Method for electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants outside electrolyzer and application
A technology for the chemical degradation of organic pollutants, applied in the field of electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants outside the tank, can solve the problems of easy danger, toxic and harmful chlorine gas, and only pressurization, so as to avoid environmental pollution, avoid electrode deactivation, reduce Effect on Total Emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
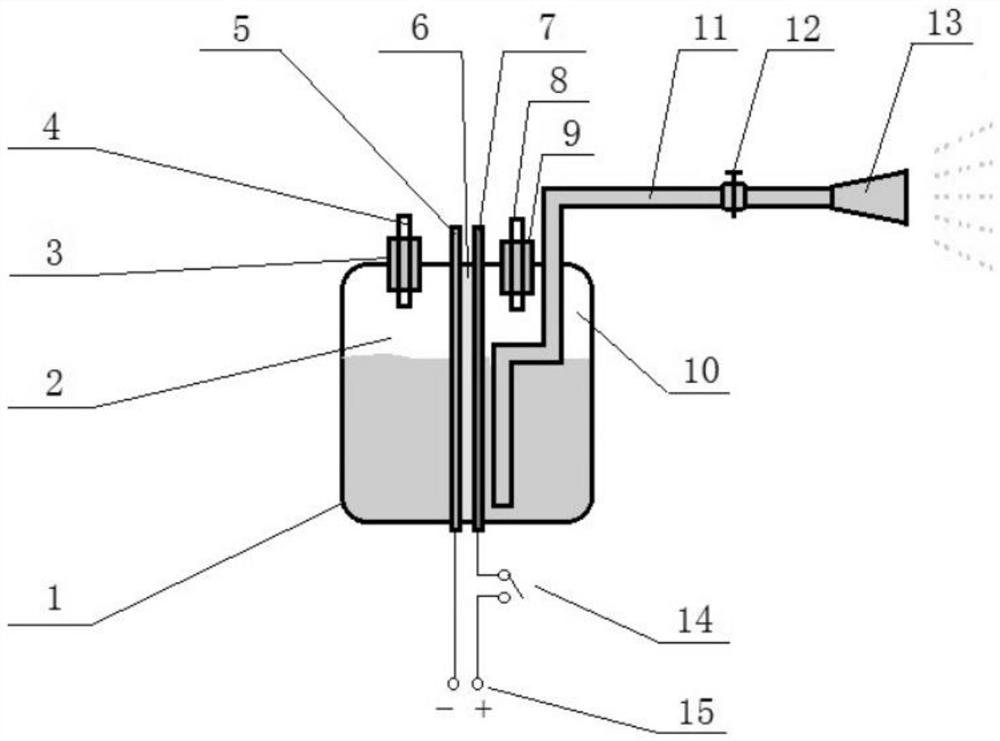
[0024]A method for electrochemically degrading organic pollutants outside the tank, comprising the following steps: (a) in a diaphragm electrolytic cell containing an electrolyte, use a material with a high oxygen evolution overpotential as the anode 7, a low hydrogen evolution overpotential and not corroded by the electrolyte The material is the cathode 5, and water electrolysis is carried out under a certain voltage and current density; (b) the highly oxidatively active water near the surface of the electrolyzed anode 7 is exported, and sprayed and infiltrated to the surface of the object to form a water film to degrade the surface of the object Organic Pollutants.
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, the diaphragm electrolyzer includes a cell body 1 and a diaphragm 6 that separates the cell body 1 into mutually independent anode chambers 10 and cathode chambers 2, the anode chamber 10 and the cathode chamber 2 are all airtightly arranged, and the anode chamber 10 An anode 7...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The above-mentioned method for degrading organic pollutants is applied to the specific steps of vehicle cleaning as follows: with Ti-based PbO 2 Anode 7 (oxygen evolution potential > 2.07eV), stainless steel is cathode 5, adopts proton exchange membrane as diaphragm 6 to build the above-mentioned diaphragm electrolyzer connected with shower head 13, the volume of anode chamber 10 and cathode chamber 2 is respectively 300 milliliters; Water is injected into the anode chamber 10 and the cathode chamber 2 respectively, the power supply 15 is switched on, the electrolysis voltage is controlled to be 4V direct current, and the current 7A (the current density is 0.35A / cm 2 ), carry out water electrolysis; as the reaction proceeds, the highly oxidatively active water near the surface of the electrolyzed anode 7 is exported through the conduit 11, atomized and sprayed on the surface of the vehicle with dirt to form a water mist film through the nozzle 13, so as to reduce Solve ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] The specific steps of applying the above-mentioned method for degrading organic pollutants to vehicle cleaning are: using perfluorosulfonic acid ion exchange membrane (Nafion membrane) as diaphragm 6, solid polymer electrolyte SPE as electrolyte, and using β-PbO 2 Adhering to the anode side of the perfluorosulfonic acid ion exchange membrane is the anode 7 (oxygen evolution potential > 2.07eV), and the platinum carbon catalyst is attached to the cathode side of the perfluorosulfonic acid ion exchange membrane as the cathode 5. The above-mentioned diaphragm electrolysis connected with the nozzle 13 is constructed. Groove, the volume of anode chamber 10 and cathode chamber 2 is respectively 300 milliliters; Pure water is injected into anode chamber 10 and cathode chamber 2 respectively, connects power supply 15, and the control electrolysis voltage is 5V direct current, and current 10A (current density is 0.5A / cm 2 ), carry out water electrolysis; as the reaction proceed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com