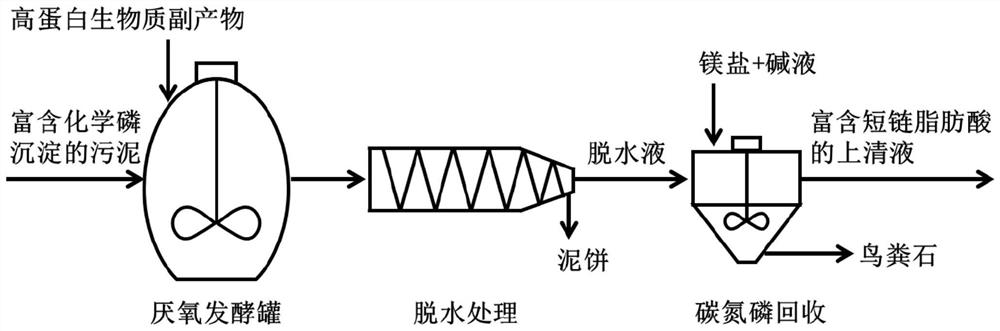
Method for recovering phosphorus from sludge rich in chemical phosphorus precipitates by using high-protein biomass waste
A biomass waste, high-protein technology, applied in the field of phosphorus recovery, can solve the problem of poor effect of improving phosphorus release from phosphate-containing precipitated sludge, achieve phosphorus resource recovery, save treatment costs, and reduce the amount of lye Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Take 450mL of pure biological sludge and put it into the anaerobic fermentation tank, add 0.65g of ferric phosphate to simulate the sludge rich in chemical phosphorus precipitation, add 2.44g of silkworm chrysalis powder to the sludge (that is, add 0.81g of silkworm chrysalis powder for total chemical oxygen demand amount / g total chemical oxygen demand of sludge), oxygen was excluded to form an anaerobic environment, the fermenter was sealed, and anaerobic co-fermentation was carried out at 35°C for 7 days. At the same time, the iron phosphate-containing sludge without silkworm chrysalis powder was used as a control.
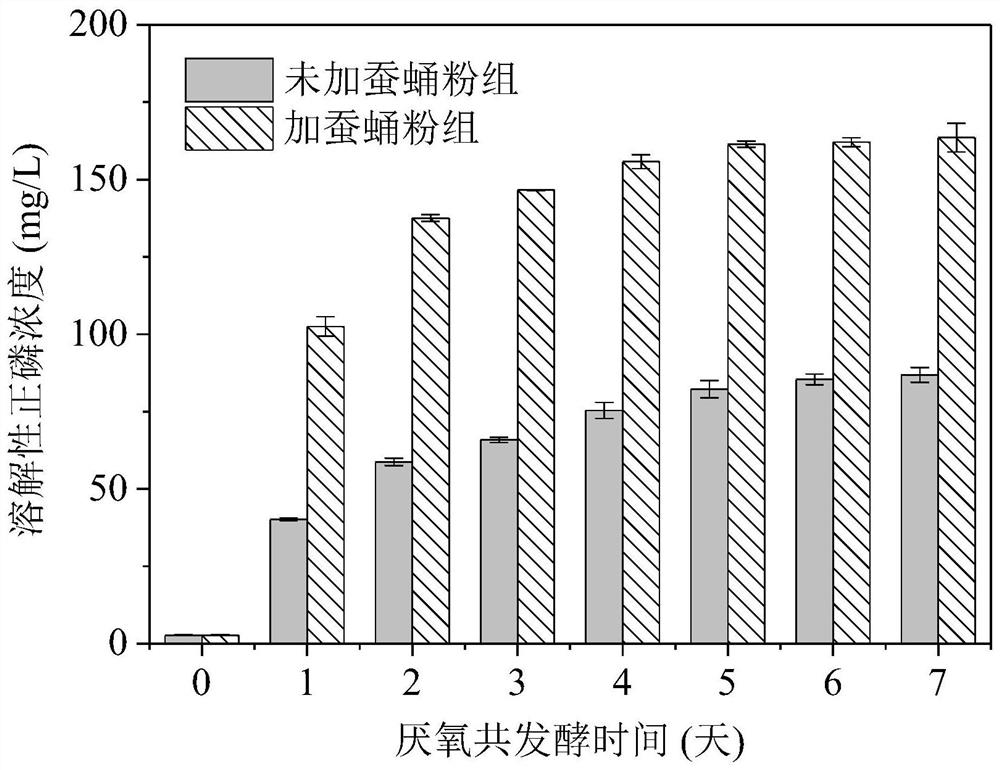
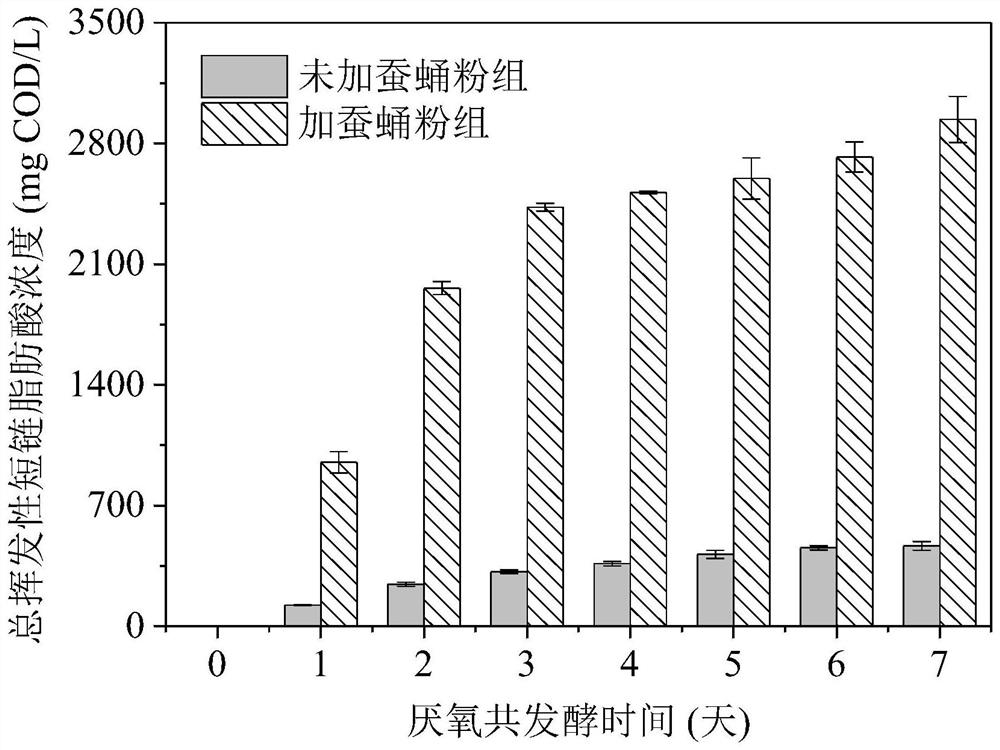
