Circulating tumor DNA fusion detection method based on next-generation sequencing technology
A second-generation sequencing technology and sequencing technology, which is applied in the direction of DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of high resource requirements, low accuracy of result breakpoint coordinates, and slow detection speed, etc., to achieve increased Library conversion, good detection effect, fast running effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
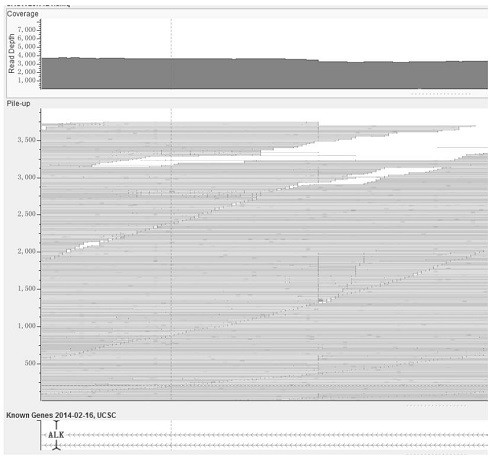
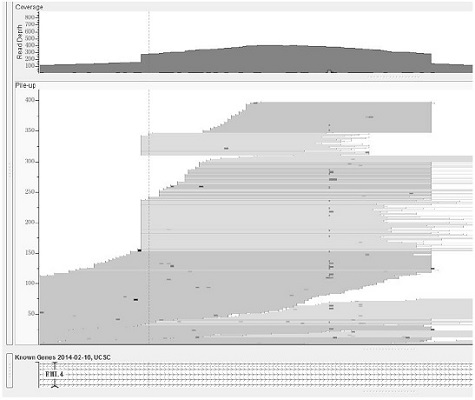
[0083] This example provides a method for detecting fusion genes based on next-generation sequencing technology. Taking a real sample data as an example, this sample carries the classic EML4-ALK fusion, which is detected by IGV at ALK and EML4. Dot plots are as figure 1 , figure 2 shown. The specific detection method is as follows:
[0084] 1. The sample was captured and sequenced, and the sequencing strategy was PE100;
[0085] 2. Perform data preprocessing, comparison, de-duplication, and extraction of unique alignment sequences on the original off-machine data to form the final BAM file, and use Samtools to build the index of the BAM file;
[0086] 3. Extract the soft truncated parts of the sequencing reads that may carry gene fusion signals: extract the soft truncated parts of the reads whose cigar tags are "MS" or "SM" in the sequencing sequence in the BAM file according to the format rules;
[0087] 4. Split the reads into different read groups according to the coor...
Embodiment 2
[0105] This embodiment provides a method for detecting fusion genes based on next-generation sequencing technology, which is used to detect clinical peripheral blood plasma samples.
[0106] Specifically, the extraction method is as follows: 1) Pre-dissolve proteinase K in the protease dissolving buffer at a ratio of 1 mg / 550 μL to form a proteinase K solution, and add 20 μL proteinase K solution and 20 μL magnetic bead suspension to the centrifuge tube; 2 ) Transfer 300 μL of serum or plasma sample to a centrifuge tube; 3) Add 450 μL of Lysis Conjugate Solution to the centrifuge tube, vortex and mix for 30 seconds, then add 2 μL of nucleic acid sedimentation aid, and mix for 15 minutes at room temperature; 4) Transfer Put it on the magnetic stand, let it stand for 3 minutes to absorb the magnetic beads, and discard the solution; 5) Add 500 μL of the first washing solution, vortex and mix for 30 seconds; 6) Transfer to the magnetic stand, let it stand for 3 minutes to absorb th...
Embodiment 3
[0116] This embodiment provides a method for detecting fusion genes based on next-generation sequencing technology to detect mutations in low-frequency samples.
[0117] Specifically, the extraction method is as follows: 1) Pre-dissolve proteinase K in the protease dissolving buffer at a ratio of 1 mg / 550 μL to form a proteinase K solution, and add 20 μL proteinase K solution and 20 μL magnetic bead suspension to the centrifuge tube; 2 ) Transfer 300 μL of serum or plasma sample to a centrifuge tube; 3) Add 450 μL of Lysis Conjugate Solution to the centrifuge tube, vortex and mix for 30 seconds, then add 2 μL of nucleic acid sedimentation aid, and mix for 15 minutes at room temperature; 4) Transfer Put it on the magnetic stand, let it stand for 3 minutes to absorb the magnetic beads, and discard the solution; 5) Add 500 μL of the first washing solution, vortex and mix for 30 seconds; 6) Transfer to the magnetic stand, let it stand for 3 minutes to absorb the magnetic beads, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com