Optimization method of fixed layer in MTJ structure
An optimization method and fixed layer technology, which is applied in the field of memory, can solve the problem of increasing the thickness of the fixed layer, and achieve the effect of reducing the thickness and reducing the thickness without affecting the stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The present invention has no particular limitations on the preparation methods of the above-mentioned layers, and the technical solutions of the preparation methods for forming the above-mentioned layer structures well known to those skilled in the art can be adopted.
[0049] The optimization method of the fixed layer in the MTJ structure provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0050] a) reducing the thickness of the first pinning layer PL1, and increasing the magnetic moment of the first pinning layer PL1;
[0051] b) reducing the magnetic moment of the second pinning layer PL2, and reducing the thickness of the second pinning layer PL2;
[0052] c) Decrease the thickness of the reference layer RL and decrease the magnetic moment of the reference layer RL.
[0053] In the present invention, preferably also includes:
[0054] Optimize the structure adjustment layer TL.
[0055] The present invention first reduces the thickness of the first...
Embodiment 1
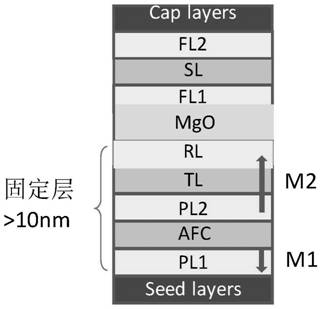
[0086] see figure 1 As shown, the following structures are formed in turn to realize the optimization of the fixed layer in the MTJ structure; the characteristics of each layer structure are:
[0087] (1) Small thickness first pinning layer PL1: Reduce the thickness of Co and Pt in the (Co / Pt)n multilayer to each molecular layer, that is, the thickness of each layer of Co and Pt is in the about n is controlled between 4 and 8; PL1 uses a high Ms Co alloy, such as Co x Fe 1-x (x is between 0.1 and 0.4), CoFeNi, etc., that is, materials with high Ms and strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy with Pt; at the same time, increase the thickness of the layer of Co in contact with the AFC.
[0088] (2) Antiferromagnetic coupling layer AFC: make PL1 and PL2 form strong antiferromagnetic coupling, typical materials are Ru, Ir, Cr; the thickness is between 0.3 and 1.0 nm, preferably around 0.45 nm.
[0089] (3) Second pinning layer PL2 with small thickness and low magnetic moment...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com