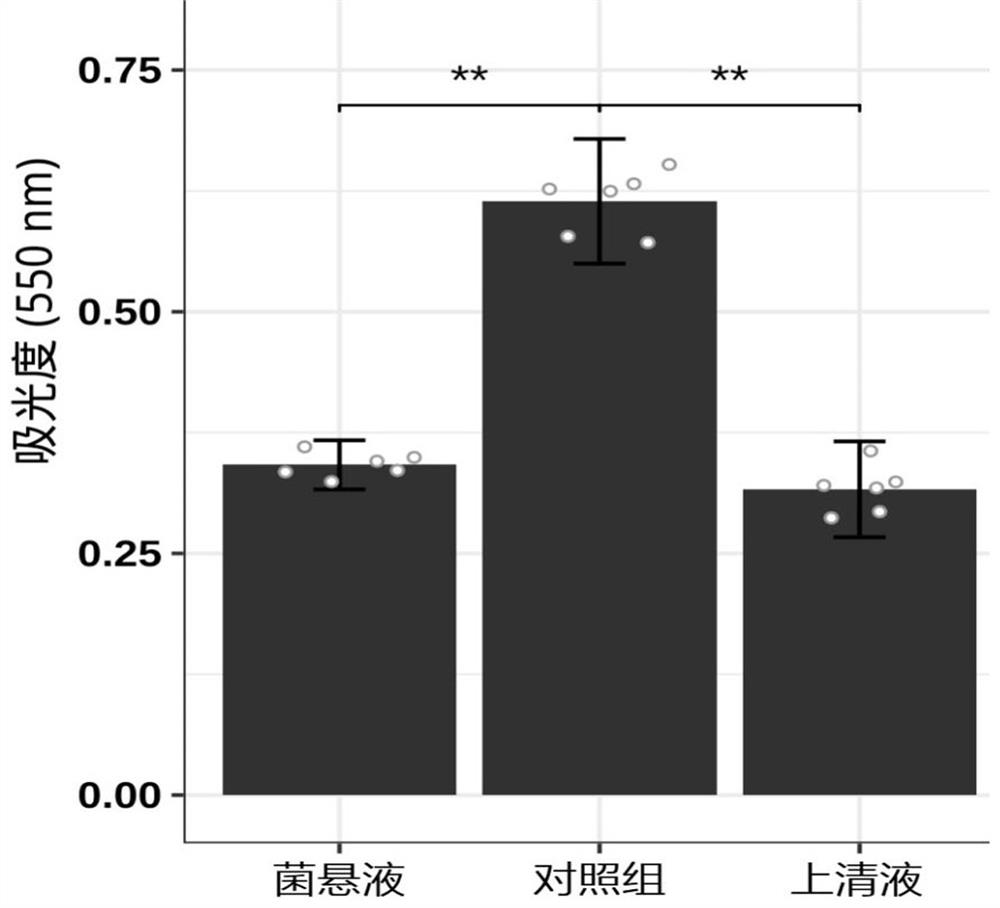
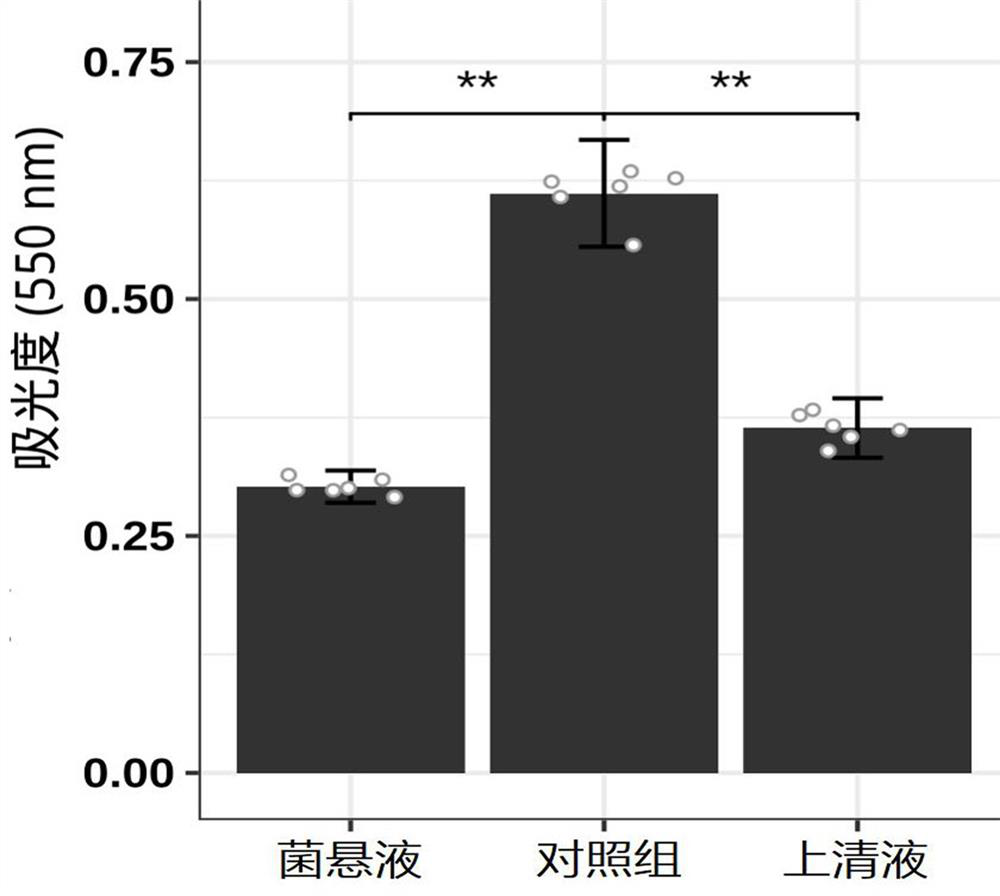
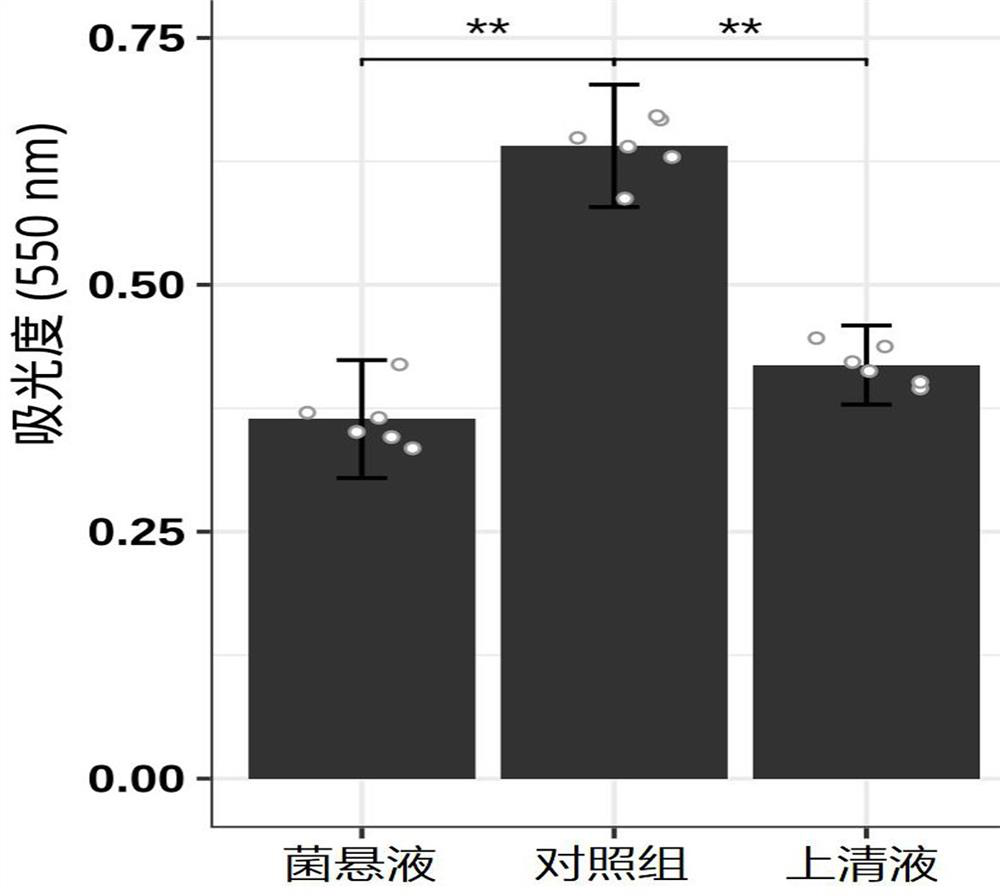
A kind of Lactobacillus plantarum against Helicobacter pylori infection and its application
A technology against Helicobacter pylori and Lactobacillus plantarum, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of long course of disease, high recurrence rate, difficult to cure completely, achieve good gastric acid resistance, inhibit the growth of Helicobacter pylori, and improve the growth of Helicobacter pylori Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] The present embodiment screens the bacterial strain that resists Helicobacter pylori infection from fermented kimchi, and the steps are as follows:
[0047] Select fermented kimchi samples, use 0.9% normal saline for 10-fold serial dilution, dilute 3 times, spread on MRS solid medium, and culture at 37°C for 48 h, pick typical bacteria and culture them on MRS solid medium The base surface was streaked and purified, and a single colony was picked and expanded in MRS liquid medium at 37°C, and then preserved in glycerol with a mass concentration of 30%.
[0048] The isolated single colony is screened according to its ability to inhibit the growth of Helicobacter pylori, the steps are as follows:
[0049] (1) Helicobacter pylori was taken out from -80°C, spread on Columbia blood agar medium containing 5% sheep blood (v / v) for activation culture, and cultured at 37°C for 48 h in a microaerobic environment;
[0050] (2) Inoculate the strain in MRS liquid medium, activate it...
Embodiment 2
[0055] In this embodiment, the morphological identification and 16S rRNA molecular biological identification of the strains screened in Example 1 are carried out, and the steps are as follows:
[0056] (1) Morphological identification:
[0057] The strains were inoculated in MRS solid medium, cultured at 37°C for 48 h, and observed under a microscope.
[0058] Observation shows that the colonies are milky white, semicircular and raised, with smooth and moist surfaces and neat edges.
[0059] (2) 16S rRNA molecular biology identification:
[0060]The strains stored at -80°C were taken out, inoculated in MRS liquid medium, and cultured at 37°C for 18 h. Pipette 1 mL of the bacterial liquid into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 min, remove the supernatant, and collect the bacterial cells.
[0061] The genome of the strain was extracted, and bacterial universal primers were added for PCR amplification, and the amplified products were sent to Shanghai Sangon Bioe...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The sequence obtained by sequencing was compared with the nucleic acid sequence in GeneBank, and the result showed that the strain was Lactobacillus plantarum.
[0067] Based on the results of 16S rRNA molecular biology identification and morphological identification of Example 2, it was confirmed that the bacterial strain belonged to Lactobacillus plantarum and was named as Lactobacillus plantarum Lactobacillus plantarum Lp05. The Lactobacillus plantarum was deposited on October 9, 2021 in the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for the Collection of Microbial Cultures. The address is No. 3, No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, postcode 100101, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. . 23547.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com