A kind of method and semiconductor that carry out p-type doping to tmdcs based on ptfe
A PTFE, p-type technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of volatile doping and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
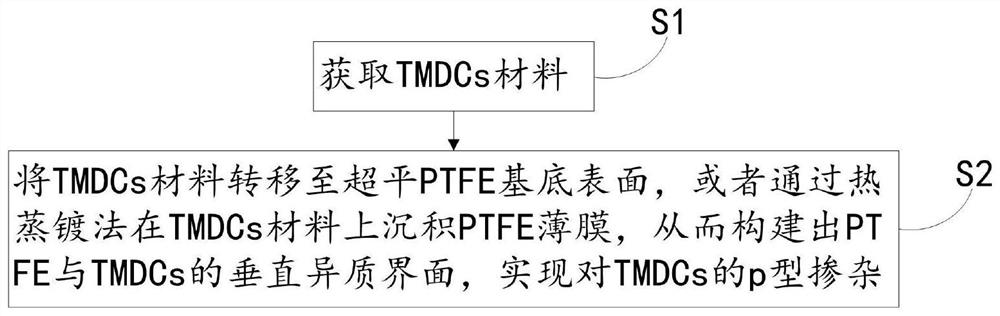
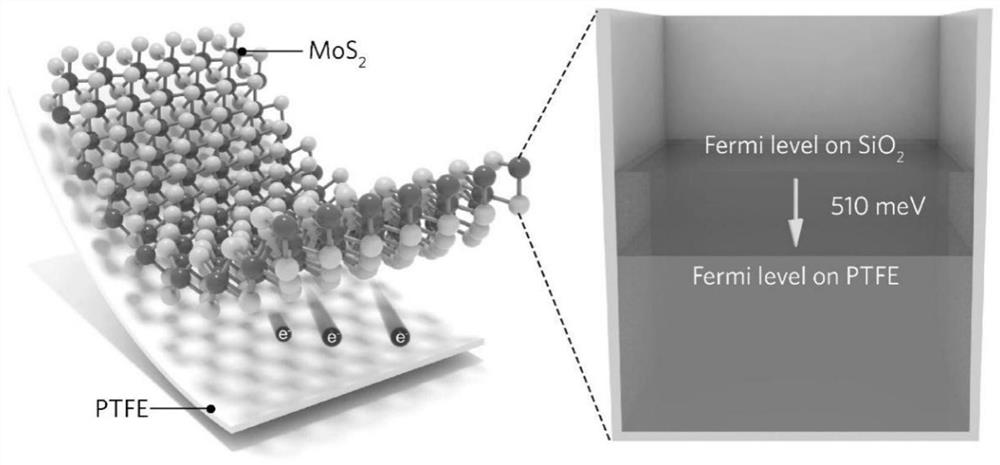
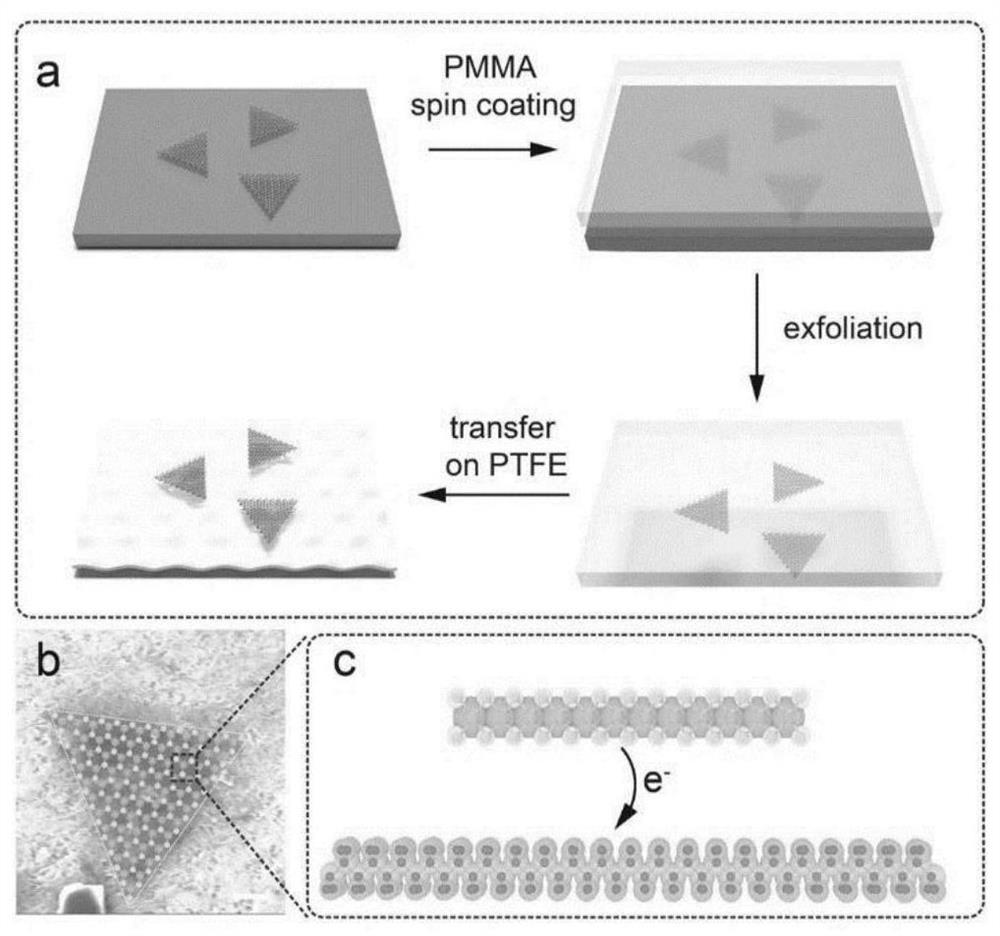
[0046] A method for p-type doping of TMDCs (two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides) based on PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), such as figure 1 As shown, step S1 and step S2 are included.
[0047] Step S1, obtaining TMDCs materials.
[0048] Among them, the representative structure of TMDCs material is MXn. Wherein, M is a metal, and the metal includes Mo, W, Pt, Hf, In, Re, Nb, Ta, Ga, Sn, Mn, Co, Zr and alloy compounds thereof. X includes O, S, Se, Te and their alloys [alloys here refer to compounds composed of chalcogen elements, such as MoSxSey, WSxTey, MoxWyS2, etc., such compounds are called alloy in English (Zhou, J., Lin, J ., Huang, X.et al.A library of atomically thin metalchalcogenides.Nature 556,355-359(2018), alloy is the meaning of alloy.] and Janus compound (Janus compound refers to replacing the chalcogen atoms in one layer with Another chalcogen atom belongs to TMDCs material structurally). Where n is a natural number greater than or equal to 1. In ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The difference between it and Embodiment 1 is that the ultra-flat PTFE substrate configured in this embodiment is a PTFE sheet with a surface roughness of 5-7.5nm or a PTFE film with a surface roughness of 3.5-6.5nm, corresponding to:
