Composition for nucleic acid detection
A composition and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of lower detection sensitivity, extremely high requirements for primer specificity, and high cost, and achieve the effects of improving primer specificity, avoiding false positive signals, and improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
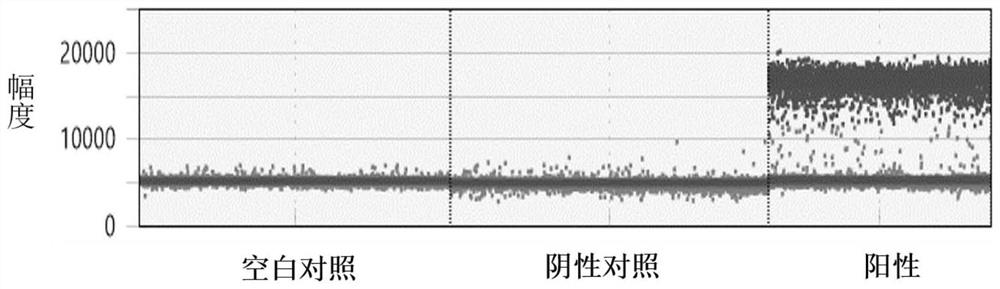
[0078] In this embodiment, a common nucleic acid variation is taken as an example to test the primer probe composition and detection system of the present invention. Specifically, EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation was used as an example to simulate clinical samples to evaluate the performance of the detection system of the present invention.
[0079] 1. Sample preparation:
[0080] Prepare fragmented 293T cell line DNA samples, quantify them with a Qubit fluorescence quantitator, and dilute to 10 ng / μL as negative control samples.
[0081] At the same time, an artificially synthesized plasmid sample containing the EGFR gene exon 20 insertion mutation (COSM12377) sequence was prepared, and after fragmentation, the negative sample was used for dilution and mixing as a positive sample.
[0082] Use Tirs-EDTA buffer without any DNA as blank control sample.
[0083] 2. Preparation of reaction system
[0084] 2.1 Primer probe composition
[0085] The primers and probes of the pres...
Embodiment 2
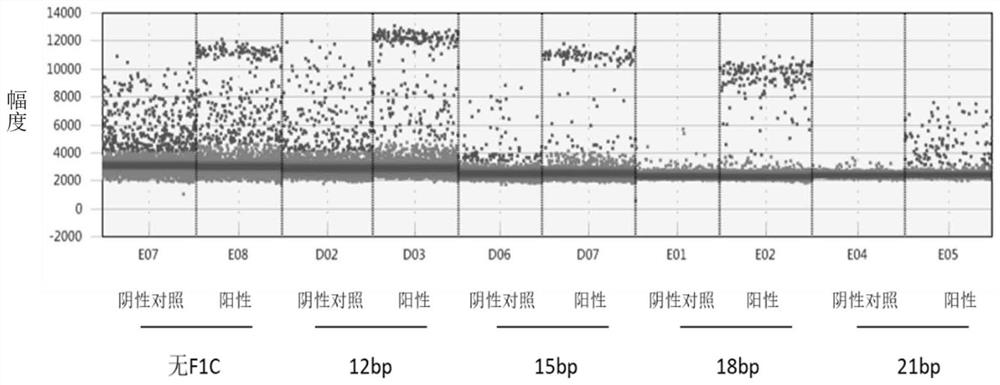
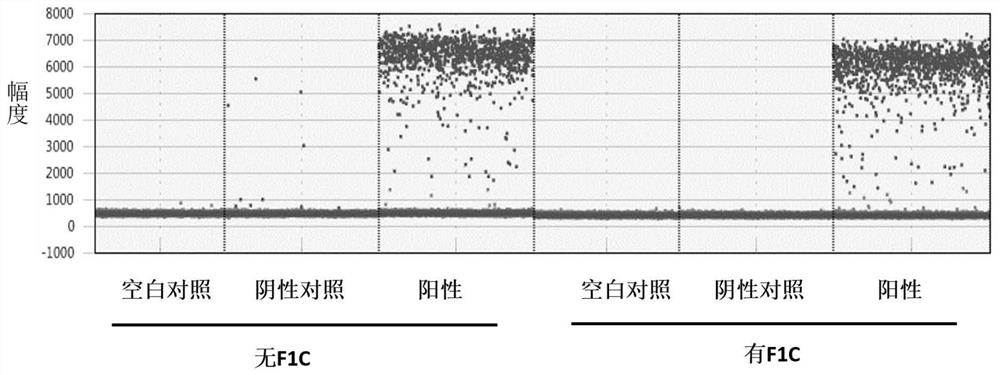
[0104] In order to reflect the effects of the present invention, this embodiment uses oligonucleotides F1C of different lengths to evaluate the impact on detection specificity.
[0105] 1. Sample preparation:
[0106] Prepare fragmented 293T cell line DNA samples, quantify them with a Qubit fluorescence quantitator, and dilute to 10 ng / μL as negative control samples.
[0107] At the same time, an artificially synthesized plasmid sample containing another mutant type sequence (COSM12378) of exon 20 insertion mutation of the EGFR gene was prepared. After fragmentation, the negative sample was used for dilution and mixing as a positive sample.
[0108] 2. Preparation of reaction system
[0109] 2.1 Primer probe composition
[0110] The specific sequence of the primer probe composition is shown in Table 3 below.
[0111] table 3:
[0112]
[0113] Among the above primer probes, the oligonucleotide F1C-2-12 is 12bp in length, and can be complementary to the 12bp at the 3' en...
Embodiment 3
[0130] In order to further verify the effects of the primers and methods of the present invention, another gene variation (EGFR gene T790M mutation) was detected in this embodiment.
[0131] 1. Sample preparation:
[0132] Prepare fragmented 293T cell line DNA samples, quantify them with a Qubit fluorescence quantitator, and dilute to 10 ng / μL as negative control samples.
[0133] At the same time, an artificially synthesized plasmid sample containing the T790M mutation (COSM6240) sequence of exon 20 of the EGFR gene was prepared. After fragmentation, the negative sample was used for dilution and mixing as a positive sample.
[0134] Use Tirs-EDTA buffer without any DNA as blank control sample.
[0135] 2. Preparation of reaction system
[0136] 2.1 Primer probe composition
[0137] The specific sequence of the primer probe composition is shown in Table 5 below.
[0138] table 5:
[0139]
[0140]
[0141] Primers and probes were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com