Difunctional heteropolyacid discharge promoting agent
A technology of heteropolyacids and excretion-promoting agents, applied in the directions of antitoxins, drug combinations, active ingredients of phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve the problems of poor selectivity, high toxicity of excretion-promoting agents, kidney damage, etc., and reduce the increase of oxidative stress. High, excellent biocompatibility, ROS reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Preparation and characterization of polyoxometalates (POMs)
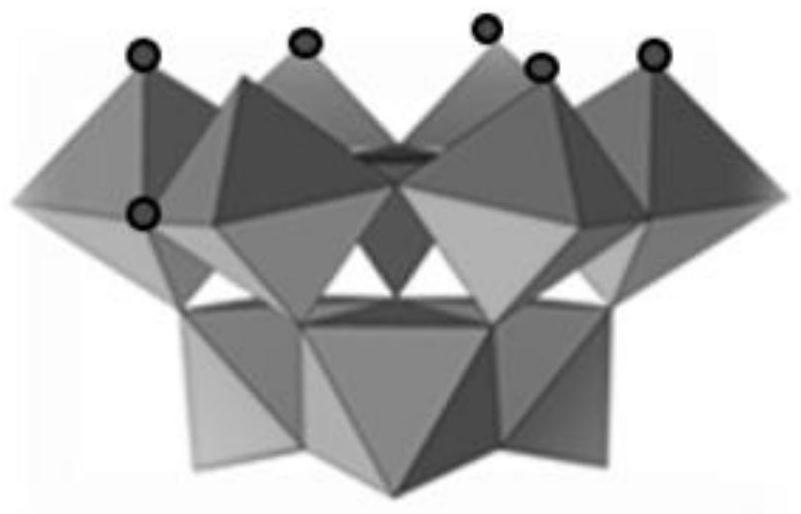
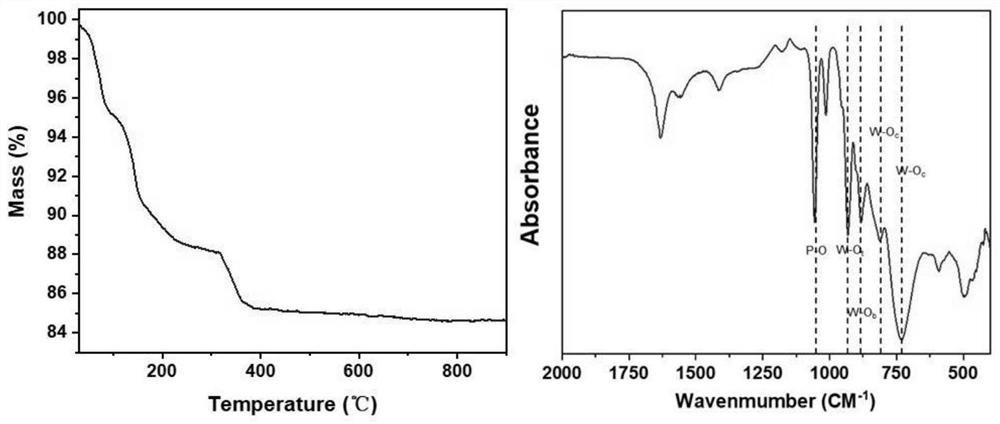
[0040] Under magnetic stirring, 120 g (0.36 mol) of sodium tungstate dihydrate Na 2 WO 4 ·2H 2 O was stirred with 150 mL of water in a 300 mL beaker until the solids were completely dissolved. Phosphoric acid (85%) was added dropwise (4.0 mL, 0.06 mol) with constant stirring. After the addition of the acid, the pH of the solution was 8.9-9.0. Glacial acetic acid (22.5 mL, 0.40 mol) was added dropwise with vigorous stirring and a large white precipitate formed during the addition. The final pH of the solution was 7.5 ± 0.3. Continue to stir for 1 h, collect the precipitate and dry it by suction filtration to obtain POMs (α-PW 9 Heteropolyacid salt), the yield of the product is 90 g (85-90%), the structure is as follows figure 1 shown, infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis as figure 2 shown.
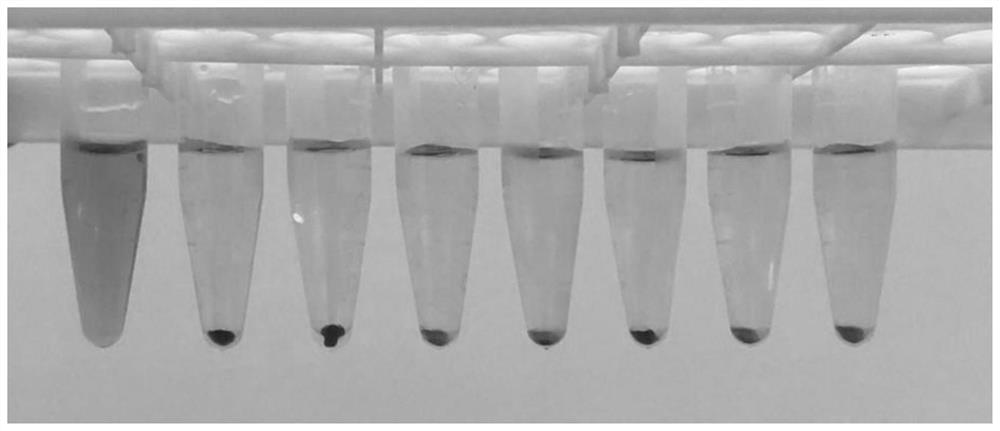
[0041] Biocompatibility experiments such as image 3 From left to right, deionized...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Preparation of polyoxometalates (POMs)
[0046]Stir 0.36 mol potassium tungstate with 150 mL water in a 300 mL beaker with magnetic stirring until the solid is completely dissolved, phosphoric acid (85%) is added dropwise (8.0 mL, 0.12 mol) with constant stirring; dropwise with vigorous stirring Glacial acetic acid (15.75 mL, 0.28 mol) was added, a large amount of white precipitate was formed during the addition, and stirring was continued for 0.5 h, the precipitate was collected and dried by suction filtration to obtain POMs.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Preparation of polyoxometalates (POMs)
[0048] 0.36 mol of sodium tungstate dihydrate and 150 mL of water were stirred in a 300 mL beaker with magnetic stirring until the solid was completely dissolved, phosphoric acid (85%) was added dropwise (2.4 mL, 0.036 mol) with constant stirring; Glacial acetic acid (27 mL, 0.48 mol) was added dropwise with stirring, a large amount of white precipitate was formed during the addition, and stirring was continued for 3 h, the precipitate was collected and dried by suction filtration to obtain POMs.
[0049] The POMs obtained in Example 1 were subjected to the following detection tests
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com