Nonvolatile memory cell and non-volatile semiconductor memory device
A non-volatile storage and storage unit technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, information storage, etc., can solve the problems that the bit line current difference cannot be increased, the manufacturing cost is greatly affected, and the storage array area is increased.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
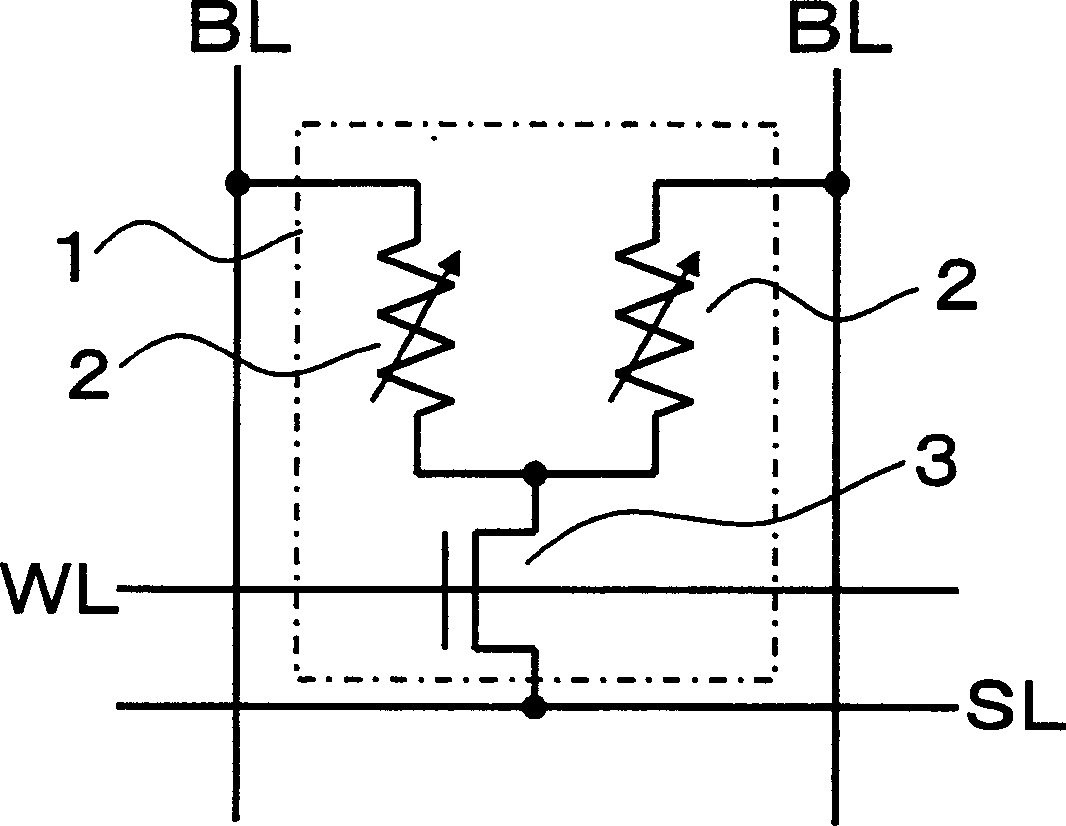
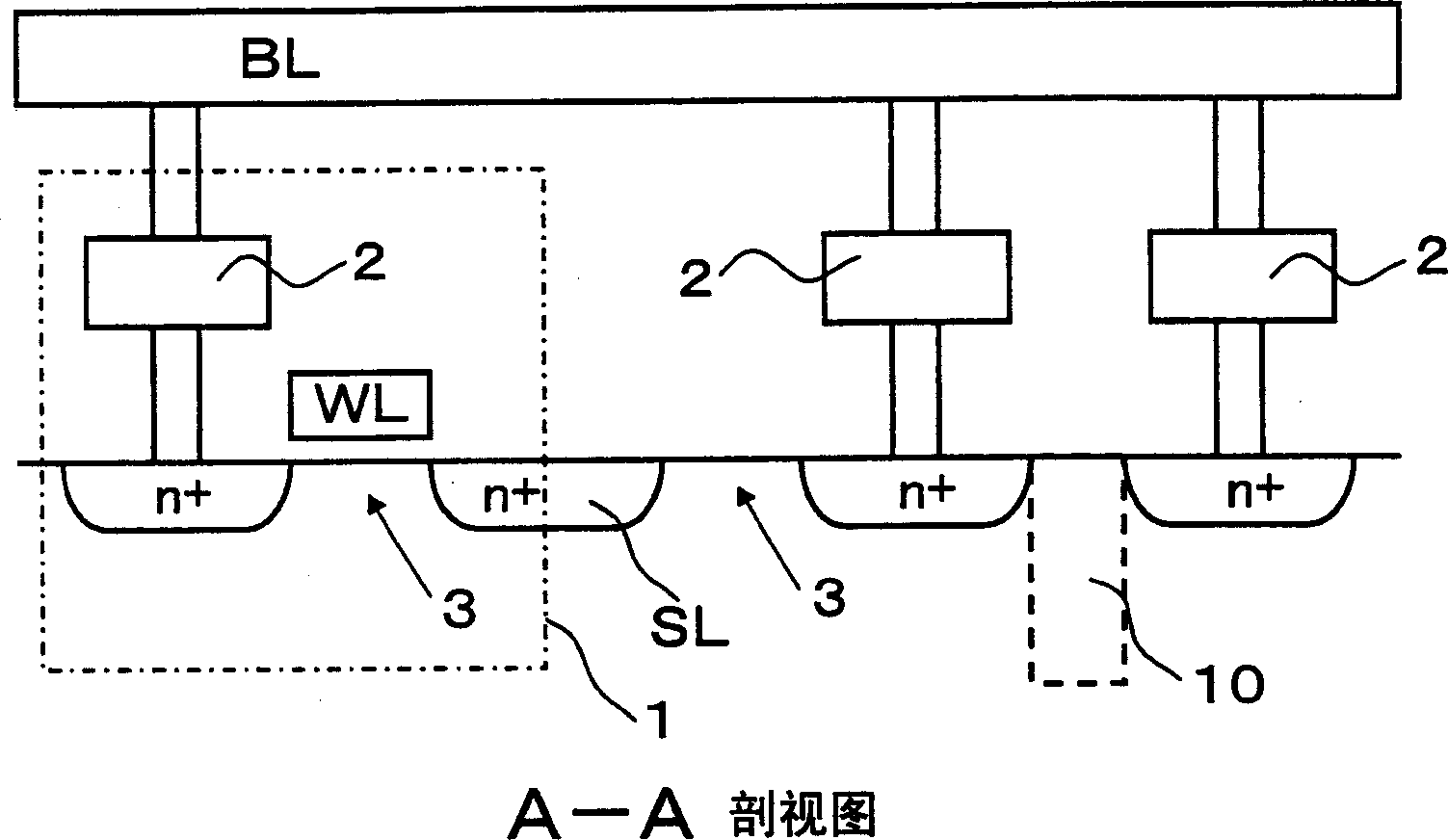
[0047] figure 1 The structure of the storage unit 1 of the apparatus of the present invention is shown in . The memory cell 1 is equipped with: two variable resistance elements; and a selection transistor 3 constituted with one N-type MOSFET as a selection element for selecting the two variable resistance elements, and one end of each variable resistance element 2 is connected to the end of the selection transistor 3 respectively. Drain connection. In addition, the other end of each variable resistance element 2 is connected to a different bit line BL, the gate of the selection transistor 3 is connected to the word line WL, and the source of the selection transistor 3 is connected to the source line SL. In this