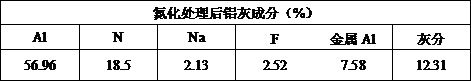
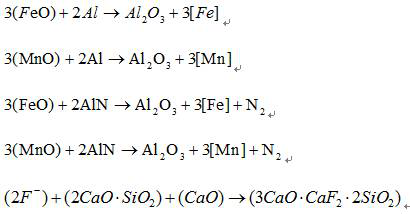Method for preparing micro-nitrogen deoxidized alloy by using aluminum ash
A technology of micro-nitrogen deoxidation alloy and aluminum ash, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of high cost of nitrogen increase and deoxidation, long environmental impact cycle, high cost of aluminum ash treatment, etc., and achieve resource utilization, good economic and social benefits , the effect of reducing the difficulty of refining
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for producing micro-nitrogen deoxidation alloys by using aluminum ash, fully mixing aluminum nitride ash and calcium oxide according to the ratio of 4:1, pressing balls and bagging, converting the steel type HRB400, the end point temperature is 1650°C, and tapping the converter Start to add at 1 / 3, the nitrogen content at the end point of the molten steel is 75ppm, the oxygen content is 540ppm, the dosage is added at 3kg / t, and the addition is completed when the steel is tapped to 2 / 3. The micro-nitrogen deoxidized alloy balls melt rapidly under the stirring of the steel flow, and the aluminum nitride in the aluminum ash decomposes rapidly, and the decomposed nitrogen [可溶] Increase the nitrogen content and decrease the oxygen content in molten steel. By the time of refining, the nitrogen content of liquid steel entering the station increased to 93ppm, and the oxygen content decreased to 50ppm, and the yields of ferrosilicon and silicon-manganese alloys increase...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for producing micro-nitrogen deoxidized alloys by using aluminum ash. The aluminum nitride ash and calcium oxide are fully mixed according to the ratio of 4:1, and the ball is packed into bags. The steel type HRB500 is smelted in a converter, and the end point temperature is 1670 ° C. The converter is tapped Adding starts at 1 / 3, the nitrogen content at the end point of molten steel is 70ppm, and the oxygen content is 580ppm. The micro-nitrogen deoxidized alloy balls melt rapidly under the stirring of the steel flow, and the aluminum nitride in the aluminum ash decomposes rapidly, and the decomposed nitrogen [可溶] Increase the nitrogen content and decrease the oxygen content in molten steel. By the time of refining, the nitrogen content of incoming steel liquid increased to 103ppm, and the oxygen content dropped to 55ppm. The yields of ferrosilicon and silicon-manganese alloys increased by 0.55% and 0.93% respectively. Under the condition of adding the same amou...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A method for producing micro-nitrogen deoxidation alloys by using aluminum ash. The aluminum nitride ash and calcium oxide are fully mixed according to the ratio of 4:1, and the ball is packed into bags. The steel type HRB400 is smelted in a converter, and the end point temperature is 1690 ° C. The converter is tapped. Start to add at 1 / 3, the nitrogen content at the end point of the molten steel is 60ppm, the oxygen content is 650ppm, the dosage is added at 8kg / t, and the addition is completed when the steel is tapped to 2 / 3. The micro-nitrogen deoxidized alloy balls melt rapidly under the stirring of the steel flow, and the aluminum nitride in the aluminum ash decomposes rapidly, and the decomposed nitrogen [可溶] Increase the nitrogen content and decrease the oxygen content in molten steel. By the time of refining, the nitrogen content of liquid steel entering the station increased to 115ppm, and the oxygen content decreased to 48ppm. The yields of ferrosilicon and sil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com