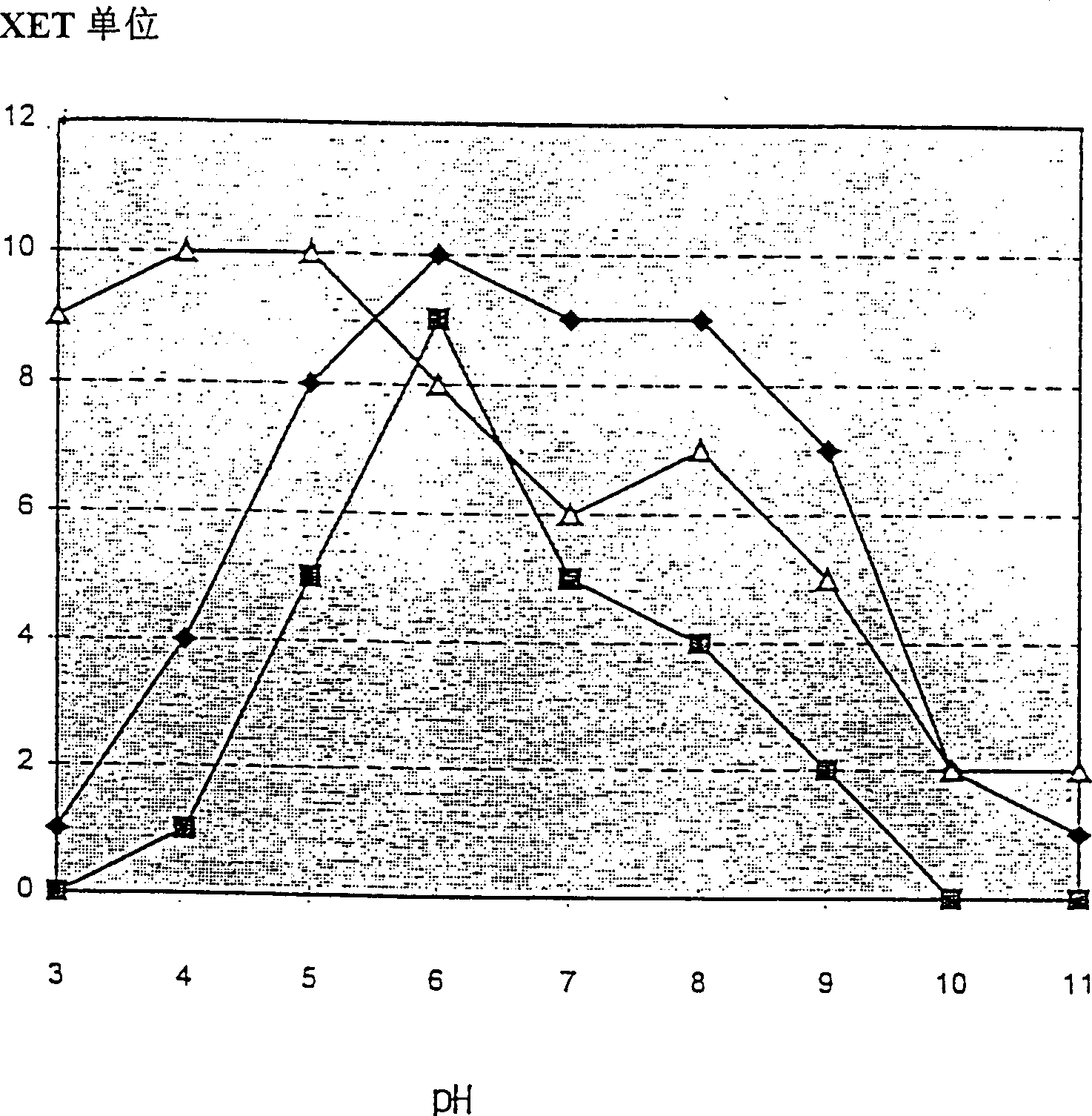
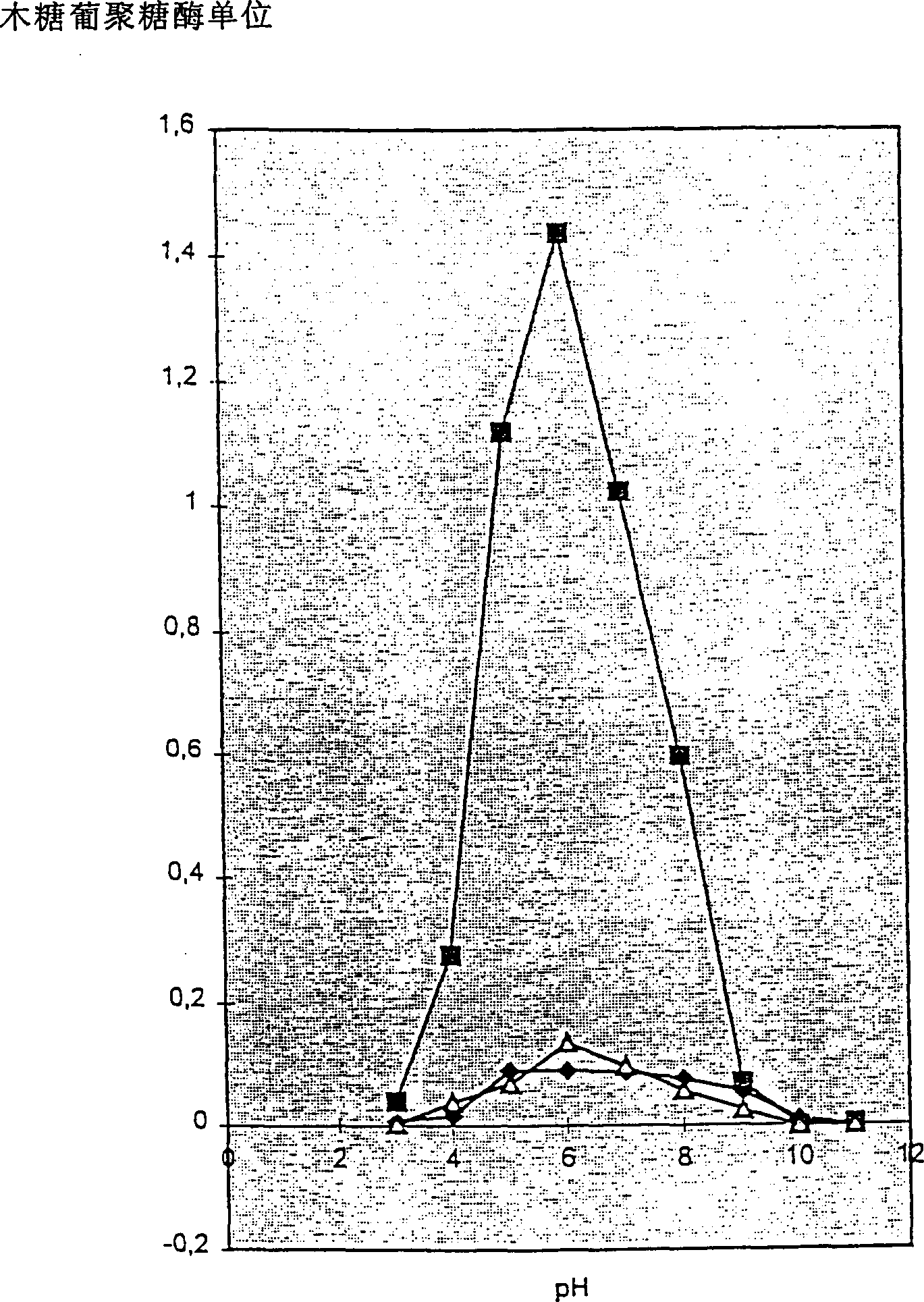
Microbial xyloglucan Endotransglycosylase (XET)
A technology of xyloglucan and production method, which is applied in the field of microbial xyloglucan endotransglycosylase, and can solve problems such as XET that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] Preparation of labeled oligosaccharides
[0022] The reducing oligosaccharide 4-O-[4-O-[4-O-[6-O-α-D-xylopyranose-β-D-glucopyranose]-6-O-(2-O -β-D-galactopyranose)-α-D-xylopyranose-β-D-glucopyranose]-6-O-(2-O-β-D-galactopyranose)-α- D-xylopyranose-β-D-glucopyranose]-D-glucose ('XLLG') (1 g) was dissolved in 25 ml containing 1 g of sodium cyanoborohydride (NaCNBH 3 ) in a saturated aqueous ammonium bicarbonate solution at 25°C in a dark place for 7 days for reductive amination. Ammonium bicarbonate is removed by drying and the (ninhydrin-reactive) aminated derivative of XLLG is purified (eg by gel filtration or cation exchange chromatography). The product should be an oligosaccharide-1-amino-1-deoxypolyhydric alcohol (deoxyalditol), a derivative in which the reducing terminal D-glucose moiety of XLLG is replaced by 1-amino-1-deoxy-D-glucitol .
[0023] Dissolve oligosaccharide-1-amino-1-deoxypolyhydric alcohol (50mg) in 3ml 3% borax (disodium tetraborate; pH=9.0-9....
Embodiment 1
[0191] Embodiment 1: screening XET positive bacterial strain
[0192] culture medium
[0193] PD agar: 39g potato dextrose agar, DIFCO0013; add deionized water to 1000ml, autoclave at 121°C for 15-20 minutes.
[0194] YPG agar: 4g yeast extract (DIFCO0127), 1g KH 2 PO 4 (Merck4873), 0.5g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O (Merck5886), 15g glucose (Roquette101-0441), 20g agar (Merck1614), deionized water to make up to 1000ml, 121 high pressure steam sterilization for 15-20 minutes.