embodiment, since two variable resistance elements 2 are provided in one memory cell, the same Figure 17 Compared with the conventional memory cell shown, although it has twice the storage capacity, if one variable resistance element 2 corresponds to one memory cell...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
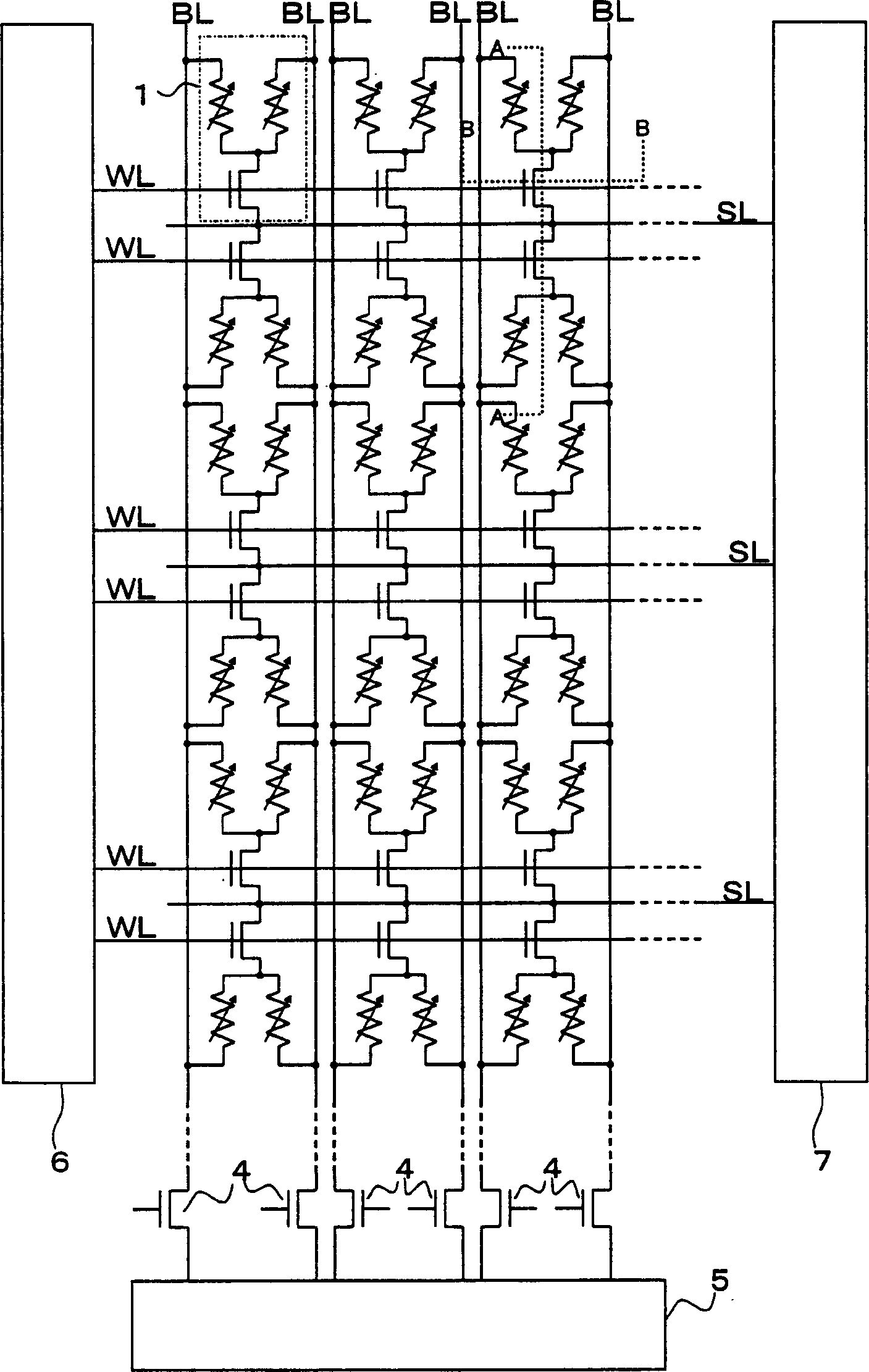
[0052] Then, respectively, in Figure 4 Indicates that a memory array with a layered bit line structure is used on the substrate. Figure 5 An example of a readout circuit in this layered bit line structure is shown in . In order to realize high-speed and stable reading of stored data from memory cell 1, it can be made as Figure 4 The memory array structure of the hierarchical bit line structure is shown.
[0053] In the hierarchical bit line structure of this embodiment, the bit line directly connected to the memory cell 1 is called a local bit line LBL. A memory array connected to the same local bit line LBL in the column direction is regarded as one block, a plurality of blocks are arranged in the column direction, and a local bit line selection transistor 11 for selecting the local bit line LBL of each block is provided, and the local bit line LBL passes through the local bit line. Bit line selection transistor 11 is connected to global bit line GBL. In addition, the ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0058] Figure 7 A third embodiment of the device of the present invention is shown. and Figure 4 The difference in the second embodiment shown is that a pair of local bit lines LBL1 and LBL2 connected to the same memory cell 1 is connected to equalize the pair of local bit lines LBL1 and LBL2 to the same potential during the charging period. Transistor 13 is used. Such as Figure 8 As shown in the signal timing waveform diagram, in the second embodiment, although the bit line selection signal BK2 is temporarily at a high level during the charging period, in the third embodiment, the local bit line selection signal BK2 is maintained at a low level , On the other hand, the equalization signal EQ1 is at a high level during the charging period, so that the equalization transistor 13 is turned on, and the local bit line LBL2 is charged. Only the method of charging a pair of local bit lines LBL1 and LBL2 is different, and other operations are the same as those of the second em...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com