Bone traction needle force sensing system based on FBG optical fiber
A bone traction needle and sensing system technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as the inability to establish a mapping relationship, the inability to establish a multi-calcaneal needle force measurement and force mapping relationship, and the six-dimensional force sensor can not respond, etc., to achieve a compact structure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
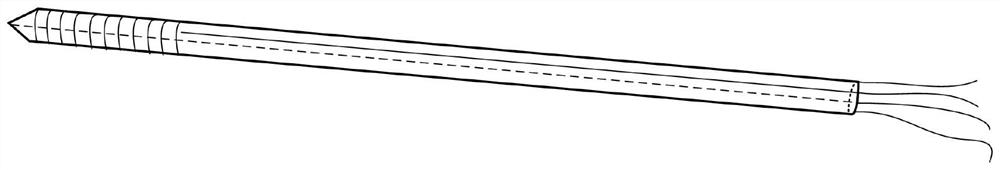
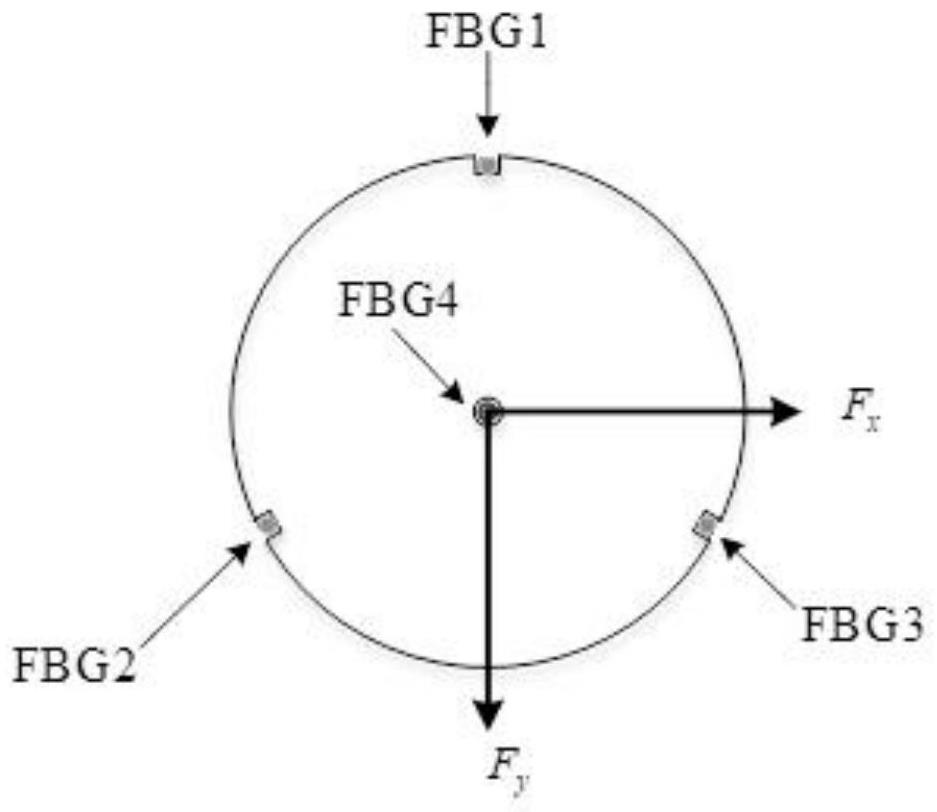
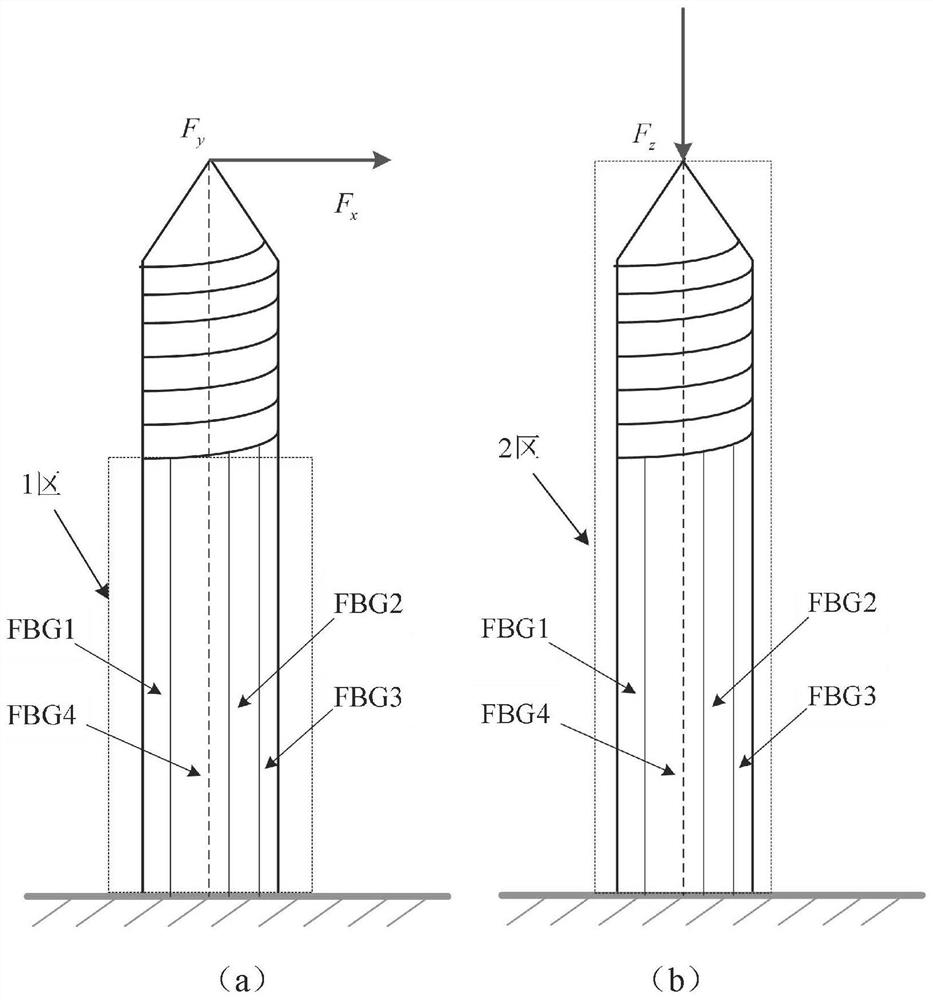
[0039] The bone traction needle force sensing system based on FBG optical fiber designed in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 shown. First of all, the number of optical fibers needs to be determined. In theory, only three optical fibers are needed to sense the three-dimensional force on the bone needle in the surgical environment. However, fiber Bragg gratings are not only affected by strain, but also easily affected by temperature, so the design and layout of FBG The four optical fibers from fiber 1 to FBG fiber 4 sense the three-dimensional force on the bone needle; secondly, it is necessary to determine the layout of the bone needle. The three-dimensional force on the bone needle is divided into axial force and radial force, so the four optical fibers are divided into Arranged in two parts, one optical fiber (FBG optical fiber 4) is arranged on the central axis of the bone needle. This optical fiber coincides with the direction of the axial force. The next three opti...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the two-dimensional force measurement method does not arrange the central FBG optical fiber 4, and the specific method is as follows:
[0078] The strain is linearly related to the moment and thus proportional to the lateral force applied to the tip of the bone pin:
[0079]
[0080] where: ε m is the strain on the FBG optical fiber, M is the bending moment caused by the lateral force, r is the radial distance from the axis of the spicule to the FBG optical fiber on the cross section of the spicule, I is the moment of inertia, F t is the external force applied to the tip of the bone needle, and d is the axial distance from the tip of the bone needle to the FBG fiber.
[0081] The displacement of the Bragg wavelength of the FBG sensor is linearly related to the local strain and the temperature change:
[0082] Δλ=k ε ε+k ΔT ΔT (17);
[0083] Among them, Δλ is the center variation of the Bragg grating, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com