Process for preparing ferric oxide hollow particle using core-shell structured ferric oxide-organic composite particle
A composite particle, iron oxide technology, applied in the direction of magnetic properties of inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain extensive and effective application, inability to obtain compact and complete, cumbersome preparation process, etc., and achieves easy popularization and application, wide range of uses, and high product purity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Take 50-150 grams of self-made (shell / core) iron oxide-organic composite microspheres (particle size is 240 nanometers), put them into a porcelain crucible, and put them into a 20-liter ordinary sintering furnace. Slowly rise to the sintering temperature of 550°C at a rate of 10°C / min, and keep at this temperature for 4 to 5 hours; then slowly cool to room temperature at a rate of 10°C / min to obtain a sintering temperature of 220 nanometers and a wall thickness of Iron oxide hollow microsphere particles of 50-70 nanometers.
Embodiment 2
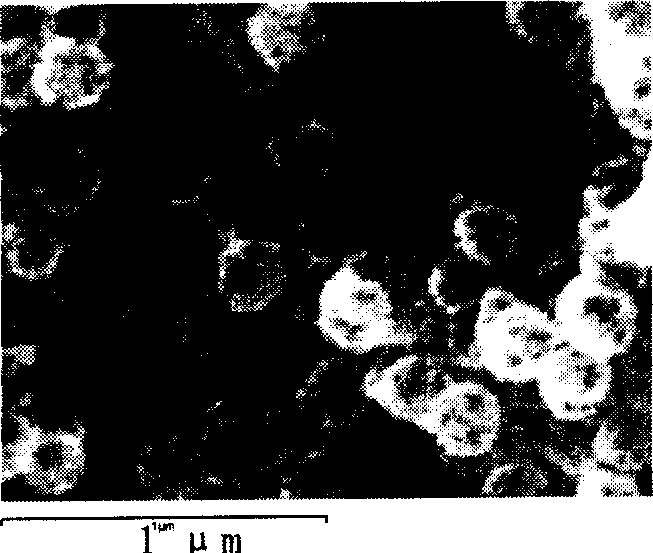
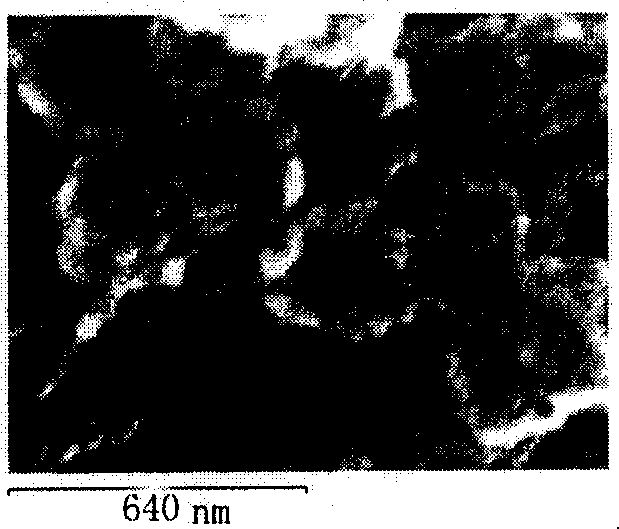
[0030] Example 2: Take 50-150 grams of self-made (core-shell) magnetic iron oxide-organic composite microspheres (with a particle size of 240 nanometers), put them into a porcelain crucible, and put them into a 20-liter airtight sintering furnace. Then pass through high-purity nitrogen protective gas, and after excluding the oxygen in the furnace for 30 minutes, slowly rise to the sintering temperature of 550°C at a speed of 10°C / min, and keep it at this temperature for 4 to 5 hours; slow cooling down to room temperature at a rate of 1 / min to obtain hollow-structured magnetic microsphere particles with a size of 220 nanometers and a wall thickness of 50-70 nanometers. attached figure 1 The hollow microspheres in are easily adsorbed on a magnetic block or an iron block, showing magnetism.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Take 50-150 grams of self-made (core-shell) magnetic iron oxide-organic composite microspheres (with a particle size of 350 nanometers), put them into a porcelain crucible, and put them into a 20-liter airtight sintering furnace. Then pass through high-purity argon protective gas, and after excluding the oxygen in the furnace for 30 minutes, slowly rise to the sintering temperature of 550°C at a speed of 10°C / min, and keep it at this temperature for 4 to 5 hours; Slowly cooling to room temperature at a rate of °C / min to obtain hollow magnetic microsphere particles with a size of 320 nanometers and a wall thickness of 60-80 nanometers. attached figure 2 The hollow microspheres in are easily adsorbed on a magnetic block or an iron block, showing magnetism.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com