PD-L1 nucleic acid aptamer as well as screening method and application thereof
A technology of PD-L1 and nucleic acid aptamer, which is applied in the application field of nucleic acid aptamer and tumor immunosuppression, and can solve the problems of application limitation, toxic and side effects, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
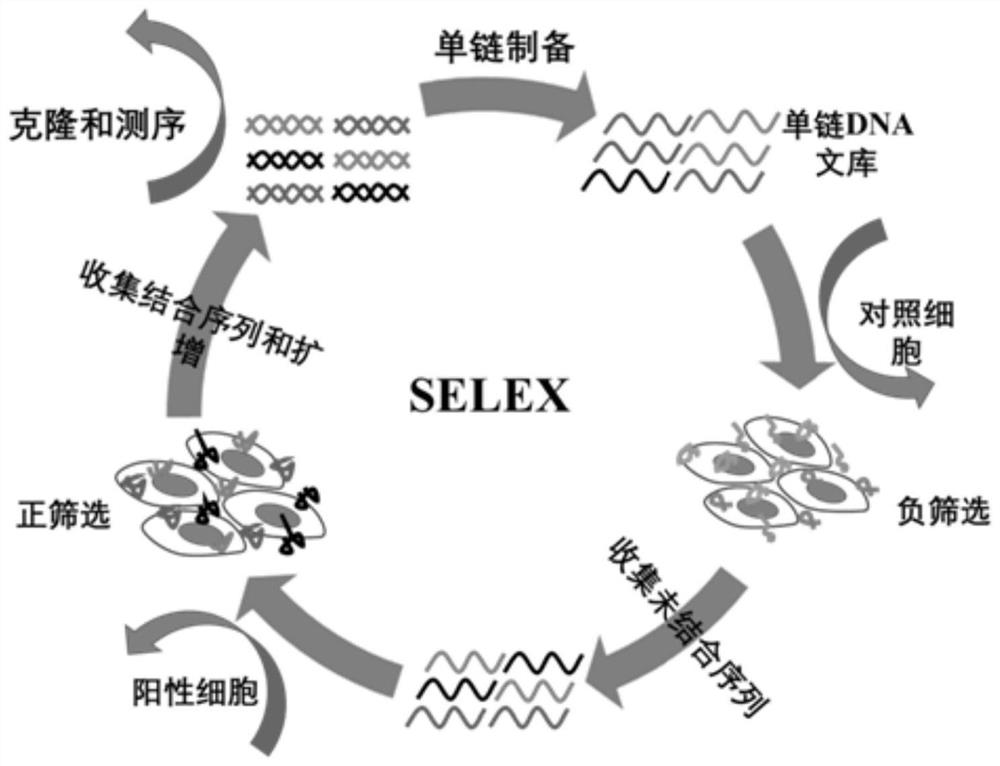
[0082] In this example, the Cell-SELEX technology was used to screen the engineered PD-L1 cell line for DNA nucleic acid aptamers. The specific methods are as follows:
[0083] 1) Using PCR technology, carry out gene amplification on the plasmid containing the PD-L1 gene fragment, after purification, digest the amplified fragment, and digest the pLVX-IRES-Pruo vector at the same time, and digest the The fragments were subjected to gel electrophoresis, and after confirming that the digested fragments were correct, the target sequence was ligated with the digested vector, and then sequenced to verify whether the PD-L1 gene fragment was connected to the specific restriction site of the vector.
[0084] 2) The vector containing the target fragment obtained in step 1) and the three-plasmid system of pSPAX2 and Pmd2.G are transfected into CHO-K1 cells. The specific method includes: mix the three-plasmid system and OPTI-MEM medium; then mix 5 μL Lipo 2000 and 150 μL OPTI-MEM and let ...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Cells with stable and high expression of PD-L1 were used as target cells for positive screening, and CHO-K1 cells without transfection treatment were used as control cells for negative screening. The screening library m-Lib (10 nmol) was dispersed in the screening buffer, then denatured in a water bath at 95° C. for 5 min, and then immediately placed for 10 min for use. After washing the PD-L1 cells cultured at 100×20mm with a confluence of about 90% with washing buffer, they were incubated with the screening library at 4°C for 60 min, and then washed with washing buffer to remove the cells that are not compatible with the target cells. Binding nucleic acid sequence. After the cells were scraped off with a cell scraper, they were denatured in a water bath at 95°C for 10 minutes and then centrifuged, and the obtained sequences were collected and used as the screening library in this round. Then, PCR amplification was performed on the obtained screening library, and a si...
Embodiment 3
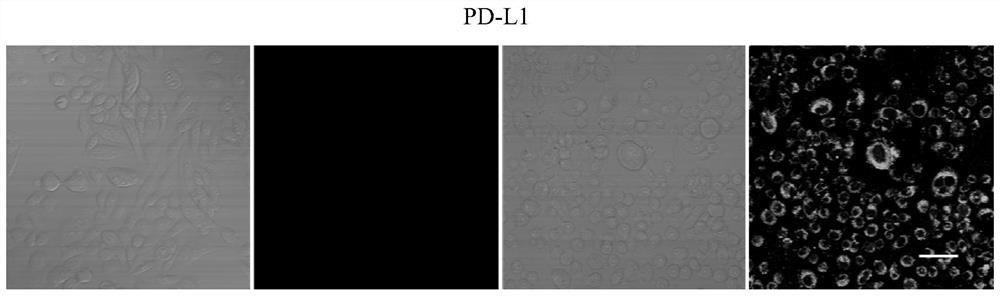
[0089] Using PD-L1 cells as target cells and CHO-K1 cells as negative control cells, confocal microscopy imaging technology was used to verify the enrichment effect of the screening library. PD-L1 and CHO-K1 cells that were cultured for 48 hours and grew well Use trypsin to digest, add fresh culture medium to pipette the cells evenly and count the cells, adjust the density of the cell suspension to 10 5 / mL. Then 0.5 mL of the above cell suspension was inoculated into a confocal imaging dish, and after culturing for 48 hours, the cells were washed 2-3 times with PBS to remove dead cells. For the selected control cells and positive cells, the fluorescently modified m-Lib and the screening library were processed respectively, incubated at 4°C for 50 min, then washed with 500 μl washing buffer, fixed with paraformaldehyde for 15 min, and then confocal imaging . Figure 2a It is the confocal imaging image of the twelfth-round enrichment library screened in this example and the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com