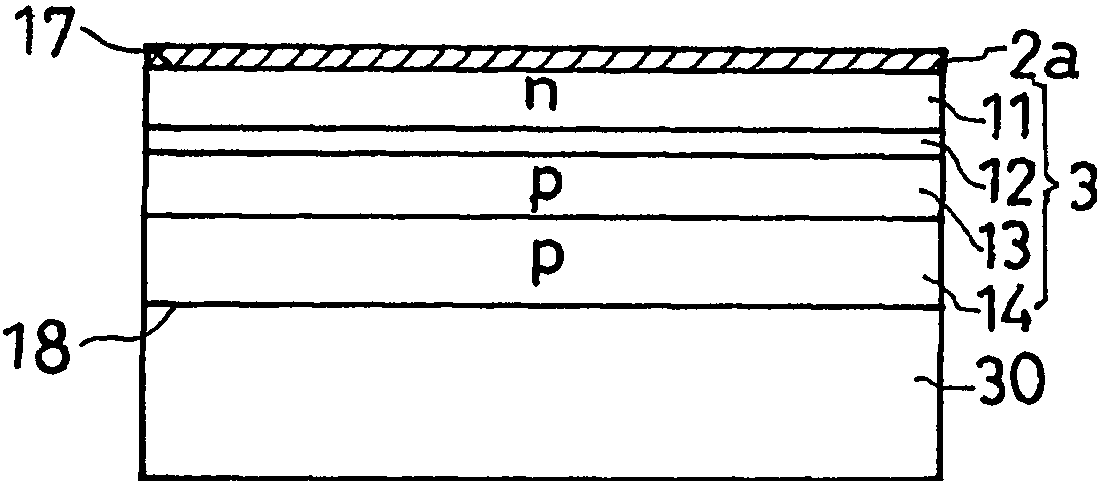
[0110] Figure 8 In the semiconductor light-emitting element of Example 2 except the deformed protective layer 6a and figure 1 same. Figure 8 The protective layer 6a is formed by making the exposed surface of the light reflection layer 2 and the exposed side surface of the semiconductor region 3 high-resistance, that is, insulated. This insulating protection layer 6 a can be formed by implanting ions into th...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Figure 9 The semiconductor light-emitting element of Example 3 shown is in addition to the deformed protective layer 6b and the current blocking layer 31 and figure 1 The same constitutes.
[0114] Figure 9 The protective layer 6b consists of the first protective layer 6b covering the side 22 of the light reflection layer 2 1 and cover the first protective layer 6b 1 The second protective layer 6b on 2 constitute. First protective layer 6b 1 and Figure 8 The protective layer 6a is also formed by ion implantation. Second protective layer 6b 2 and figure 1 The protective layer 6 is also formed by coating an insulating inorganic substance, except for covering the first protective layer 6b 1 In addition, the side surface 23 of the semiconductor region 3 , the other main surface 18 and part of the side surface of the substrate 1 are also covered. Figure 9 The side surface 22 of the light reflection layer 2 is covered by the first and second protective layers 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com