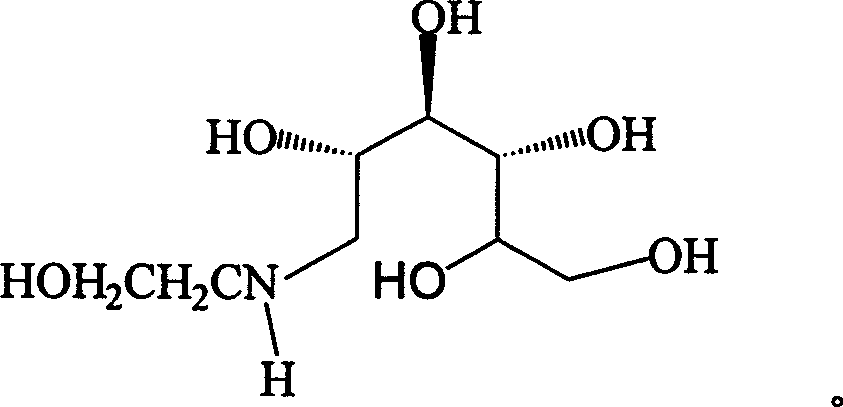
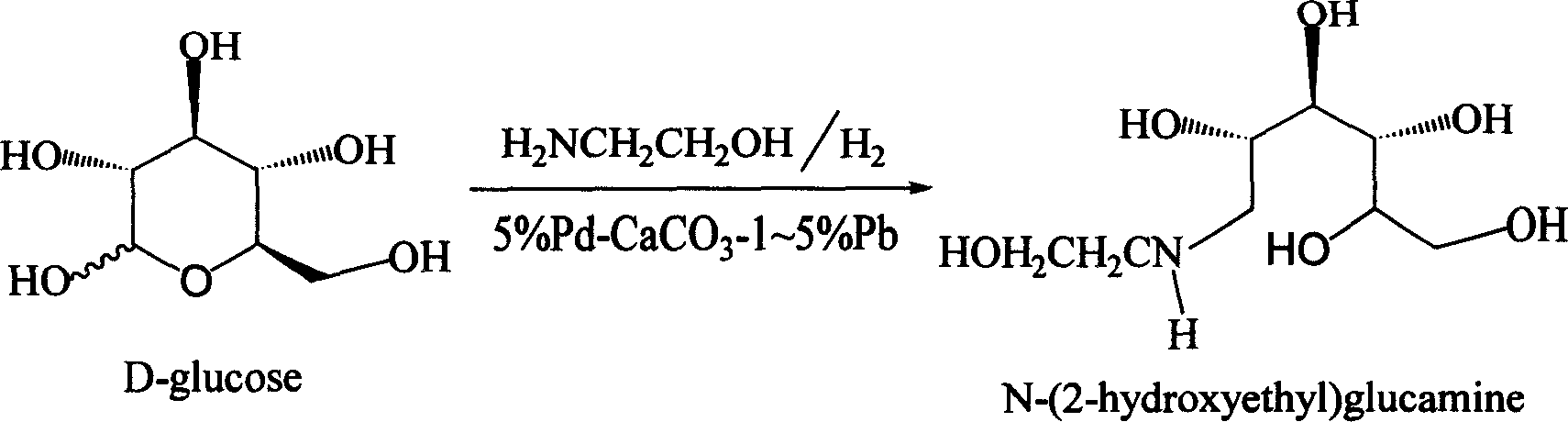Method for synthesizing N- (2-hydroxyethyl)-glucosamine
A synthesis method, glucosamine technology, applied in the field of synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, can solve problems such as inability to obtain products, achieve high conversion rate, mild reaction conditions, and easy reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] A. Feeding: In a 20L autoclave, add 2kg (10.1mol) of D-glucose, 650g (10.7mol) of ethanolamine, and then add 18L of 90% methanol (10% water content) solvent. After replacing with nitrogen, add 5% Pd-CaCO 3 - 60g of 2% Pb catalyst, blow in high-purity hydrogen, keep the hydrogen pressure at 2-3Mpa, and slowly raise the temperature to 35°C for reaction.
[0016] B. Reaction: Control the reaction temperature to 35-45° C. and the hydrogen pressure to 2-4 MPa to react for 24 hours. The reaction was followed by TLC, and the glucose spot disappeared, and the reaction was terminated.
[0017] C. Post-processing: After the reaction is finished, release the hydrogen pressure and replace with nitrogen. Nitrogen pressure filtration, the filter residue is waste 5% Pd-CaCO 3 -1~5% Pb catalyst, stored in deionized water, recovered after centralized treatment. The light yellow filtrate was put into a 300L glass-lined reaction kettle, and 100L acetonitrile was slowly added under str...
Embodiment 2
[0020] A. Feeding: In a 50L autoclave, add 5kg (25.2mol) of D-glucose, 1.6kg (26.7mol) of ethanolamine, and then add 35L of solvent of 85% isopropanol (15% water content). Add 5% Pd-CaCO after nitrogen replacement 3 - 200g of 4% Pb catalyst, bubbling high-purity hydrogen, keeping the pressure of hydrogen at 2-3Mpa, slowly raising the temperature to 35°C for reaction.
[0021] B. Reaction: Control the reaction temperature to 35-45° C., and the hydrogen pressure to 2-4 MPa to react for 22 hours. The reaction was followed by TLC, and the glucose spot disappeared, and the reaction was terminated.
[0022] C. Post-processing: After the reaction is finished, release the hydrogen pressure and replace with nitrogen. Nitrogen pressure filtration, the filter residue is waste 5% Pd-CaCO 3 -1~5% Pb catalyst, stored in deionized water, recovered after centralized treatment. The light yellow filtrate was put into a 300L glass-lined reaction kettle, and 200L tetrahydrofuran was slowly ad...
Embodiment 3
[0025] A, feed intake: in 400L autoclave, add D-glucose 30kg (151.5mol), ethanolamine 10kg (166.2mol), add the solvent 250L of 80% n-butanol (water content 20%) again. Add 5% Pd-CaCO after nitrogen replacement 3 - 3% Pb catalyst 1.2kg. Bubble high-purity hydrogen, keep the hydrogen pressure at 2-3Mpa, and slowly raise the temperature to 35°C for reaction.
[0026] B. Reaction: Control the reaction temperature to 35-45° C. and the hydrogen pressure to 2-4 MPa to react for 20 hours. The reaction was followed by TLC, and the glucose spot disappeared, and the reaction was terminated.
[0027] C. Post-processing: After the reaction is finished, release the hydrogen pressure and replace with nitrogen. Nitrogen pressure filtration, the filter residue is waste 5% Pd-CaCO 3 -1~5% Pb catalyst, stored in deionized water, recovered after centralized treatment. The light yellow filtrate was put into a 2000L glass-lined reaction kettle, and 1000L acetone was slowly added under strong s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com