Arsenic adsorption material and preparation and recycling method thereof
A technology of adsorption materials and biomass materials, which is applied in the field of arsenic adsorption materials and its preparation and recycling, can solve the problem of low conversion rate, achieve good recyclable characteristics, easy recycling, and easy recycling and reuse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] see figure 1 , a preparation method of arsenic adsorption material, comprising:
[0041] After drying and pulverizing the biomass material, it is dispersed in the carbonate-containing alkaline solution according to the set concentration to obtain suspension A;
[0042] The metal cation mixed solution B of the set concentration is added dropwise to the suspension A at a set rate, and the biomass-loaded layered double metal hydroxide is obtained through mineralization and centrifugal separation;
[0043] The biomass-loaded layered bimetallic hydroxide is pyrolyzed anaerobic to obtain an arsenic adsorption material, which is the biochar-supported layered bimetallic oxide.
[0044] It should be noted that the biomass material can be one of orange peel, bagasse, and rice straw; usually, orange peel can be used. Of course, it can also be waste, tailings, etc. of other agricultural biomass, which is convenient for resource reuse.
[0045] In order to facilitate the reaction...
Embodiment 1
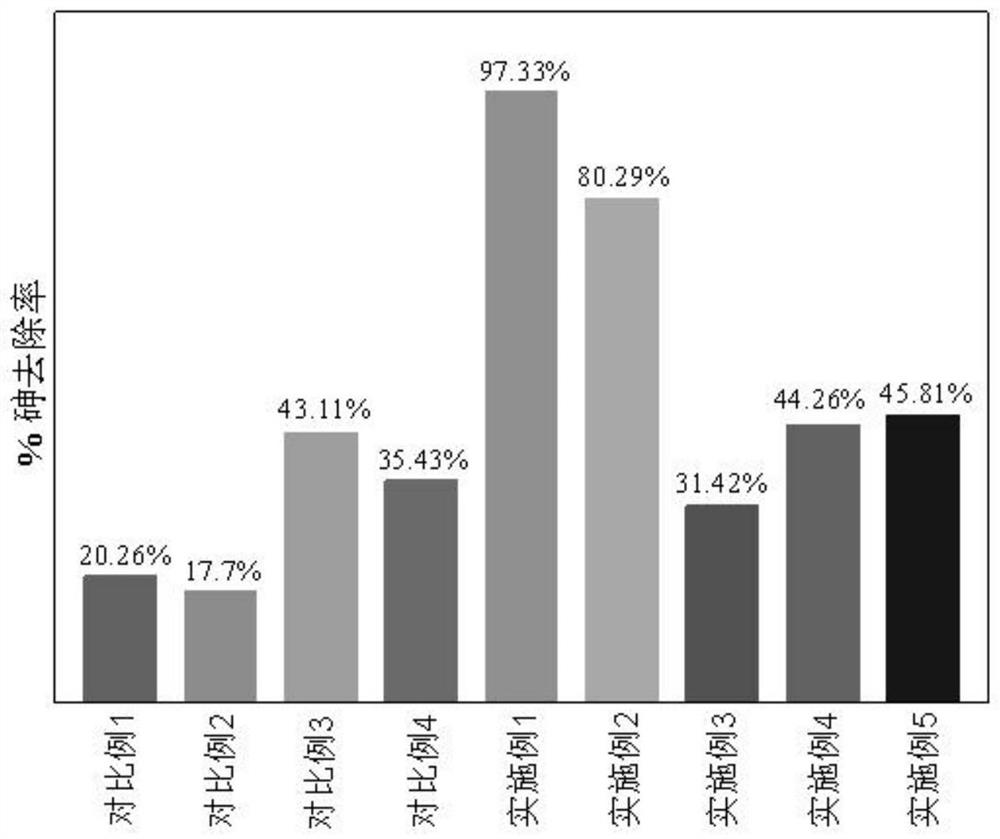
[0061] Prepare 750mL of mixed solution A of 0.9mol / L sodium hydroxide and 0.1mol / L sodium carbonate; weigh 40g of dry orange peel powder, stir and disperse in mixed solution A to obtain suspension A; prepare 750mL of 0.2mol / L Mixed solution B of ferric nitrate and 0.6 mol / L magnesium nitrate; mixed solution B was added dropwise to suspension A at a rate of 5 ml / min through a peristaltic pump; Through centrifugation, drying and grinding, solid component A, that is, biomass-loaded layered double metal hydroxide, was obtained; the solid component A was placed in a tube furnace for high-temperature anaerobic cracking, the cracking temperature was 550 °C, and the temperature was programmed for 10 ℃ / min, the cracking time is 2h, the anaerobic atmosphere is N 2 , to obtain an arsenic adsorption material, that is, biochar-supported layered bimetallic oxides.
Embodiment 2
[0063] Compared with Example 1, the main difference is that the biomass selects bagasse, as follows:
[0064] Prepare 750mL of mixed solution A of 0.9mol / L sodium hydroxide and 0.1mol / L sodium carbonate; weigh 40g of dry bagasse powder, stir and disperse in mixed solution A to obtain suspension A; prepare 750mL of 0.2mol / L Mixed solution B of ferric nitrate and 0.6 mol / L magnesium nitrate; mixed solution B was added dropwise to suspension A at a rate of 5 ml / min through a peristaltic pump; The solid component A was obtained by centrifugation, drying and grinding; the solid component A was placed in a tube furnace for high-temperature anaerobic cracking, the cracking temperature was 550 °C, the temperature was programmed at 10 °C / min, the cracking time was 2 h, and the anaerobic atmosphere was N 2 , to obtain arsenic adsorption materials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com