Regulatory gene for improving utilization rate and tolerance of capric acid in streptomyces roseosporus and application of regulatory gene
A technology of Streptomyces roseospora and gene regulation, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unreported CRP gene tolerance, different effects, etc., and achieve the effects of improving tolerance, improving utilization rate and having broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
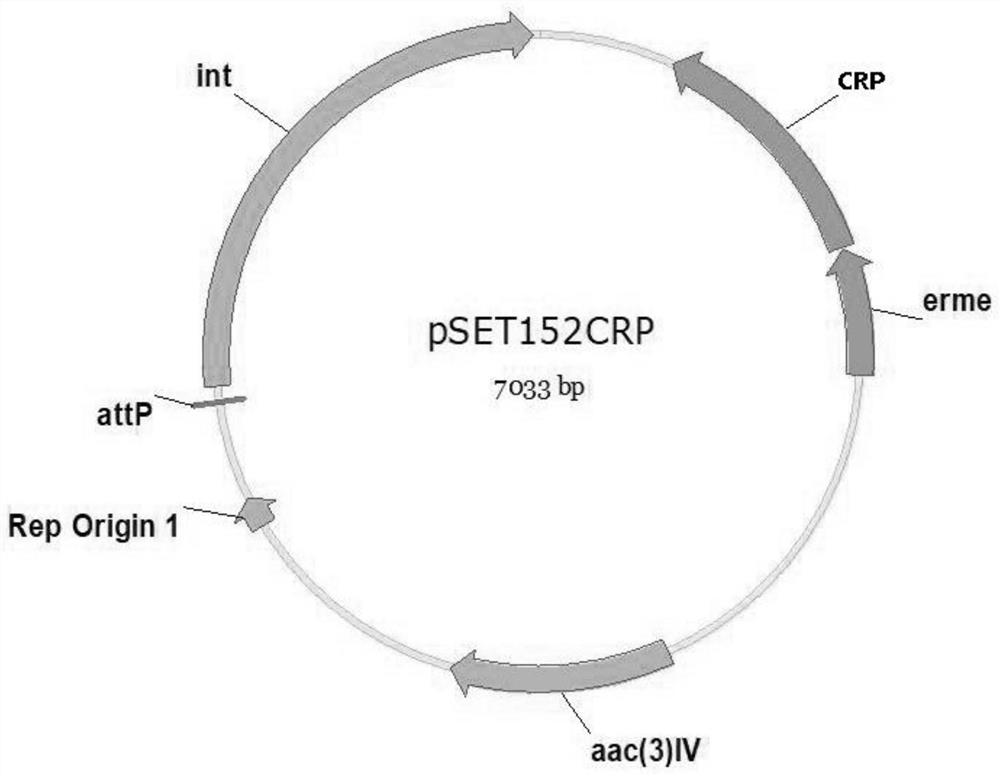
[0040] Embodiment 1: Construction of the pSET152CRP comprising the recombinant plasmid of CRP gene:
[0041] Blast the nucleotide sequence of the homologous gene CRP reported in Streptomyces coelicolor with the genome sequence of Streptomyces roseospora from NCBI (website: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), and obtain the The target gene CRP, its size is 672bp.
[0042] Primers were designed with primer 5.0 as follows:
[0043] CRPS: ATTTCTAGAAATACCTGACCGAGCACG;
[0044] CRPA: ATTGGATCCATCGCACTGTTTTACCGT.
[0045] The total DNA of Streptomyces roseospora was extracted, and the CRP gene was amplified to obtain the target gene fragment.
[0046] Use the SanPerp Column Plasmid DNA Mini-Extraction Kit to extract the pSET152 plasmid according to the kit instructions. The resulting plasmid DNA solution was stored at -20°C or used for subsequent experiments.
