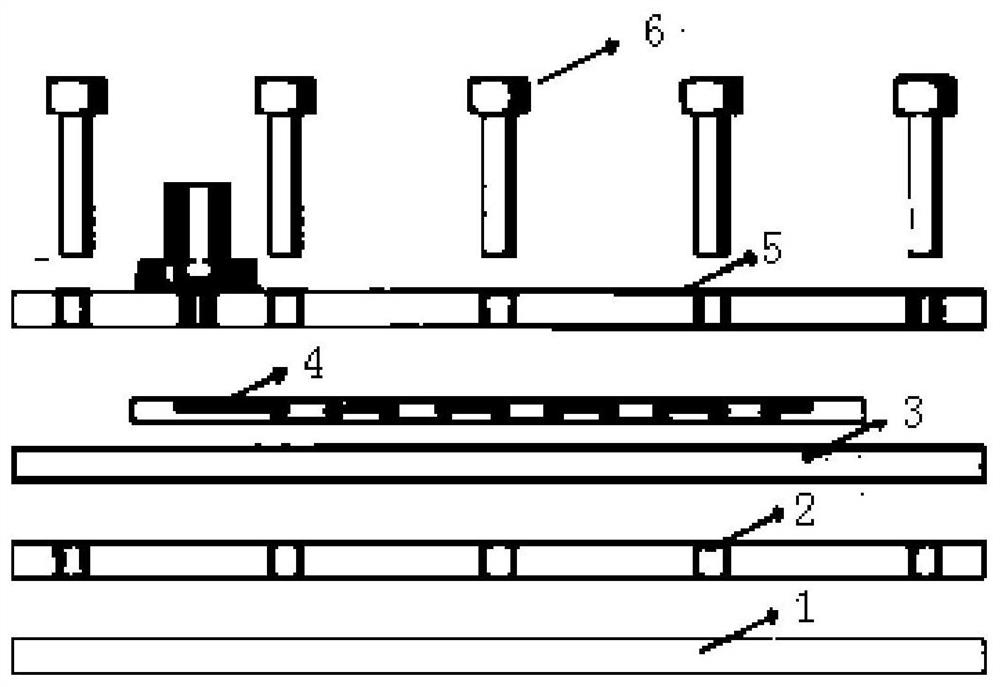
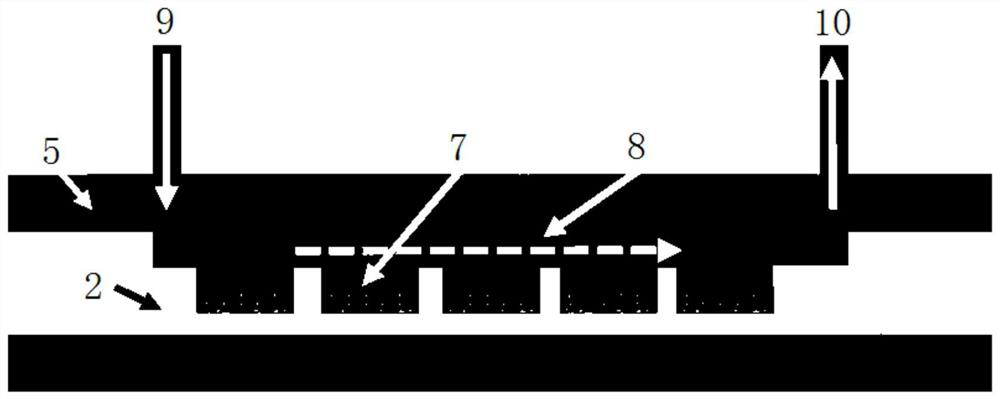
Micro-fluidic cell chip and virus isolated culture method based on same
A cell chip and virus isolation technology, applied in the field of biological sciences, can solve the problem of rapid isolation and culture of virus-sensitive host cells, high-throughput screening of viruses, difficulty in obtaining infected samples of major viral infectious diseases, virus classification, and identification and vaccine development obstacles, etc., to achieve the effect of improving sample utilization, increasing throughput processing capacity, and shortening separation and identification time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1, Simulated screening of sensitive host cells of enterovirus EV71 (Chinese vaccine strain, GenBank No. HQ328793) in a microfluidic cell chip at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI).
[0053] The cell line can be a conventional virus-amplified cell line, or an in vitro cultured cell line from other species.
[0054] (1) Characterization of typical CPE (cytopathic effect) of EV71: human lung cancer cells (A549), African green monkey kidney cells (Vero cells) and human malignant embryonic rhabdoid tumor cells (RD cells), 1×10 4 The number of cells was seeded into a 96-well plate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After culturing in the incubator for 12 hours, EV71 was infected at MOI=40.0; 24 hours and 36 hours after infection, the cytopathic changes were observed with a bright field inverted microscope. The results showed that all three types of cells produced cytopathic changes, decreased cell adhesion ability, rounded and shrunken cell shape, and poor light transmission, among...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2, Simulated screening of EV71 sensitive host cells in a microfluidic cell chip at extremely low MOI.
[0057] The cell line can be a conventional virus-amplified cell line, or an in vitro cultured cell line from other species.
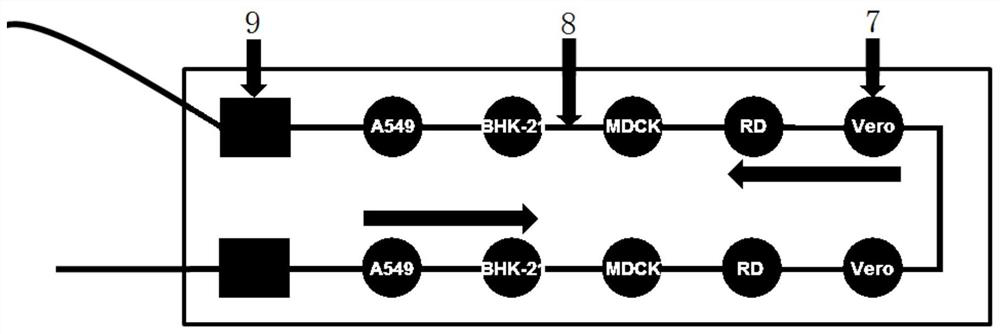
[0058] Very low MOI infection: A549, Vero and RD cells at 1 x 10 4 The number of cells was seeded into the microfluidic cell chip culture chamber at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured in the incubator for 12h, EV71 at MOI=3.89×10 -4 Infection was carried out; cytopathic changes were observed with a bright-field inverted microscope 48 hours after infection. The results show that RD cells produce cytopathy the earliest and are the most significant, consistent with the results in the 96-well plate in Example 1 (such as Image 6 shown).
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3, Simulated screening of influenza virus (A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 1934, H1N1) sensitive host cells in a microfluidic cell chip at high MOI.
[0060] The cell line can be a conventional virus-amplified cell line, or an in vitro cultured cell line from other species.
[0061] (1) H1N1 typical CPE characterization: A549, baby hamster kidney cells (BHK-21), canine kidney cells (MDCK), Vero and RD cells, 1×10 4 The number of cells was seeded into a 96-well plate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After being cultured in an incubator for 12 hours, H1N1 was infected at MOI=12.3; 24 hours after infection, cytopathic changes were observed with a bright-field inverted microscope. The results showed that MDCK cells produced obvious cytopathic changes, the inherent shape of the cells disappeared, the cells fell off and produced vacuoles, and other cell lines had no obvious lesions (such as Figure 7 shown).
[0062] (2) High MOI infection: A549, BHK-21, MDCK, Vero and RD cells, at 1×10 4 The nu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com