Method for large-scale production of CMP-sialic acid through coupled fermentation of genetically engineered bacteria and yeast
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and genetically engineered strains, applied in the field of fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of high CTP production cost, reduced production cost, high price and the like, and achieves the effects of low price, broad market prospect and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1: Construction of engineering bacteria expressing CMP-sialidase gene heterologously
[0048] 1. Acquisition of CMP-sialidase gene (neuA)
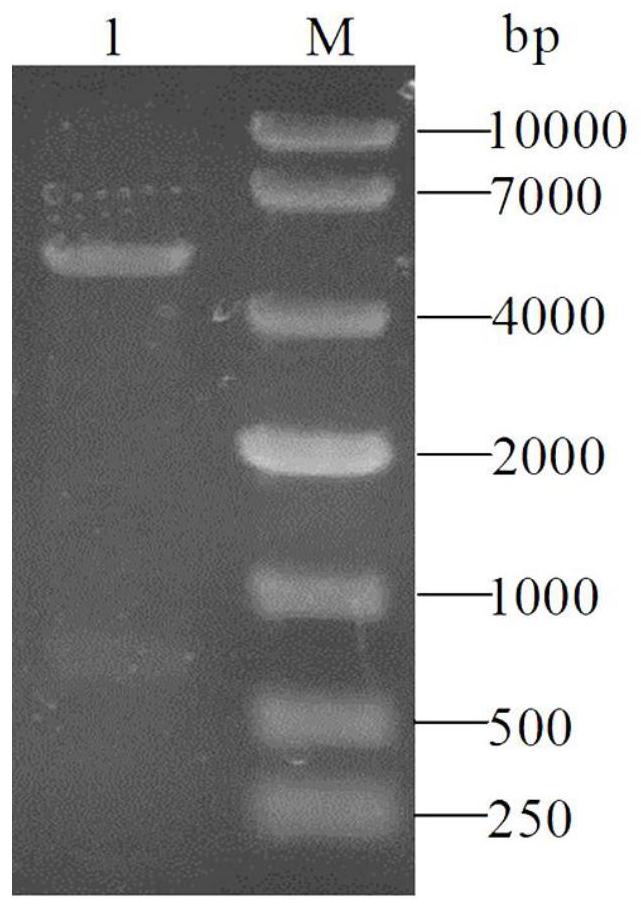
[0049] 分别以来源于Neisseria meningitidis M0579、Neisseria meningitidisstrain M22819、Pasteurella multocida ATCC43137、Haemophillus ducreyi 35000HP的neuA基因序列为模板(GenBank号分别为CP007668.1(1012519…1013205)、CP016646.1(1413007…1414122)、CP008918. 1 (1975338…1976009), AE017143.1 (540594…541283)), and primers were designed according to the nucleotide sequence (respectively, the enzyme cutting sites are Nde I and Sal I). The corresponding forward and reverse primers were used to amplify the neuA gene, and the resulting amplified products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. The size of the amplified product was about 0.7kb (neuA), and its size was completely consistent with the size of the target gene. .
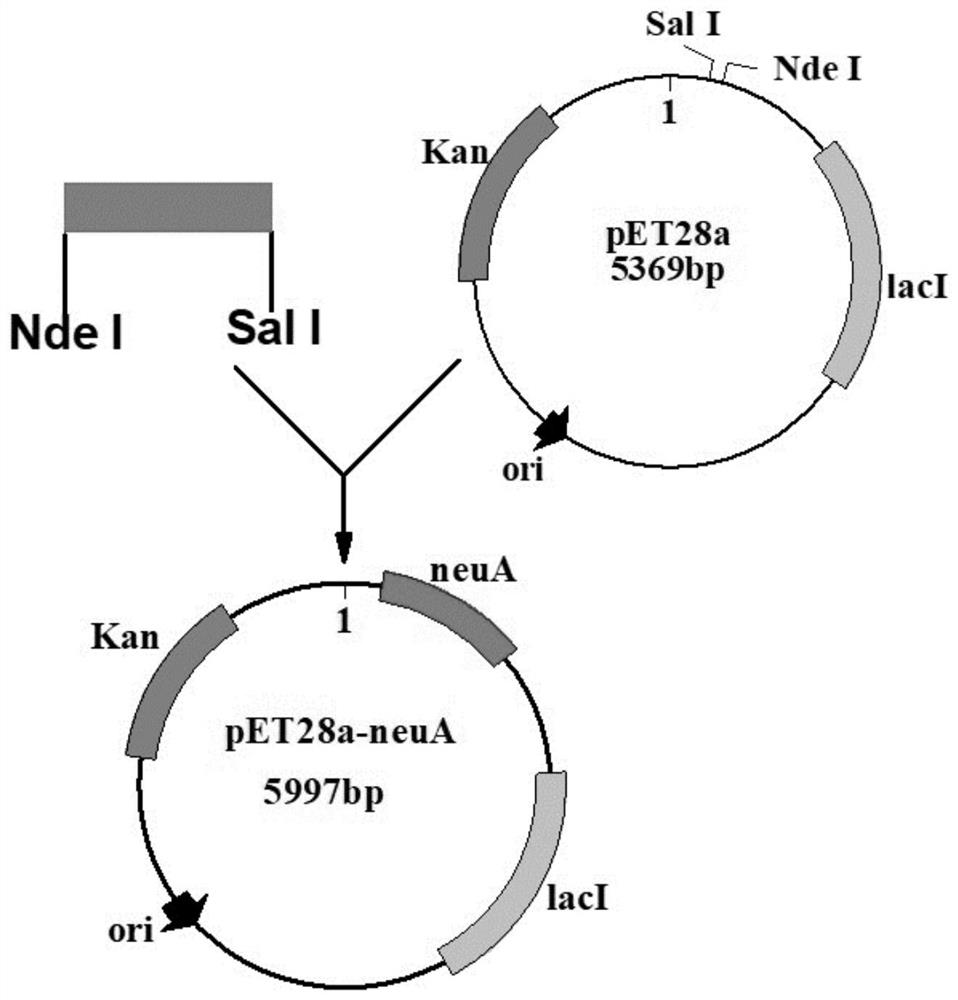
[0050] 2. Construction of recombinant protein expression plasmids
[0051] After the PCR products obtained in step 1 were purif...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: Transformation and synthesis of CMP-Neu5Ac by single-gene engineering bacteria
[0061] Transformation conditions: 20mM MgCl 2 , 1mM DTT, 150mM Tris, 60mM CTP, 60mM Neu5Ac and 50g / L JM109(DE3) / pET28a-neuA cells (wet weight), react at 30°C and 200r / min for 2h.
