Elastomer composite blends and method for producing them
A technology of elastomers and blends, applied in chemical instruments and methods, mixers, fluid mixers, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the molecular weight of a composition of natural rubber masterbatch
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0074] Test Methods
[0075] In the following examples and comparative examples, the following test methods were used.
[0076] 1. Bonded Rubber: A sample weighing 0.5g ± 0.025g was weighed and placed in 100ml of toluene in a sealed flask at room temperature for about 24 hours. The original toluene was then replaced with 100 ml of fresh toluene, and the flask was left for 4 days. The samples were then removed from the solvent and air dried in a fume hood at room temperature for 24 hours. The samples were then further dried in a vacuum oven at room temperature for 24 hours. The samples were then weighed and the bound rubber calculated from the weight loss data.
[0077] 2. MW sol : MW used in this specification and claims sol It refers to the weight average molecular weight of the sol portion of natural rubber. Standard GPC procedures for molecular weight determinations were performed as follows:
[0078] 2.1 Two 10 μm 10 from Polymer Laboratories, UK 6 Angstrom colum...
Embodiment A
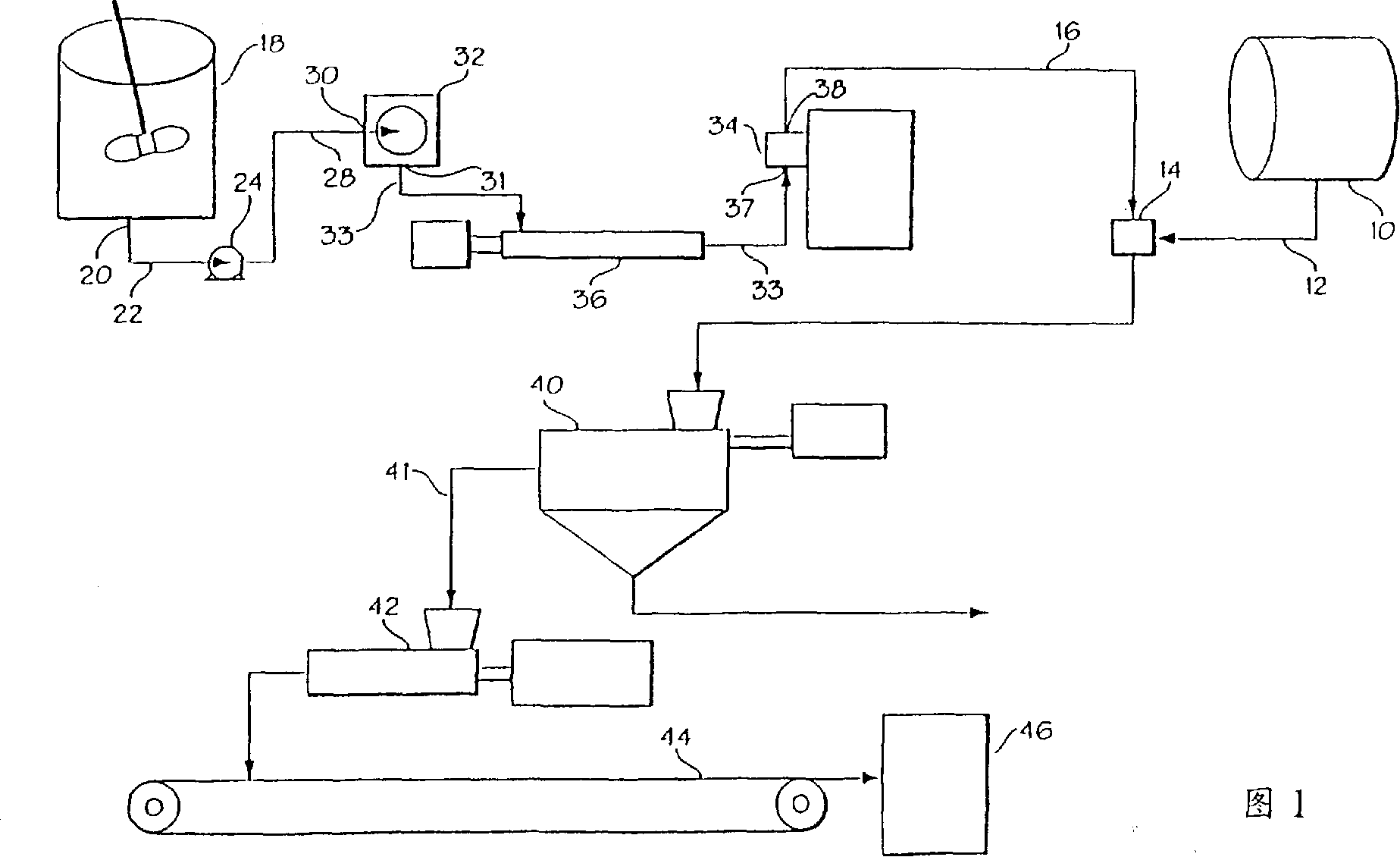
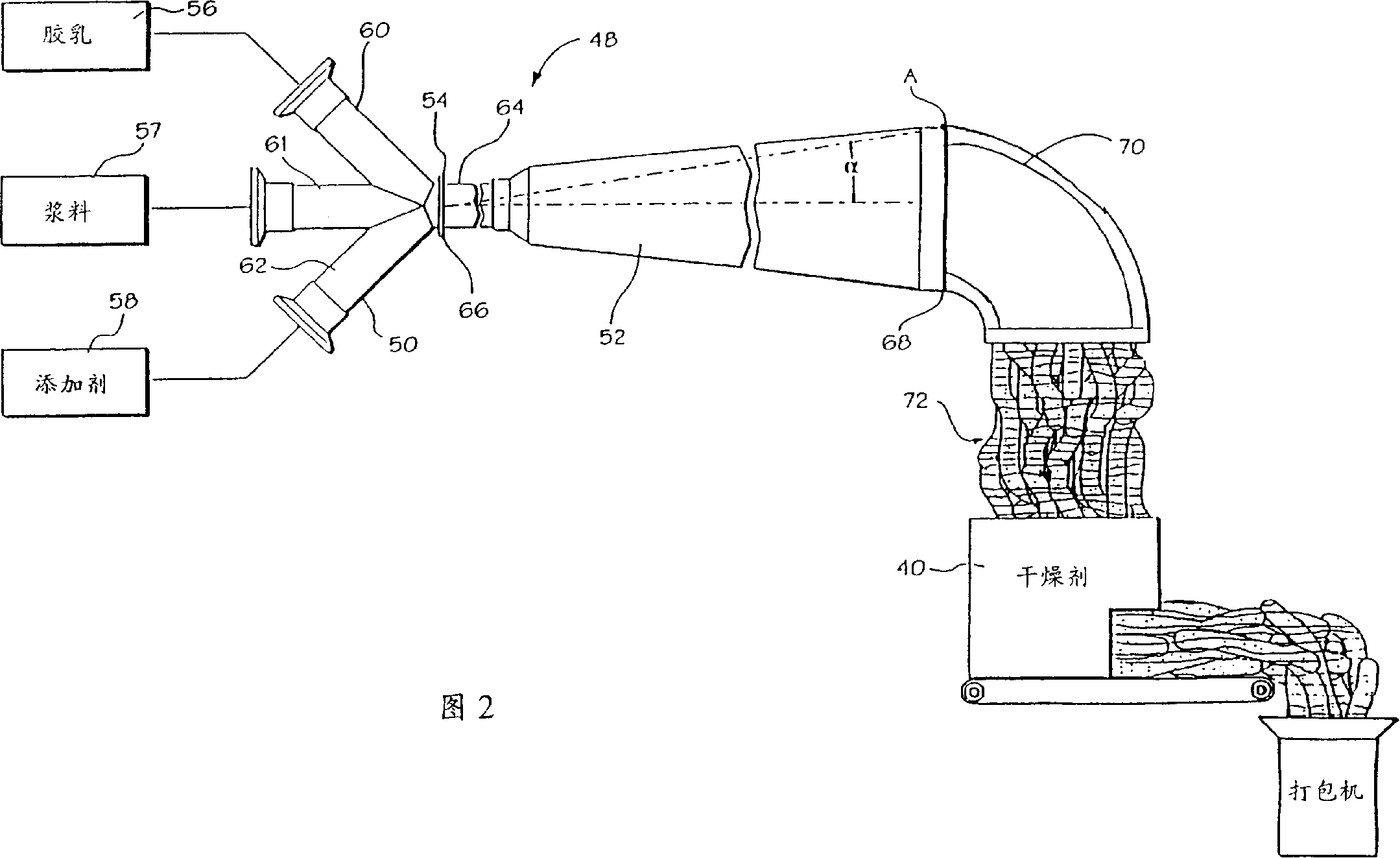
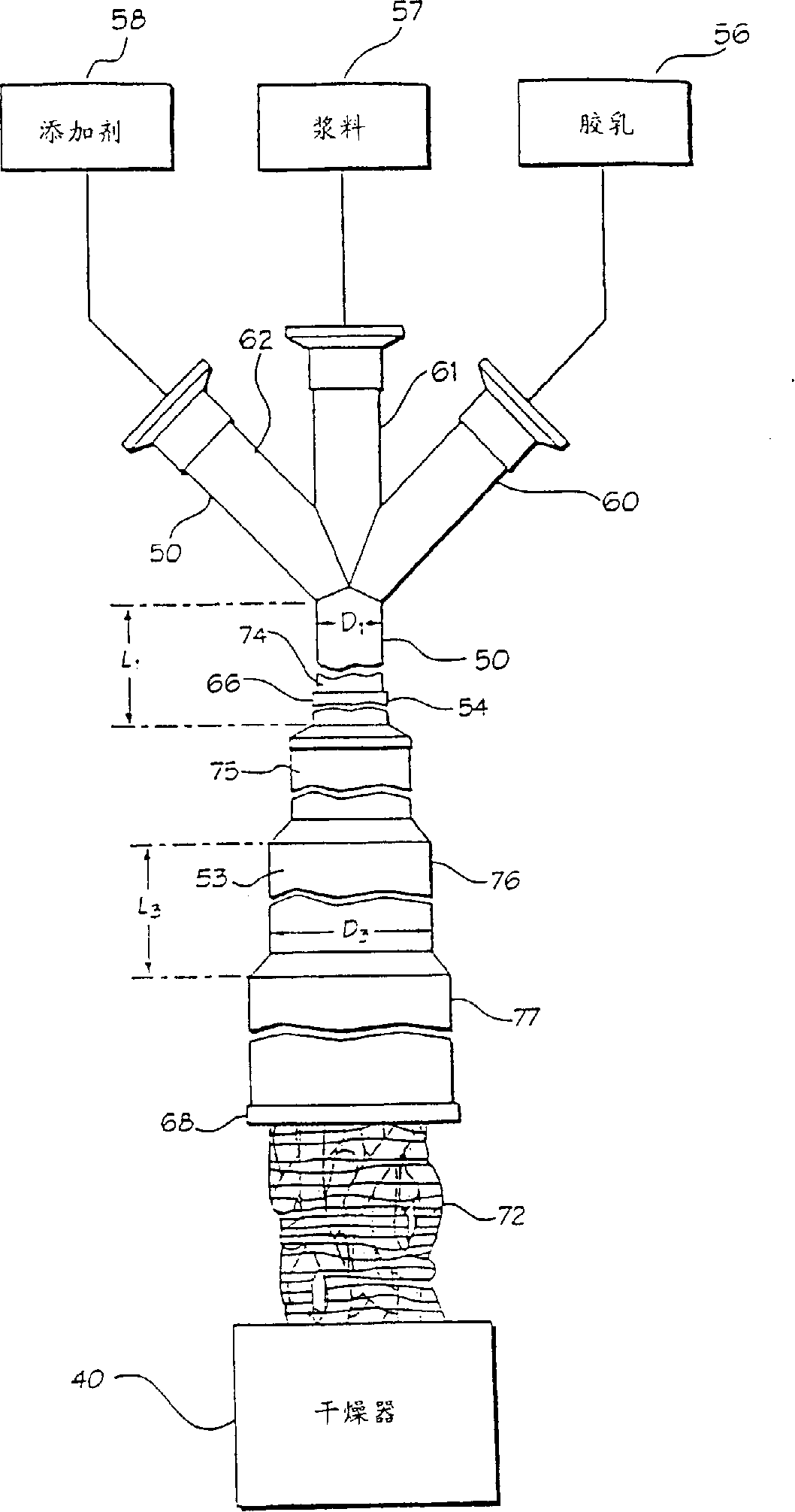
[0107] Elastomer masterbatches were prepared according to the invention. In particular, an elastomeric masterbatch was prepared containing standard natural rubber field latex from Malaysia, and a filler consisting of 52.5 phr of commercial grade N234 carbon black obtained from Cabot Corporation. Table 1 below shows the properties of the natural rubber field latex.
[0108] Additives
% dry
rubber
%total
%
Ash
nitrogen ppm
volatility
ML(1+4)
@100℃
[0109] 0.15% HNS a 0.3% NH 3 ,
ZnO, TMTD b
28.4
34.2
0.38
0.366
0.052
68
[0110] a. HNS: neutral hydroxylamine sulfate, Mooney viscosity stabilizer.
[0111] b. ZnO / TMTD: for biological preservation, typically 0.025% in a 1:1 mixture.
[0112] The full furnish formulation given in Table 2 below is typical of commercial truck tire tread formulations which ar...
Embodiment B
[0130] A control masterbatch was prepared by dry smelting. The control used the same formulation as in Example A (see Table 2 above), except that the natural rubber was SMR10 instead of latex. It was prepared by pre-mastication of the rubber with 10 phr carbon black at 50 rpm in a 0OC Banbury mixer (approximately 3 kg). Pre-fine refining for about 3 minutes, to a total of 800MJ / m 3 .
[0131] The contrast of embodiment A and embodiment B
[0132] The masterbatch of Example A and the control masterbatch of Example B were compounded and compounded in a two-step mixing operation in an OOC Banbury mixer (approximately 3 kg). Table 3 below lists the mixing scheme for the first step. It can be seen that an improved mixing scheme results from the masterbatch of Example A.
[0133] time (minutes)
Example A
Embodiment B dry mix control substance
0.0
all components
Pre-Mulched Rubber
0.5
carbon black and oil
1.0
sweep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Axial length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Axial length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Axial length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com