[0032] refer to Figure 2-Figure 4 , after adding silkworm chrysalis powder and ferric phosphate sludge for 7 days, the concentration of soluble orthophosphorus increased by 88% compared with that of iron phosphate sludge without adding silkworm chrysalis powder. Adding silkworm chrysalis powder and ferric phosphate-containing sludge for 7 days of co-fer...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Take 450mL of the remaining activated sludge rich in iron phosphate from a sewage treatment plant and put it into an anaerobic fermentation tank, and add 5.67g silkworm chrysalis powder to the sludge (that is, add 0.81g silkworm chrysalis powder total chemical oxygen demand / g sludge total chemical oxygen demand Oxygen content), get rid of oxygen to form anaerobic environment, airtight fermenter, anaerobic co-fermentation under the condition of 35 ℃ for 7 days. At the same time, the iron phosphate-containing sludge without silkworm chrysalis powder was used as a control.
[0036] refer to Figure 5-Figure 7 , after 7 days of co-fermentation with silkworm chrysalis powder and ferric phosphate sludge, the concentration of soluble orthophosphorus increased by 954% compared with that of ferric phosphate sludge without silkworm chrysalis powder. After 7 days of co-fermentation with silkworm chrysalis powder and iron phosphate-containing sludge, the concentration of total vol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com