Method for improving electrothermal performance of electrothermal film by using intercalation bridging method and application
An electric heating film and electric heating technology, applied in applications, electric heating devices, ohmic resistance heating, etc., can solve problems affecting applications, graphene oxide sheet diameter is difficult to control, etc., to simplify production steps, excellent practical performance, and solve filler dispersion The effect of uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
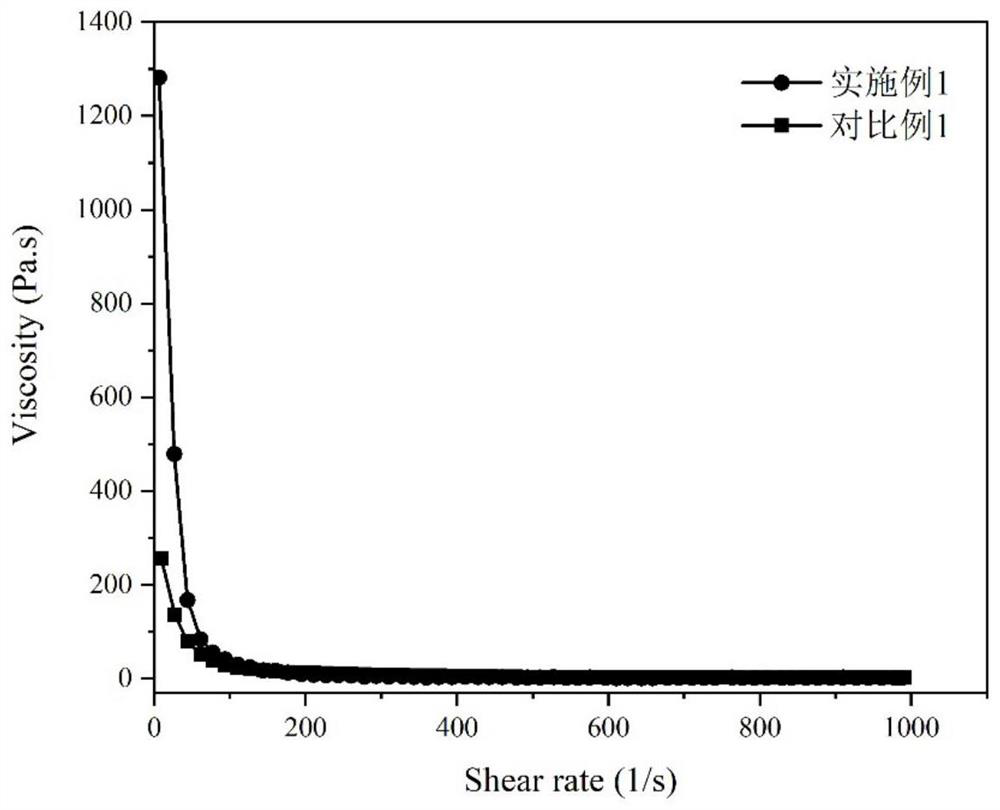
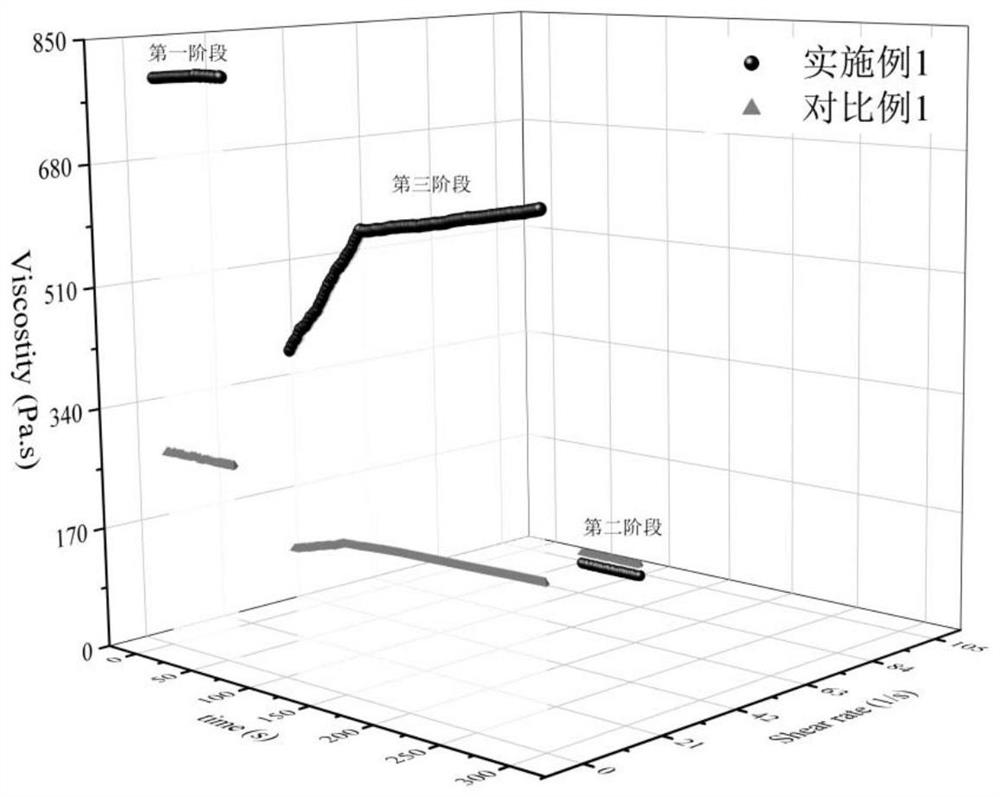
[0036] In terms of parts by mass, 6 parts of graphite nanosheets, 19 parts of 100nm ultrafine carbon powder, 39.5 parts of diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 25 parts of phenolic resin, 5 parts of epoxy resin, 0.5 parts of Silok4010 as a defoamer, Silok355 As a leveling agent 1 part, Silok7045 as a wetting and dispersing agent 2 parts, 2246 as an antioxidant 1 part, DBP as a plasticizer 1 part. The conductive ink was prepared by a ball mill. The ball mill was first pre-mixed at a ball mill speed of 200 rad / min for 10 minutes, and then ground at a speed of 300 rad / min until the fineness dropped below 15 μm. The rheological properties of conductive ink were tested by rotational rheometer, the results are as follows Figure 1a and Figure 1b shown. Print a wet film on a PET film substrate by screen printing, and cure it at 140°C for 30 minutes to form an electric heating film. The volume resistivity, electrothermal performance and adhesion level of the electrothermal film were ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In terms of parts by mass, 10 parts of graphite powder, 30 parts of 100nm superfine carbon powder, 21.5 parts of diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 20 