Process for improving cetane number of diesel oil and reducing aromatic hydrocarbon of diesel oil simultaneously
A technology of cetane number and diesel oil, which is applied in the field of increasing the cetane number of diesel oil while reducing its aromatics, and can solve problems such as difficult operation, difficult realization, and complicated components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
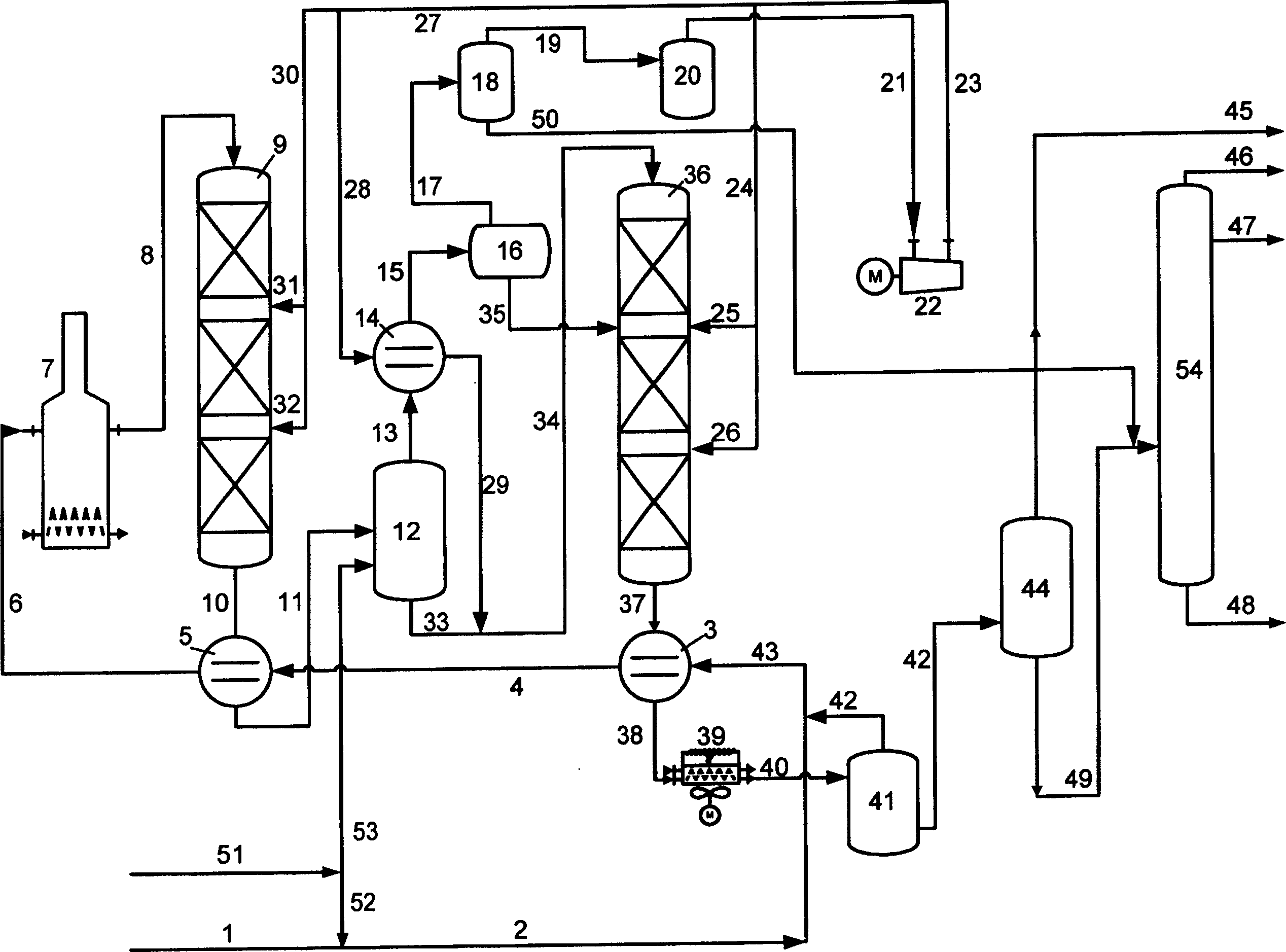
[0022] The preparation method of this catalyst is as follows:
[0023] First, the mesoporous silica-alumina carrier is shaped, the shaped carrier is dried at 80-140°C for 2-10 hours, and then calcined at 400-650°C for 2-10 hours. The platinum and palladium solutions used are platinum, palladium chloride, chlorate or ammonium salt. Immerse for 1 to 8 hours using the saturated immersion method, then dry at 80°C to 140°C for 2 to 10 hours, and bake at 400 to 650°C for 2 to 10 hours. The content of precious metals platinum and palladium is 0.1-10% by weight, and the weight ratio of platinum and palladium is 0.1-10:1.
[0024] The hydrodearomatization catalyst has excellent aromatics hydrogenation activity, anti-sulfur and nitrogen poisoning performance and low cracking performance, and can avoid the splitting of diesel oil fractions into small molecular by-products.
[0025] The method provided by the present invention will be further described below with reference to the accomp...
Embodiment 1
[0041] The raw material of this example is catalytic cracking diesel A, and the properties of this raw material are shown in Table 2.
[0042] The raw material is first contacted with hydrogen and hydrogenation-upgrading catalyst RIC-1 in the first-stage hydrogenation-upgrading reactor. The hydrogen partial pressure is 6.4MPa, the temperature is 360℃, and the hydrogen-oil volume ratio is 600Nm 3 / m 3 , liquid hourly space velocity 1.3h -1 The effluent of the first-stage hydro-upgrading reactor directly enters the hot high-pressure separator. The bottom of the hot high fraction is fed with hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas for stripping to remove impurities such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia in the first-stage reactant stream. The hot high-fraction stripping gas is cooled in two steps to obtain diesel fraction and part of the naphtha generated by cracking in the first stage. The diesel fraction is sent to the second-stage hydrodearomatization reactor as cold oil, and the naphth...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The raw material of this example is catalytic cracking diesel B, and the properties of this raw material are shown in Table 2.
[0046] The raw material is first contacted with hydrogen and the hydrogenation-upgrading catalyst RIC-1 in the first-stage hydrogenation-upgrading reactor. 3 / m 3 , liquid hourly space velocity 1.5h -1 The effluent of the first-stage hydro-upgrading reactor directly enters the hot high-pressure separator. The bottom of the hot high fraction is fed with hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas for stripping to remove impurities such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia in the first-stage reactant stream. The hot high-fraction stripping gas is cooled in two steps to obtain diesel fraction and part of the naphtha generated by cracking in the first stage. The diesel fraction is sent to the second-stage hydrodearomatization reactor as cold oil, and the naphtha directly enters the fractional distillation. system. The hydrogen separated from the stripping gas is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com