Construction method and application of yarrowia lipolytica with reduced fermentation foam production capacity
A technology of Yarrowia lipolytica and Yarrowia lipolytica, which is applied in the field of food additive biosynthesis, can solve the problems of reduced foam-producing ability and large amount of foam, and achieves the effects of easy separation, cost reduction, and improvement of effective utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
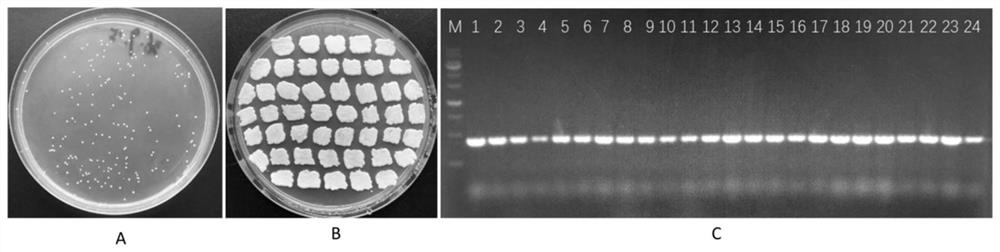
[0038] Example 1. The method of site-directed insertion of exogenous DNA into Yarrowia lipolytica genome to obtain mutants
[0039] In this example, a section of artificial DNA sequence was constructed. The DNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1. It was synthesized by the method of whole gene synthesis and directly used to transform the competent Yarrowia lipolytica. The transformation method used lithium acetate heat shock For the method, please refer to the method described by Cheng et al. (Cheng et al., 2018, Microb. Cell Fact., 17:133), and convert the in vitro synthesized DNA sequence SEQ ID No.2 into lipolytic synthesis of erythritol Yarrowia CGMCC NO.7326. 5 micrograms of this in vitro synthesized DNA sequence are contained in 100 microliters of transformation reaction solution. After transformation, spread on the nutrient plate containing screening (medium composition: glucose 20g / L, yeast powder 2g / L, peptone 2g / L, yeast nitrogen base 5g / L, ammonium sulfate 5g / L, hygro...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, mutant strain primary screening method
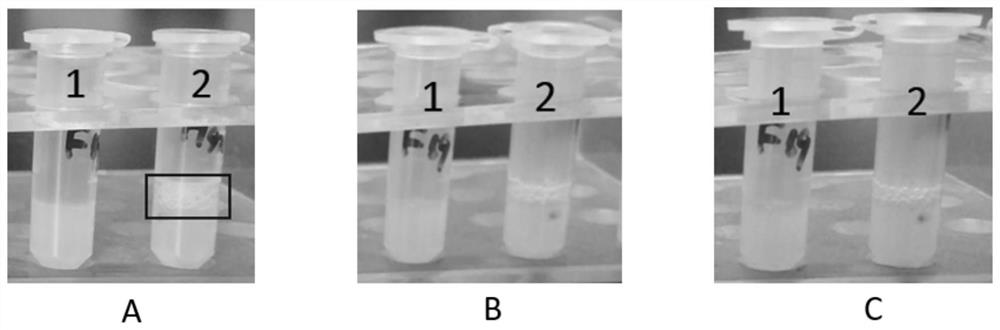
[0041] Select the single colony grown on the screening plate and transfer it to a 2mL centrifuge tube containing 0.5ml liquid medium (200g / L glucose, 10g / L yeast powder, 3.5g / L ammonium citrate, 3g / L Peptone, initial pH 6.0), placed on a tube rack at 30°C, 800r / min shaking and shaking culture (MBR-420FL, Japan TAITEC company). The foam production performance of the mutant transformants was initially screened. The test results showed that the selected mutant transformants did not produce bubbles, while the comparison strain (Yarrowialipolytica CGMCC NO.7326, patent application number 201310282059.X) produced bubbles, and the bubbles were 2-3 mm above the liquid surface. figure 2 Show the bubble production performance of selected mutant strains and control strains in 2 ml centrifuge tubes. It can be seen from the figure that the selected mutant strain No. 1 has basically no foam production. After leaving standstil...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3, the shaking flask foaming test of mutant strain
[0044] The non-foaming mutants obtained through preliminary screening were inoculated into 250 mL shake flasks containing 30 mL liquid medium and 2000 mL shake flasks containing 150 mL liquid medium, and the composition of the medium was the same as that described in Example 2. At the same time, the unmutated wild strain was used for comparative experiments. Cultivate in a shaker at 30°C (230r / min) for 2-3 days, and observe the foam production. The foam production performance of the mutant strain and the control strain were compared in 250mL and 2000mL shake flasks respectively. The result is as image 3 shown.
[0045] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that No. 1 mutant strain did not produce foam after 40 h of cultivation in the 250 mL shake flask, while the control strain produced more foam. In a 2000mL shake flask, the No. 1 mutant strain produced only a small amount of foam when cultured in a reci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com