[0047] The pSET152 plasmid was treated with restriction endonucleases, DNA agarose gel electrophoresis was performed after digestion, ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Transfer of Recombinant Plasmids to Streptomyces roseospora by Intragenus Conjugation
[0053] Escherichia coli ET12567 containing the recombinant plasmid PSET152 CRP was conjugatively transferred to Streptomyces roseospora NO.CGMCC4.7231, and the zygote containing the PSET152 CRP plasmid was obtained by screening with apramycin and nalidixic acid. The vector of pSET152 empty plasmid was used as a control.
[0054] Method for indirect conjugative transfer of Escherichia coli and Streptomyces roseospora NO.CGMCC4.7231:
[0055] Inoculate ET12567 (PUZ8002 / PSET152) and ET12567 (PUZ8002 / PSET152CRP) into LB (containing kanamycin / chloramphenicol / ampicillin) medium and culture overnight at 37°C in a shaker at 220rpm. Transfer ET12567 (PUZ8002 / PSET152) and ET12567 (PUZ8002 / PSET152CRP) to fresh LB medium (containing kanamycin / chloramphenicol / ampicillin) at a ratio of 1:100, shake at 220 rpm at 37°C Cultivate in bed until OD600 reaches 0.3-0.4. Resuspend the cells t...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Recombinant bacteria fermentation process
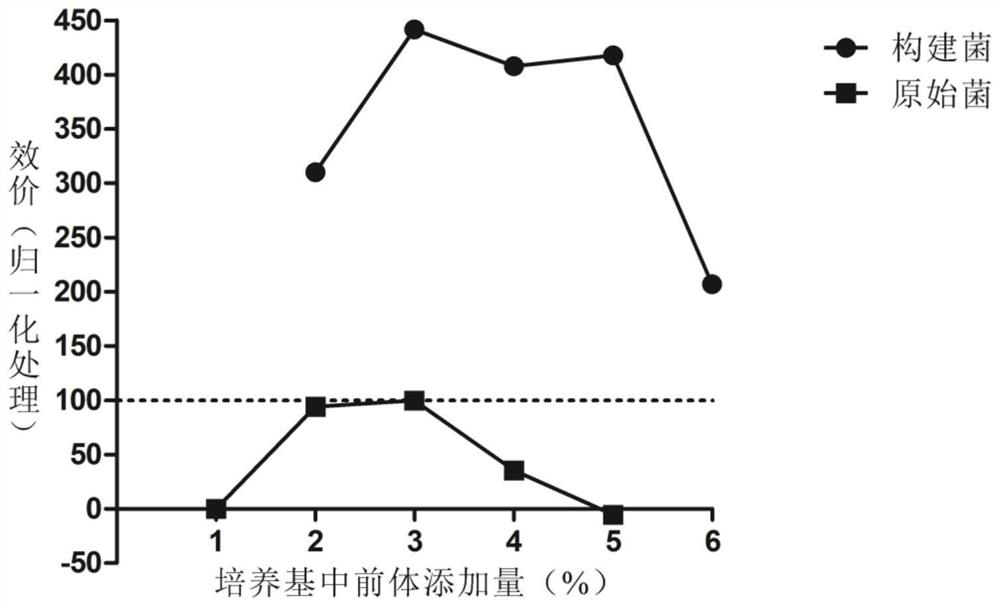
[0061] After the constructed Streptomyces roseospora strain was cultured in R5 slant medium at 30°C for 5 days, it was transferred to a shaker flask containing 50ml of YEME liquid medium, and cultured at 30°C for 25 hours with shaking (220rpm / min). Feed capric acid as the fermentation precursor, cultivate until the end of fermentation, measure the fermentation unit by HPLC, and select high-yield strains. attached by the manual figure 1 Compared with the existing Streptomyces roseospore (starting bacteria), the high antibiotic yield Streptomyces roseospore produced in the present invention has a higher fermentation yield, that is, a better daptomycin yield, and the fermentation Yield increased by more than 200%.
[0062] TSB liquid medium formula:
[0063] Tryptone 17g, soybean peptone 3g, D-glucose 2.5g, sodium chloride 5g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.5g, add deionized water to 1000ml, sterilize at 121°C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com