[0062] (1) Optimization of IPTG induction concentration
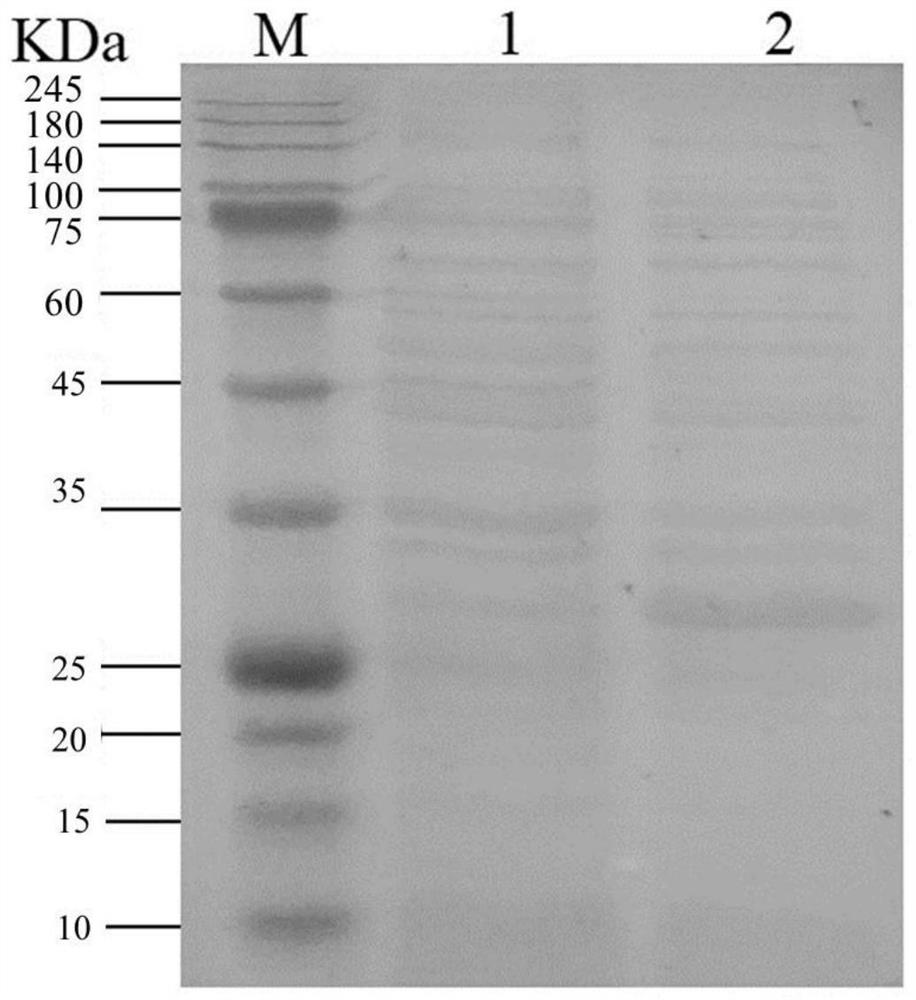
[0063] JM109(DE3) / pET28a-nst were respectively inoculated into 10 mL LB liquid medium containing 20 μg / mL Kan, cultured in shake flasks at 37 °C and 200 r / min for 12 h, and then transferred at an inoculum volume of 2% (v / v). Into 100mL LB liquid medium containing 20μg / mL Kan, shake the flask at 37°C and 200r / min and culture until OD600 After about 0.6, add IPTG with final concentrations of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0 and 1.5mmol / L to induce, respectively. The induction temperature is 16°C, and the bacteria are collected after 200r / min induction for 20h. The obtained bacterial cells catalyzed the reaction in the above transformation solution, an...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Synthesis of CMP-Neu5Ac through coupled fermentation of brewer's yeast and engineering strains
[0069] 1. Large-scale acquisition of genetically engineered bacterial cells
[0070] There are two sources of engineering bacteria cells: (1) high-density fermentation medium contains lactose, and the expression of lactose-induced enzymes; (2) IPTG induction.
[0071] Method 1, high-density fermentation: first pick a single colony of engineering bacteria and inoculate it in 50ml LB liquid medium with 20μg / ml Kan, at 37°C, 200r / min, and culture overnight (12h) to the logarithmic phase of growth. Then inoculate 500ml high-density fermentation medium containing 25μg / ml Kan according to 5% (5mL / 100mL) inoculum amount, culture in shake flask at 37°C and 200r / min for 2h. Then culture at 20°C and 200r / min for 20h. Centrifuge at 6000rmp to collect the cells, wash the cell sludge once with 0.5% normal saline, and then collect by centrifugation, the cells are used for fur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com