[0067] 1. When the ultra-flat PTFE substrate is a PTFE sheet with a surface roughness of 5-7.5nm, it can be obtained by softening and reshaping the commercial PTFE sheet by hot pressing. The specific steps include:
[0068] First clamp and fix the commercial PTFE sheet between two ultra-flat carriers, the ultra-flat carrier is the same as Example 1, the difference lies in its SiO 2 Layer thickness is 200-300nm, surface roughness is 0.5-0.8nm;
[0069] Then, under the conditions of softening temperature of 280-320°C and softening time of 20-40min, the commercial PTFE sheet is softened and reshaped by hot pressing to obtain a PTFE sheet with a surface roughness of 5-7.5nm.
[0070] 2. When the ultra-flat PTFE substrate is a PTFE film with...
Embodiment 3
[0075] It differs from Embodiment 1 or 2 in that: before constructing the vertical heterogeneous interface between PTFE and TMDCs, it is also necessary to place the ultra-flat PTFE substrate in plasma for plasma treatment, thereby regulating the fluorine-containing surface layer of the ultra-flat PTFE substrate. quantity.
[0076] Specifically, in this embodiment, the plasma is set to be hydrogen or nitrogen, the flow rate is 1-2000 sccm, the plasma power is 1-5000 W, and the reaction time is 1-120 min.
[0077] For example, the PTFE sheet or PTFE film obtained in the above-mentioned embodiment one is placed in a hydrogen or nitrogen atmosphere with a gas flow rate of 1 sccm for plasma treatment, the plasma power is 10W, and the treatment time is 5min to regulate the PTFE sheet or PTFE film The fluorine content of the surface layer. Those skilled in the art can understand that the above-mentioned flow rate, power and reaction time will vary according to the different requirem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com