parts of phenolic resin, 10 parts of epoxy resin, 0.5 parts of Silok4010 as defoamer, and 0.5 parts of Silok355 as 1 part of leveling agent, 5 parts of Silok7045 as wetting and dispersing agent, 1 part of 2246 as antioxidant, and 1 part of DBP as plasticizer. The conductive ink was prepared by a ball mill. The ball mill was first pre-mixed at a ball mill speed of 150 rad / min for 20 minutes, and then ground at a speed of 350 rad / min until the fineness dropped below 15 μm. Afterwards, a wet film was printed on the PET film substrate by screen printing, and cured at 140°C for 20 minutes to form an electric heating film. The volume resistivity, electrothermal performance and adhesion level of the electrothermal film were tested, and the results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0040] In terms of parts by mass, 15 parts of graphite nanosheets, 20 parts of 100nm ultrafine carbon powder, 26.5 parts of diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 15 parts of phenolic resin, 15 parts of epoxy resin, 0.5 parts of Silok4010 as a defoamer, Silok355 As a leveling agent 1 part, Silok7045 as a wetting and dispersing agent 5 parts, 2246 as an antioxidant 1 part, DBP as a plasticizer 1 part. The conductive ink was prepared by a ball mill. The ball mill was first pre-mixed at a ball mill speed of 200 rad / min for 20 minutes, and then ground at a speed of 350 rad / min until the fineness dropped below 15 μm. Afterwards, a wet film was printed on the PET film substrate by screen printing, and cured at 140°C for 30 minutes to form an electric heating film. The volume resistivity, electrothermal performance and adhesion level of the electrothermal film were tested, and the results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| rate of change | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com