[0195] MEA: 20g malt extract powder (DIFC00186), 1g peptone (DIFC00118), 20g glucose (Roquette France1010441), 20g agar (Merck1614), make up to 1000ml with deionized water, and autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes.
[0196] Medium A (per bottle): 30g wheat bran, 45ml of the following solution: 10g rofec (Roquette 101-0441), 10g NH 4 NO 3 (Merck1187), 10g KH 2 PO 4 (Merck4873), 40g Solcafloc (Dicacel, available from Dicalite-Europe-Nord, 9000 Gent, Belgium), 0.75g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O (Merck 5886), 15g CaCO 3 , make...
Embodiment 2
[0307] Example 2: Purification and identification of Dichotomocladium hesseltinei XET
[0308] Dichotomocladium hesseltinei (CBS164.61) was inoculated on 15 PDA agar slants, and cultured at 26° C. for 7 days. The bacterial cells were washed with about 250 ml of sterile distilled water containing 0.1% Tween80, and used to inoculate 80 shake flasks containing medium B (2-3 ml / bottle). The shake flask was cultured at 26° C. with shaking at 200 rpm for 5 days, and after that, the culture solution was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes.
[0309] Purify the supernatant containing xyloglucan endotransglycosylase (XET) as follows:
[0310] A filter aid was added to the culture solution filtered through the filter cloth, and the solution was further filtered with a Chua depth filter disc to obtain a clear solution. The pH of the filtrate was adjusted to pH 8.0, and the filtrate was diluted with deionized water to achieve the same conductivity as 20 mM Tris / HCl (pH 8.0).
[0311] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com