Grafting method for congeneric fruit tree varieties
A kind of fruit tree variety and fruit tree technology, applied in the field of grafting of the same fruit tree variety, can solve the problems of single variety and inability to produce multiple fruits, achieve the effect of increasing variety, improving value and market ability, and solving single variety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
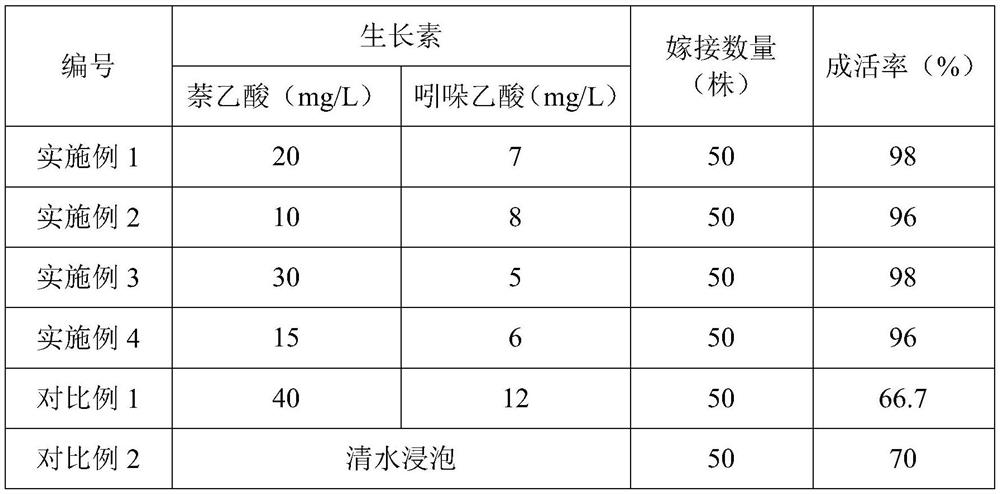
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A grafting method of the same genus fruit tree variety, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Step (1): choose the 3-4-year-old plants of normal growth, robust growth, and no pests and diseases as rootstock, the rootstock needs to be fertilized one week before the grafting, and after the rootstock is selected and completed, the rootstock is cut off at the height that needs to be grafted, and the cross-section of the rootstock is Smooth and do not damage the cortex;
[0030] Step (2): choose the annual mature semi-lignified, non-obvious pest-free branch of the same fruit tree as the scion, remove the terminal bud and the blade of the chosen branch, only keep the petiole, and the scion is trimmed into 3cm-7cm, leaving the bud. 2-4, wherein the number of scions is determined according to the number of varieties to be grafted;
[0031] The grafting time is: choose from late February to mid-March, graft before germination in spring, and control the temperature during gra...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A grafting method of the same genus fruit tree variety, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step (1): choose the 3-4-year-old plants of normal growth, robust growth, and no pests and diseases as rootstock, the rootstock needs to be fertilized one week before the grafting, and after the rootstock is selected and completed, the rootstock is cut off at the height that needs to be grafted, and the cross-section of the rootstock is Smooth and do not damage the cortex;
[0041] Step (2): choose the annual mature semi-lignified, non-obvious pest-free branch of the same fruit tree as the scion, remove the terminal bud and the blade of the chosen branch, only keep the petiole, and the scion is trimmed into 3cm-7cm, leaving the bud. 2-4, wherein the number of scions is determined according to the number of varieties to be grafted;
[0042] The grafting time is: choose from late February to mid-March, graft before germination in spring, and control the temperature during gra...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A grafting method of the same genus fruit tree variety, comprising the following steps:
[0051] Step (1): choose the 3-4-year-old plants of normal growth, robust growth, and no pests and diseases as rootstock, the rootstock needs to be fertilized one week before the grafting, and after the rootstock is selected and completed, the rootstock is cut off at the height that needs to be grafted, and the cross-section of the rootstock is Smooth and do not damage the cortex;
[0052] Step (2): choose the annual mature semi-lignified, non-obvious pest-free branch of the same fruit tree as the scion, remove the terminal bud and the blade of the chosen branch, only keep the petiole, and the scion is trimmed into 3cm-7cm, leaving the bud. 2-4, wherein the number of scions is determined according to the number of varieties to be grafted;
[0053] The grafting time is: choose from late February to mid-March, graft before germination in spring, and control the temperature during gra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com